Online FirstMore>
Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
Display Method:
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202405024
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of midazolam on neuronal damage in ischemic stroke (IS) rats and its regulatory effect on PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1)/E3 ubiquitin ligase (PARKIN) signaling pathway. Methods An IS rat model was established using arterial occlusion method. The rats with successful model were randomly divided into IS group, drug-low, medium, high-dose (drug-L, M, H, 30, 60, 90 mg/kg midazolam) groups, drug-H+autophagy inhibitor 3-MA group (90 mg/kg midazolam+30 mg/kg 3-MA), and rats with only isolated blood vessels were used as sham surgery groups. Each group received corresponding doses of drugs or physiological saline intervention, and the neurological function scoring, brain histopathology, neuronal apoptosis, ultrastructure, and expression of PINK1, PARKIN, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3), and P62 protein in mitochondria were detected. Results Compared with the IS group, the pathological damage of the drug-L group, drug-M group, and drug-H group was improved, and autophagosomes showed an increasing trend, the expression of PINK1, PARKIN, and LC3 proteins increased, the neurological function score, neuronal apoptosis rate, and P62 protein obviously decreased in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.01 or P<0.001); compared with the drug-H group, the pathological damage in the drug-H+3-MA group increased and autophagosomes decreased, the expression of PINK1, PARKIN, and LC3 proteins decreased, the neurological function score, neuronal apoptosis rate, and P62 protein obviously increased (P<0.001). Conclusion Midazolam induced mitochondrial autophagy in IS rats by activating the PINK1/PARKIN signaling pathway, neuronal apoptosis was reduced and neuronal damage were improved in IS rats.
In Press
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202503063
Abstract:
Objective To design and synthesize PROTAC degraders targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro)based on PROTAC technology. Methods Compound 3w was used as the Mpro ligand, and the indole N atom in the solvent-exposed region was selected as the linker attachment site. A series of Mpro PROTACs were designed and synthesized by conjugating compound 3w with the CRBN ligand pomalidomide through alkane linkers of different lengths. The structures of the target compounds were confirmed by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and HRMS. Western Blot analysis was employed to evaluate their degradation activity and explore its mechanism in Mpro-HEK-293T cells. Results Four novel Mpro PROTACs( A1 - A4 )were successfully synthesized. The most potent compound A4 demonstrated Mpro degradation activity with a DC50 value of 5.2 μmol/L, and its degradation mechanism was validated. Conclusion A novel class of Mpro PROTAC degraders were successfully designed and synthesized, and their protein degradation capability and mechanism of action were demonstrated. These results provided lead compounds for the research and development of antiviral degraders against SARS-CoV-2.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202503005
Abstract:
Objective The alkaloids contained in the Chinese herb Sophora flavescens have good anti-inflammatory activity. To investigate the structure-activity relationship between the novel Matrine and the anti-inflammatory activity by modifying the structure of Matrine . Methods Fourteen novel Matrine derivatives were obtained by chemical modification using Matrine as the lead compound with Matrine and M19 as positive controls. The cytotoxicity of Matrine derivatives against RAW264.7 cells was detected by the Cell Counting Kit 8 (CCK8) assay, and the relative amount of Nitric Oxide (NO) produced by Matrine derivatives against Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation model of RAW264.7 cells was detected using an NO assay kit. The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) d was used to detect the secretion of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) by Matrine derivatives in LPS-induced inflammation model of RAW264.7 cells. Results The novel Matrine derivatives all exhibited lower cytotoxicity compared with M19. The NO inhibition rates of the novel Matrine derivatives were all higher than that of Matrine, and some were higher than that of M19 , with compound A12 having the highest NO inhibition rate. Compounds A11 and A12 showed higher IL-6 inhibition than the control M19 . Additionally, compound A12 had higher TNF-α inhibition than the control M19 . Conclusion Compound A12 inhibited the strongest inhibition of NO, IL-6 and TNF-α release and had the best anti-inflammatory activity, which provided an important lead compound for this subsequent in-depth study.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202412057
Abstract:
Objective To clarify the effect and mechanisms of astaxanthin on the calcification of aortic valve interstitial cells (VICs) induced by osteogenic medium (OM). Methods The CCK-8 assay was used to analyze the effects of different concentrations of astaxanthin on the proliferation of VICs. After treating VICs with astaxanthin in OM, Alizarin Red staining was performed to detect calcified nodules, and Western blotting was used to measure the expression levels of osteogenic differentiation markers ALP and Runx2. Additionally, Western blotting and immunofluorescence detection were utilized to assess the expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 proteins. The levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured by DCFH-DA fluorescence staining. Results The CCK-8 results indicated that the optimal concentration of astaxanthin for intervention was 25 μmol/L. Astaxanthin treatment reduced the formation of calcified nodules induced by OM in VICs, and inhibited the expression of osteogenic differentiation markers ALP and Runx2 (P<0.01). Furthermore, Astaxanthin treatment decreased the expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 (P<0.01), and reduced intracellular reactive oxygen species levels (P<0.01). Conclusion Astaxanthin may mitigate oxidative stress and calcification in VICs by enhancing the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant signaling pathway.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202311021
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of Triptolide on cerebral ischemia- reperfusion injury (CIRI) and explore its molecular mechanism. Methods One hundred and forty-four Wistar rats were randomly divided into sham operation group, model group, low, medium, high dose of triptolide group and butylphthalide group, with 24 rats in each group. The CIRI rat model was established by blocking the middle cerebral artery for 2 hours. 3 days before modeling, the rats in each group were ip administration once a day. 24 hours after reperfusion, the neurological deficit score was detected, the rate of cerebral infarction was measured by TTC staining, the blood brain barrier (BBB) permeability was detected by EB penetration test. The pathological changes neurons in the ischemic penumbra cortex were observed by HE and TUNEL staining. The content of inflammatory factors in ischemic cerebral cortex were detected by ELISA method. The expression of TLR4/NF-κB pathway related proteins were detected by Western blot. Results Compared with the model group, the neurological deficit score, cerebral infarction rate and EB content in the Triptolide middle, high dose groups and the Butylphthalide group were significantly decreased (P<0.05). The pathological changes of cortical neurons in the ischemic penumbra were significantly improved, and the apoptosis rate of neurons was significantly decreased (P<0.05). The content of TNF-α, IL-1β and the expression of TLR4, p-NF-κB, cleaved Caspase-3, Bax were significantly decreased, the expression of Bcl-2 was significantly increased, the ratio of p-NF-κB/NF-κB and Bax/Bcl-2 were significantly decreased (P<0.05). The regulatory effect of the high dose triptolide group on various detection indexes were better than that of the Butylphthalide group (P<0.05). Conclusion Triptolide could protect the permeability of BBB, improve the neurological deficit and neuropathy in CIRI rats, and reduce the rate of cerebral infarction, its mechanism may be related to the inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB pathway and which mediated inflammatory response and neuronal apoptosis.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202408053
Abstract:
Objectives To study the antitumor activities of RRx-001 derivatives with novel covalent fragments Methods Four targeted compounds were designed and synthesized. The structures were confirmed by 1H NMR and HRMS. A549 and HCT116 cancer cell lines were selected for antiproliferative activity assays. Results All the compounds revealed antitumor activities and compound ZM528 showed the best antitumor activity against these two cell lines with IC50 values of (5.1±4.8) and (6.0±2.7) μmol/L, respectively. Conclusions The result indicated that bromoacetyl group of RRx-001 could be substituted with other covalent fragments.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202312012
Abstract:
Objective To explore the drug selection, usage, dosage and effect of clinical pharmacists in the treatment of secondary Candida bloodstream infection in patients with digestive tract perforation, and provide reference for rational clinical use of such anti-infection therapy. Methods During the treatment of Candida infection, anti-infection specialist clinical pharmacists suggested replacing fluconazole for anti-infection treatment, and adjusted the usage and dosage of caspofungin to ensure the application of full treatment course. Results The patient’s Candida bloodstream infection was effectively controlled. Conclusion Echininocandins such as caspofungin are the first choice for Candida infection. The maintenance dose should be reduced to 35 mg qd in patient of moderate liver function injury, and the anti-infection treatment should be done at least 14 days after the blood culture being negative. Clinical pharmacists participate in clinical pharmaceutical care practices such as clinical ward rounds, and actively assist doctors to develop individualized anti-infection programs, which could improve the level of clinical drug use and improve the clinical outcome of diseases.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202408021
Abstract:
Hypertension is a systemic chronic vascular disease. From the perspective of Traditional Chinese Syndromes, hypertension belongs to the category of liver fire, vertigo, liver yang, headache and so on. Chinese medicine treatment of hypertension has gradually become a hot research topic, and using Chinese herbal medicine to reduce blood pressure has also achieved good results. In recent years, researches on anti-hypotension of Bidens pilosa L. has gradually increased. The related research of Bidens pilosa L., including the ancient literature, modern research, functional components and mechanism were mainly summarized, the application of Bidens pilosa L. in lowering blood pressure were anticipated, with a view to provide reference for the further development and utilization of Bidens pilosa L. in treatment of hypertension.
Hypertension is a systemic chronic vascular disease. From the perspective of Traditional Chinese Syndromes, hypertension belongs to the category of liver fire, vertigo, liver yang, headache and so on. Chinese medicine treatment of hypertension has gradually become a hot research topic, and using Chinese herbal medicine to reduce blood pressure has also achieved good results. In recent years, researches on anti-hypotension of Bidens pilosa L. has gradually increased. The related research of Bidens pilosa L., including the ancient literature, modern research, functional components and mechanism were mainly summarized, the application of Bidens pilosa L. in lowering blood pressure were anticipated, with a view to provide reference for the further development and utilization of Bidens pilosa L. in treatment of hypertension.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202404059
Abstract:
Objective To establish a HPLC method for determining thimerosal compounds in eye drops. Methods A gradient HPLC system was used in the quantitative analysis of thimerosal compounds on Shiseido MGII C18 column (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm), using 1% triethylamine solution ( pH adjusted to 3.0 with phosphate) as mobile phase A, the methanol as mobile phase B, gradient elution, The column temperature was 40 ℃, the detection wavelength was 222 nm , the flow rate was 1 ml/min and the injection volume was 20 µl. Results The established method had good linearity within the concentration range of 4.3-216.7 μg/ml (r>0.999) for thimerosal, with average recoveries was 102.1%, RSD2.7%. Conclusion This method is simple, accurate and highly specific, and can be used for determination of thimerosal compound in eye drops.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202406029
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the preventive and therapeutic effects of ethanol extracts derived from three sources of traditional Chinese medicine: Stellera chamaejasme L., Euphorbia fischeriana Steud., and Euphorbia kansuensis Prokh., on imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis in mice. Methods Thirty-six male BALB/c mice were randomly divided into the following 6 groups with 6 mice in each group: blank control, model, Stellera chamaejasme, Euphorbia fischeriana, Euphorbia kansuensis, and calcipotriol. PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index) scores were used to record the changes of skin lesions in each group; HE (hematoxylin-eosin) staining was used to observe the pathological morphology of skin and measure the thickness of the epidermis. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of nuclear antigen Ki67 in the skin tissues of mice. Results Compared with the model group, the three kinds of ethanol extracts can reduce the PASI score, inhibit epidermal thickening, and decrease expression of Ki67 in the psoriasis mice. Among them, the therapeutic effect of Stellera chamaejasme was the most significant and it was better than the commonly used topical drug calcipotriol. Conclusion The ethanol extract of Stellera chamaejasme has good anti-psoriatic activity, can inhibit the abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes, can reduce the expression of Ki67, and can significantly improve psoriasis-like skin lesions.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202306020
Abstract:
Objective To establish a central cutting two-dimensional liquid chromatography for the determination of lamotrigine in human plasma. Methods External standard method was used. The first dimensional chromatographic column: SNCB(T)-1A(silica gel, 4.6 mm×50 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase A:VCV-1D mobile phase, flow rate: 0.4 ml/min; mobile phase B: water, flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; second dimensional chromatographic column: Symmetry C18 (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase: acetonitrile-10 mmol/L ammonium acetate solution(V/V=25∶75), flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; Intermediate column: SBX 4-MA(resin, 3.0 mm×10 mm, 5µm). The UV detection wavelength: 306 nm, the column temperature: 45 ℃, and the injection volume: 200 μl. Results The linear range of lamotrigine was 1.24-39.50 μg/ml, the lower limit of quantification was 1.24 μg/ml, the detection limit was 0.02 μg/ml, the intra-day precision RSD was less than 5%, the day-to-day precision RSD was less than 10%, the variation of intra-day accuracy ranged from 102.17% to 111.17%, and the daytime accuracy variation ranged from 99.80% to 107.31% the recovery RSD was less than 5%, and the variation range was 89.95% -96.16%. After 24 hours storage at room temperature, repeated freezing and thawing for 3 times and storage at-40 ℃ for 2 weeks, the ratio of the measured value / labeled value ranged from 87.01% to 115.88%. Conclusion In this study, a method with simple operation, good stability, high sensitivity and good reproducibility was established, which could be suitable for clinical monitoring of blood concentration of lamotrigine and provides reliable monitoring data support for clinical individualized medication guidance.
Objective To establish a central cutting two-dimensional liquid chromatography for the determination of lamotrigine in human plasma. Methods External standard method was used. The first dimensional chromatographic column: SNCB(T)-1A(silica gel, 4.6 mm×50 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase A:VCV-1D mobile phase, flow rate: 0.4 ml/min; mobile phase B: water, flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; second dimensional chromatographic column: Symmetry C18 (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm), mobile phase: acetonitrile-10 mmol/L ammonium acetate solution(V/V=25∶75), flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; Intermediate column: SBX 4-MA(resin, 3.0 mm×10 mm, 5µm). The UV detection wavelength: 306 nm, the column temperature: 45 ℃, and the injection volume: 200 μl. Results The linear range of lamotrigine was 1.24-39.50 μg/ml, the lower limit of quantification was 1.24 μg/ml, the detection limit was 0.02 μg/ml, the intra-day precision RSD was less than 5%, the day-to-day precision RSD was less than 10%, the variation of intra-day accuracy ranged from 102.17% to 111.17%, and the daytime accuracy variation ranged from 99.80% to 107.31% the recovery RSD was less than 5%, and the variation range was 89.95% -96.16%. After 24 hours storage at room temperature, repeated freezing and thawing for 3 times and storage at-40 ℃ for 2 weeks, the ratio of the measured value / labeled value ranged from 87.01% to 115.88%. Conclusion In this study, a method with simple operation, good stability, high sensitivity and good reproducibility was established, which could be suitable for clinical monitoring of blood concentration of lamotrigine and provides reliable monitoring data support for clinical individualized medication guidance.
In Press
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202204094
Abstract:
Objective To study the compliance and influencing factors of inhalation therapy in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD),and carry out patient education and management accordingly. Methods COPD patients were selected from Respiratory Clinic of Luodian Hospital of Baoshan District of Shanghai from June to December of 2021. Compliance and inhalation techniques were assessed with the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale and the ten-step inhalation technique, and the factors influencing compliance were analyzed. Results A total of 58 outpatients with COPD were included, in which 25 cases (43.1%) with moderate or above compliance. Univariate analysis showed that the patients with course of disease ≥5 years, CAT(COPD assessment test)≥10 points, used 2 inhalation devices and inhalation technique score ≥8 points had better compliance when compared with other patients (P<0.05). Conclusion Patient education and management should be carried out actively. The patients with course of disease<5 years, CAT<10 points should be highly concerned. The patients' ability to use inhalation devices and personal preference should be fully considered. Training on the use of devices should be strengthened and regularly follow-up evaluation should be carried out.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.
Abstract:
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202309021
Abstract:
Lactic acid bacteria is a good candidate in living drug delivery system for its safety, beneficial nature, and intestinal colonizability. At present, most studies use it as a protein drug delivery carrier for disease treatment. As a model organism, a variety of gene modification schemes enable it to be applied to various diseases and can play a significant therapeutic effect. Lactic acid bacteria drug carrier has many advantages, including non-invasive drug delivery, gene editing, large-scale production Therefore, the use of lactic acid bacteria as recombinant protein expression vector has attracted global attention. In this review, the application basis, bioavailability improvement, gene editing strategy and research and application status of lactobacillus drug delivery system were summarized.
Lactic acid bacteria is a good candidate in living drug delivery system for its safety, beneficial nature, and intestinal colonizability. At present, most studies use it as a protein drug delivery carrier for disease treatment. As a model organism, a variety of gene modification schemes enable it to be applied to various diseases and can play a significant therapeutic effect. Lactic acid bacteria drug carrier has many advantages, including non-invasive drug delivery, gene editing, large-scale production Therefore, the use of lactic acid bacteria as recombinant protein expression vector has attracted global attention. In this review, the application basis, bioavailability improvement, gene editing strategy and research and application status of lactobacillus drug delivery system were summarized.
Accepted Manuscript
, Available online
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202303006
Abstract:
Objective Study on the effect of Lishukang capsule on learning and memory impairment in mice with high altitude hypoxia based on Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway. Methods Sixty male Balb/C mice were randomly divided into normal control group, hypoxia model group, Rhodiola capsule group: 400 mg/kg, low, medium and high dose groups of Lishukang capsule: 400 mg/kg, 600 mg/kg, 800 mg/kg, with 10 mice in each group. The normal control group was fed at the local altitude (1500m) after 7 days of intragastric administration in each group, and the rest groups were fed at the low pressure and hypoxia animal experimental cabin to simulate the altitude of 7500 m for hypoxia for 3 days. During this period, the normal control group and the hypoxia model group were given normal saline once a day, and 1 hour after the last administration, the eight arm maze was used to test the spatial memory ability of mice under simulated high altitude hypoxia; HE staining was used to observe the morphological changes of hippocampus in mice; Western blot was used to detect the changes of protein content of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway and apoptosis related protein in hippocampus of mice. Results Compared with the normal control group, the spatial memory ability of mice in the hypoxia model group was significantly impaired (P<0.01); HE staining showed that hippocampal neurons in mice were seriously injured; the content of brain tissue Keap1 protein and apoptosis related protein Bax and Caspase-3 increased (P<0.01); the content of Nrf2, HO-1 and apoptosis related protein Bcl-2 decreased (P<0.01). Compared with the hypoxia model group, the error rate of mice in the high dose group of Lishukang capsule in the eight arm maze behavior experiment was significantly reduced (P<0.05, P<0.01); HE staining showed that the neurons were arranged orderly and the cell morphology was good; the content of Keap1 protein and apoptosis related protein Bax and Caspase-3 decreased (P<0.01); the content of Nrf2, HO-1 and apoptosis related protein Bcl-2 increased (P<0.01). Conclusion High altitude hypoxia can lead to oxidative stress injury in mice and induce the expression of apoptosis related genes, thus aggravating the cognitive dysfunction of mice; Lishukang capsule can effectively improve the learning and memory impairment in mice caused by hypoxia, and its mechanism may be related to regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway and reducing apoptosis.
currentMore>
Display Method:
2025, 43(4): 151-155, 173.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202408045
Abstract:
The method of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis refers to the use of traditional Chinese medicine with a dispersing effect that can eliminate blood stasis in the body to treat the syndrome of blood stasis, which has the effects of unblocking blood vessels, dissipating stasis, regulating menstruation and relieving pain and are widely used for conditions such as chest tightness, heartache, dementia, menstrual disorders caused by blood stasis. Common medicines include Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, Panax notoginseng (Burkill), Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort, Radix Curcumae, etc. Blood activating and stasis removing drugs generally have the effects of improving microcirculation, relaxing blood vessels, inhibiting thromboxane formation, and inhibiting platelet aggregation. They have good therapeutic effects on blood stasis syndrome in diseases such as coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, and vascular dementia. The research progress on traditional Chinese medicine and modern medicine on the treatment of vascular dementia with blood activating and stasis removing drugs were reviewed, in order to provide reference for the clinical application of blood activating and stasis removing methods in the treatment of vascular dementia.
The method of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis refers to the use of traditional Chinese medicine with a dispersing effect that can eliminate blood stasis in the body to treat the syndrome of blood stasis, which has the effects of unblocking blood vessels, dissipating stasis, regulating menstruation and relieving pain and are widely used for conditions such as chest tightness, heartache, dementia, menstrual disorders caused by blood stasis. Common medicines include Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, Panax notoginseng (Burkill), Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort, Radix Curcumae, etc. Blood activating and stasis removing drugs generally have the effects of improving microcirculation, relaxing blood vessels, inhibiting thromboxane formation, and inhibiting platelet aggregation. They have good therapeutic effects on blood stasis syndrome in diseases such as coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, and vascular dementia. The research progress on traditional Chinese medicine and modern medicine on the treatment of vascular dementia with blood activating and stasis removing drugs were reviewed, in order to provide reference for the clinical application of blood activating and stasis removing methods in the treatment of vascular dementia.
2025, 43(4): 156-162.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202406053
Abstract:
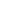
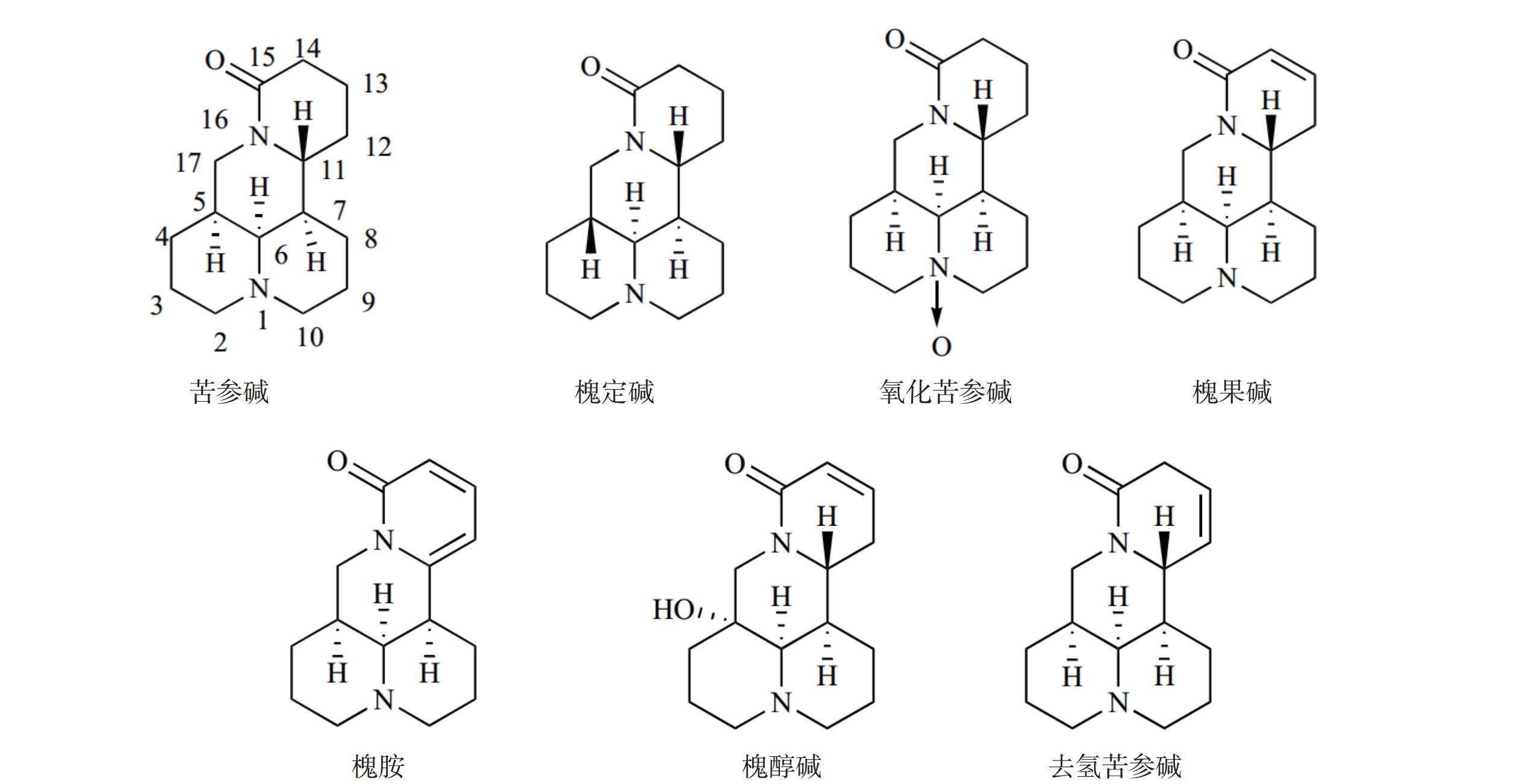
Sophora Flavescens is the dried root of the leguminous plant Sophora Flavescens Ait. It was first published in Shen Nong's Herbal Classic. Sophora Flavescens contains a variety of active ingredients, mainly including matrine and oxymatrine, with anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, anti-arrhythmia, disease-resistant pathogenic microorganisms and other pharmacological effects. Clinically, the compound preparations of Sophora Flavescens include Compound KuShen injection and KuShen gel and so on, which can be used to treat many types of cancers and improve skin, mucous pruritus, pain and other symptoms. Due to the poor bioavailability, the structure of matrine needs to be reformed. MASM, matrine derivative, only needs a low concentration to have a good therapeutic effect on sepsis and liver fibrosis. In this article, the chemical composition, pharmacological effects, compound preparations and structural modification of matrine were mainly discussed, aiming to provide a theoretical basis for the clinical application of Sophora Flavescens and the development of new drugs.
Sophora Flavescens is the dried root of the leguminous plant Sophora Flavescens Ait. It was first published in Shen Nong's Herbal Classic. Sophora Flavescens contains a variety of active ingredients, mainly including matrine and oxymatrine, with anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, anti-arrhythmia, disease-resistant pathogenic microorganisms and other pharmacological effects. Clinically, the compound preparations of Sophora Flavescens include Compound KuShen injection and KuShen gel and so on, which can be used to treat many types of cancers and improve skin, mucous pruritus, pain and other symptoms. Due to the poor bioavailability, the structure of matrine needs to be reformed. MASM, matrine derivative, only needs a low concentration to have a good therapeutic effect on sepsis and liver fibrosis. In this article, the chemical composition, pharmacological effects, compound preparations and structural modification of matrine were mainly discussed, aiming to provide a theoretical basis for the clinical application of Sophora Flavescens and the development of new drugs.
2025, 43(4): 163-168, 194.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202406035
Abstract:
Matrine is an alkaloid compound isolated and extracted from the traditional Chinese medicinal plant Sophora flavescens, which has anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and anti-viral effects. However, its clinical application has been limited due to its low in vivo activity, short duration of efficacy, and significant toxic side effects. In response to this challenge, pharmaceutical experts modified the structure of Matrine to obtain derivatives that addressed its limitations. Currently, research on the anti-tumor effects of Matrine and its derivatives is more prevalent, while research in inflammatory-related diseases still needs further strengthening.The progress on the role and mechanism of Matrine and its derivatives in inflammatory diseases were summarized in this paper, which offered valuable insights for the development of therapeutic agents based on Matrine.
Matrine is an alkaloid compound isolated and extracted from the traditional Chinese medicinal plant Sophora flavescens, which has anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and anti-viral effects. However, its clinical application has been limited due to its low in vivo activity, short duration of efficacy, and significant toxic side effects. In response to this challenge, pharmaceutical experts modified the structure of Matrine to obtain derivatives that addressed its limitations. Currently, research on the anti-tumor effects of Matrine and its derivatives is more prevalent, while research in inflammatory-related diseases still needs further strengthening.The progress on the role and mechanism of Matrine and its derivatives in inflammatory diseases were summarized in this paper, which offered valuable insights for the development of therapeutic agents based on Matrine.
2025, 43(4): 169-173.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202409060
Abstract:
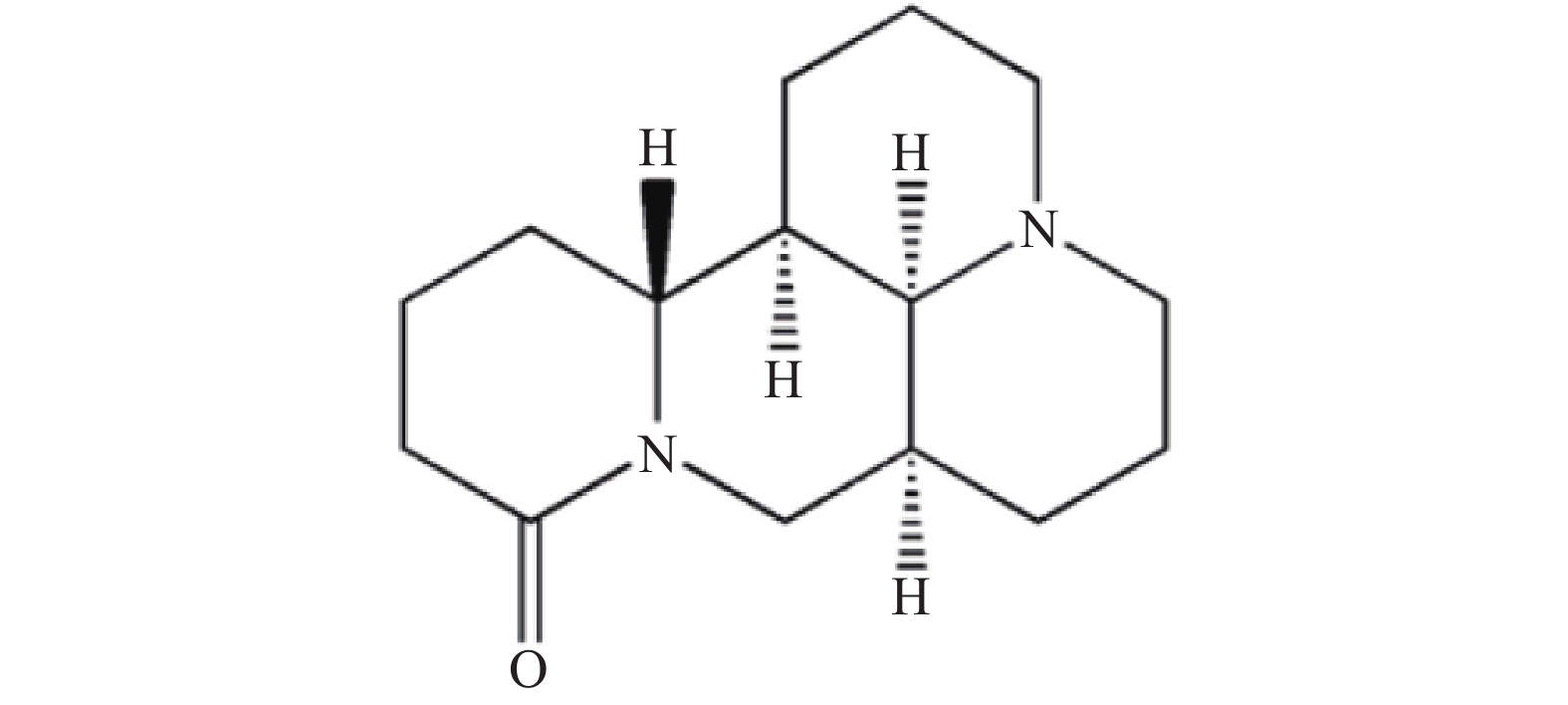
Objective To identify flavonoid glycosides with quorum sensing inhibitory activity from Epimedium brevicornum and evaluate their bioactivity. Methods The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of five major flavonoid glycosides (baohuoside, icariin, epimedin A/B/C) and the extract of E. brevicornum were firstly determined. Subsequently, the inhibitory effects on the production of purple pigments in Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 were measured. Additionally, the biofilm formation and chitin quantification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 were assessed. Results The extract of E. brevicornum and its primary components exhibited significant quorum sensing inhibitory activity. Particularly, icariin and epimedin C demonstrated superior inhibitory activity. Conclusion E. brevicornum demonstrates the ability to inhibit the quorum sensing system of Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Furthermore, icariin and epimedin C (100 μg/ml) show promise for development into novel drugs for quorum sensing inhibitor.
2025, 43(4): 174-179.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202404069
Abstract:
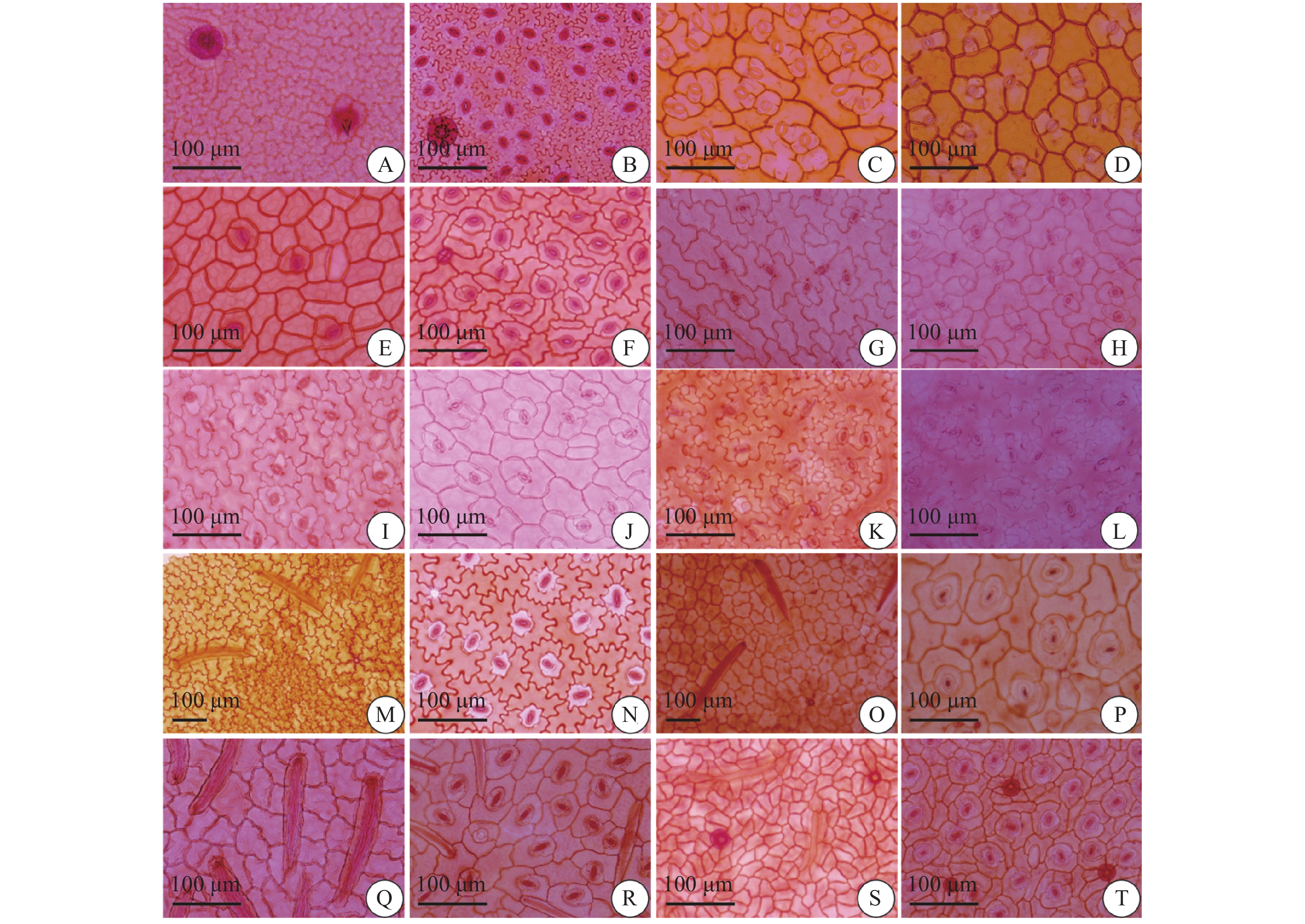
Objective The complex evolutionary history of the origin of medicinal blue herbs might result in the presence of adulterants, affecting the accuracy and safety of clinical medication. To provide a reference basis for the identification of medicinal blue herbs with leaves as the medicinal part, based on the leaf epidermis microstructure. Methods The species belonging to medicinal blue herbs and their close relatives (10 species from 4 genera) were systematically investigated. The leaf epidermis microstructure of these species was observed and analyzed by optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. A species retrieval table was established based on the microstructure characteristics. Results By combining the distribution of stomata, types of subsidiary cells, stomatal index, stomatal density, characteristics of the periclinal walls of epidermal cells, and epidermal appendages, the species Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum, Polygonum tinctorium, Isatis indigotica, I. violascens, I. costata, I. minima, Strobilanthes wallichii, S. dalzielii, S. pentstemonoides, and S. cusia can be accurately distinguished. Conclusion Microscopic characteristics of leaf epidermis can provide reference data for accurately differentiating the botanical origins of medicinal blue herbs.
2025, 43(4): 180-184.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202409055
Abstract:
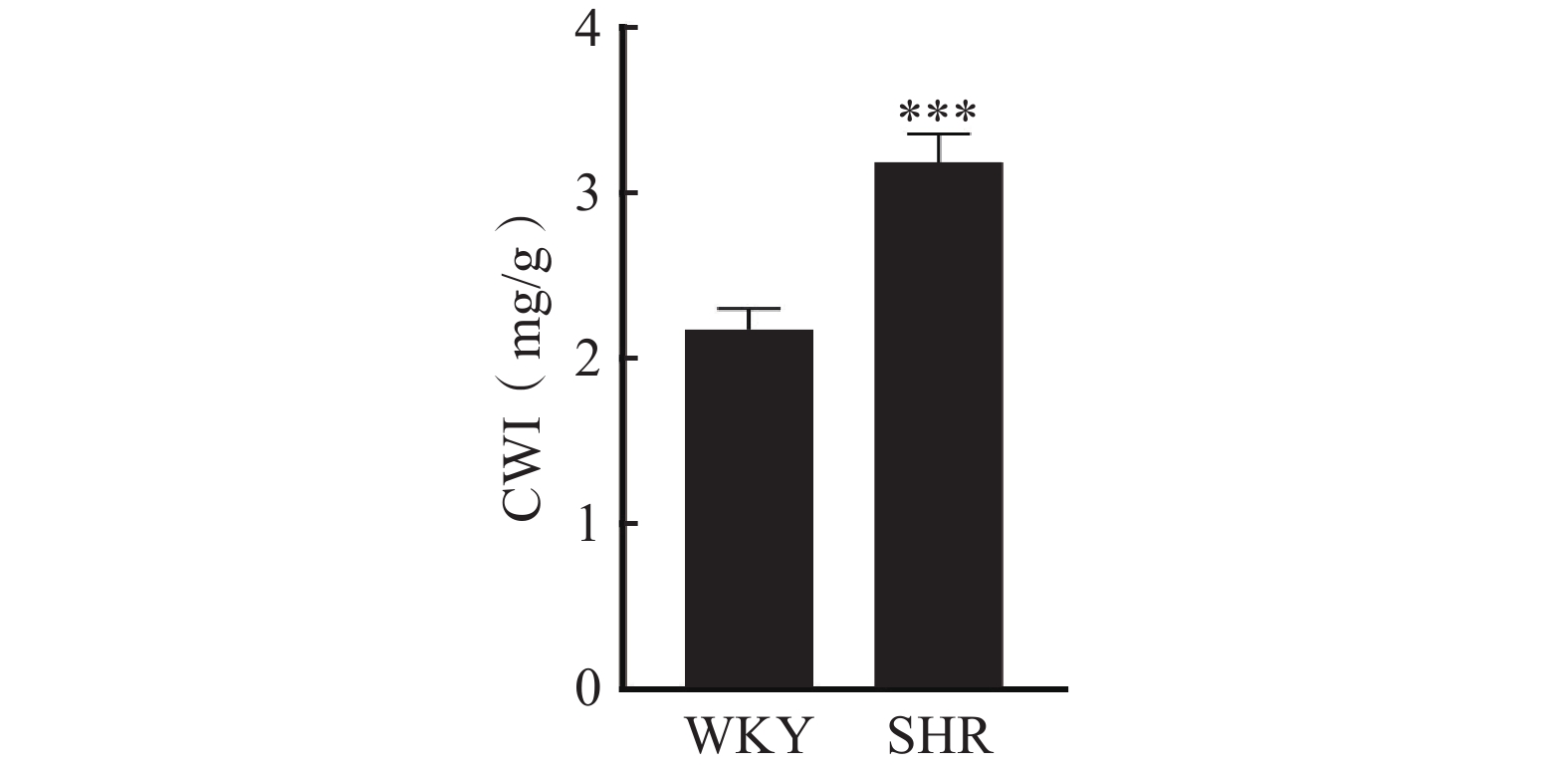
Objective To investigate the effect of spontaneous hypertension on the remodeling of cardiac and aortic tissues in rats, with special attention to the changes in the content of collagen fibers, elastic fibers and secreted Frizzled-related protein 2 (sFRP2) in cardiac and aortic tissues. Methods 28-week-old SHR rats (Spontaneously Hypertensive rats) and WKY (Wistar-Kyoto rats) of the same age were selected as experimental animals. Cardiac load was assessed by calculating the cardiac weight index. Collagen fibers and elastic fibers were isolated from the rat thoracic aorta by hot alkali method, and their content was determined by biochemical analysis. In addition, pathological evaluation of tissue sections of the left ventricle and thoracic aorta were performed by H&E staining, Sirius red staining, and lichen red staining. Western blotting was used to determine the expression level of sFRP2 protein in cardiac tissues. Results Compared with WKY rats, the heart weight index of SHR rats increased significantly (P<0.001), and the results of biochemical analysis and staining of pathological sections showed that the content of collagen fibers in the aorta in the SHR group was higher than that in the WKY group, while the content of elastic fibers was lower, but the difference did not have statistical significance. The content of collagen fibers in the heart of the SHR group was significantly higher than that in the WKY group (P<0.01). Western blotting showed that there was no significant difference in the expression level of sFRP2 protein in heart tissues between the two groups. Conclusion The remodeling of cardiac and aortic tissues in a rat model of spontaneous hypertension may involve complex molecular mechanisms, not just changes in the content of collagen fibers and elastic fibers. The detailed mechanism of the progression of spontaneous hypertension and target organs damage still need further investigation.
2025, 43(4): 185-189.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202401072
Abstract:
Objective To establish a method for rapid detection of tramadol in urine by liquid-liquid extraction(LLE)-surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Methods Tramadol was extracted from urine with chloroform∶isopropyl alcohol (9∶1) extractant and detected in urine samples by enhanced Raman spectroscopy (wavelength 785 nm). Results The quantitative curve of tramadol was Y=204.35 X−465.62, r=0.9952 , and the linear range was 1-100 μg/ml. The detection limit of tramadol by this method (S/N=3) was 0.53 μg/ml. The sensitivity of SERS was higher than that of conventional methods, and it had reasonable reproducibility. Conclusion This method is simple, efficient and economical, and can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of tramadol personalized medicine.
2025, 43(4): 190-194.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202403059
Abstract:
Objective To establish the functional constipated mouse model by compound diphenoxylate, and explore the anti-constipation effect of black garlic polysaccharide. Methods Mouse small intestine ink propulsion experiment and mouse defecation experiment were carried out respectively. The mice in each experiment were randomly divided into blank group, model group, positive group and black garlic polysaccharide (0.25, 0.5, 1 g/kg) groups. Mice in blank group and model group were given distilled water, and in positive group were given lactulose oral solution. Compound diphenoxylate (5 mg/kg) was intragastric administrated after 1 week of administration, and small intestine propulsion experiment and defecation experiment were conducted respectively. Results Compared with model group, intestinal propulsion rate of black garlic polysaccharide groups was significantly increased and first dejection time was significantly shorten, and the number, weight and fecal water content increased significantly at 6 h in middle and high dose groups. Conclusion Black garlic polysaccharide could promote intestinal propelling, shorten defecation time and increase fecal water content.
2025, 43(4): 195-199.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202410019
Abstract:
Objective To provide theoretical basis for the clinical application of the rational compatibility of C. odorata by studying the related domestic and international literature and explore the properties of C. odorata according to the theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Methods The medical literature related to C. odorata was retrieved and screened from CNKI, VIP, Wanfang Data, China Biomedical Literature Database and foreign literature databases such as PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and SciFinder. A total of 397 English articles and 50 Chinese articles were included in the study, which were systematically classified according to clinical application, chemical composition, pharmacological effect, toxic and side effects, and were analyzed according to the theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Results C. odorata features spicy, astringent tastes, a cool nature, entering heart and liver meridians, and a slightly toxic.Its functions included astringing to stop bleeding, detoxifying and promoting tissue regeneration, as well as intercepting malaria and killing parasites. It was used for conditions such as hematemesis, haemoptysis, traumatic bleeding, sores and abscesses, malaria, and leech bites. Conclusion The exploration of the properties and efficacy of C. odorata could provide reference for its clinical research and application in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
2025, 43(4): 200-204.
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202404041
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the characteristics of adverse drug reactions (ADR) reported in Sixth People’s Hospital South Campus, Shanghai Jiaotong University from 2021 to 2023, to provide reference for promoting rational clinical drug use. Methods ADR data reported in our hospital were collected retrospectively, including patients’ basic information, drugs causing adverse reactions, types of adverse reactions and outcomes. Descriptive analysis methods were used to summarize and analyze the data. Results A total of 979 cases of ADR were reported in our hospital from 2021 to 2023. The highest proportion of patients with ADR occurred in the age range of 31 to 50, and more male patients (63.5%). The top five drugs involved with adverse reactions were antibiotics (48.8%), Chinese medicine injections(19.2%), vitamins(7.5%), Chinese traditional medicine(7.2%), equine tetanus immunoglobulin(6.3%). Among antibiotics, cefuroxime, ceftazidime and cefotiam were the majority. The organs/systems involved in all ADR were mainly skin and accessories damage (55.4%). The clinical manifestations were rash, itching, and maculopapular rash. Conclusion From 2021 to 2023, the most common drugs causing adverse drug reactions in our hospital were mainly antibacterial drugs, and the rational clinical use of antibacterial drugs still needs to be concerned.
过刊浏览
- 2025 3 2 1
- 2024 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2023 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2022 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2021 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2020 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2019 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2018 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2017 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2016 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2015 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2014 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2013 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2012 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2011 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2010 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2009 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2008 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2007 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2006 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2005 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2004 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2003 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2002 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2001 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 2000 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1999 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1998 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1997 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1996 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1995 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 1994 4 3 2 1
- 1993 4 3 2 1
- 1992 4 3 2 1
- 1991 4 3 2 1
- 1990 4 3 2 1
- 1989 4 3 2 1
- 1988 4 3 2 1
- 1987 4 3 2 1
- 1986 4 3 2 1
- 1985 4 3 2 1
- 1984 4 3 2 1
- 1983 3 2 1
Chief Editor: LI Jie Wei
Publication Number:
ISSN 2097-2024
CN 31-2185/R
Website: www.yxsjzz.cn or yxsj.smmu.edu.cn
Email: [email protected]
 NewsMore >
NewsMore >
Top View
Top Down
- 1Research progress on action mechanism and clinical application of hyaluronic acid
- 2Advances in mosquito repellents
- 3
- 4Progress on drug treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 5Determination of four major steroid glycosides in Anemarrhena asphodeloides by HPLC-ELSD
- 6The latest research progress of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
- 7Rapid separation and identification of chemical components in Danxiangguanxin injection by HPLC-TOFMS
- 8Surveillance and analysis of quality of pharmaceutical Tween 80
- 9Progress on the impurities in Oxaliplatin
- 10Progress on positron emission tomography drugs
- More >
 Wechat
Wechat






 Contribution System
Contribution System Author Login
Author Login Review Login
Review Login Editor Login
Editor Login Reader Login
Reader Login



 友情链接
友情链接