-
癌症的发病率和病死率呈逐年上升趋势,对大多数癌症的主要治疗方法是手术、放射疗法、化学疗法和免疫疗法。但由于其具有易转移、复发和对放/化疗耐受的产生,使得临床疗效和预后不满意,而传统中药一直被认为是改善肿瘤化疗不良反应的一种新的抗癌药物来源。黄芩的干燥根在我国广泛用于多种疾病的治疗,包括抗癌、抗炎、抗心血管疾病和感染等。研究表明,黄芩素在肿瘤的体外活性实验中效果显著,被认为是治疗肿瘤的潜在药物,推测其作用与黄酮含量有关。据报道,饮食中摄入类黄酮成分与降低癌症风险显著相关[1]。
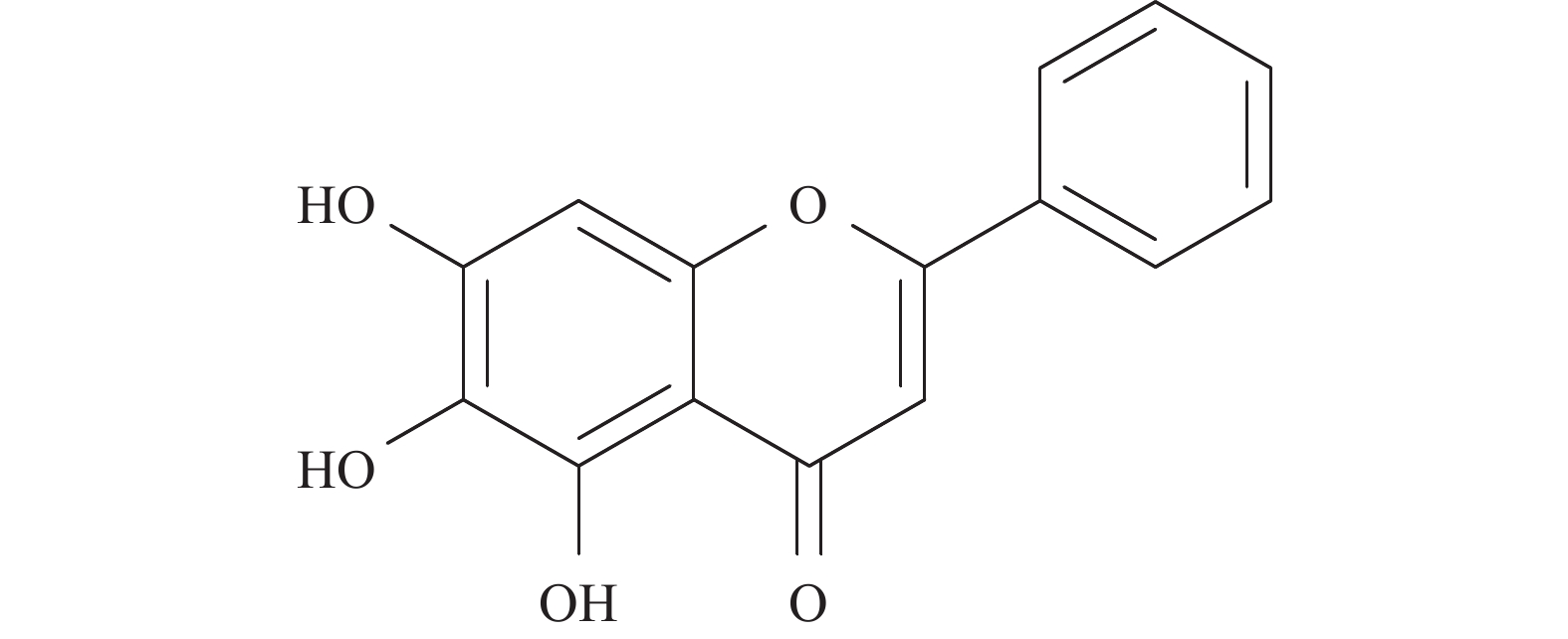
黄芩素(baicalein,BE),全名5, 6, 7-三羟基-2苯基-4H-1-苯并吡喃-4-酮(图1),是从唇形科植物黄芩的干燥根中分离出来的一种多羟基黄酮类化合物。研究表明,BE是一种多靶点的天然抗肿瘤化合物,目前已提出多种针对植物BE的抗肿瘤作用机制,例如清除氧化自由基、抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK),抑制蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B, PKB,又称Akt)或哺乳动物的雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR)活性、诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡和抑制其侵袭和表达等。因此,本文旨在结合国内外研究现状,综述BE对肺癌、乳腺癌、肝癌、结肠癌、膀胱癌等多种肿瘤的药理作用及其机制 [2-3]。
HTML
-
在多种类型的癌症中都发现了分化抑制因子1(inhibitor of diferentiation 1, Id1)蛋白的过表达,包括肺癌。据报道,Src信号通路是Id1表达的必要途径,诱导Id1的表达可促进肺癌细胞的生长和转移,反之,则可显著抑制其细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭。因此,Id1是癌症治疗中的潜在分子靶标[4]。Zhao等[4]通过向裸鼠注射A549细胞来建立原位肺癌模型,并评估了黄芩素的抗肿瘤作用以及Id1相关蛋白在体内外的表达。结果表明,黄芩素可以使肿瘤组织体积减小,抑制Id1蛋白、上皮-间质转化(EMT)、间质细胞标志物(N-钙黏蛋白, 波形蛋白)的表达,并且首次证实了黄芩素通过靶向Src/Id1途径抑制原位移植非小细胞肺癌的肿瘤生长。
-
Gao等[5]研究了黄芩素对人肺癌细胞A549、SK-LU-1和SK-MES-1的生长和凋亡的影响,发现黄芩素可抑制A549和SK-MES-1细胞的增殖。其中对A549细胞的作用是通过降低细胞周期蛋白(cyclin)A的表达来阻断细胞分裂S期,而对SK-MES-1细胞的作用是通过降低细胞周期蛋白D1的表达阻断细胞分裂的G0/G1期。此外,黄芩素还可通过增加p53和Bax的表达来加快肺癌细胞的凋亡。
BE可通过调节不同类型的细胞周期蛋白(cyclins)和细胞周期依赖性激酶(cyclin dependent kinase,CDKs)水平来抑制细胞周期进展,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖。Su等[6]发现当黄芩素浓度为0、20、40、60、80、100 µmol/ L时,可以抑制A549和H1299细胞的增殖。该小组发现当黄芩素的浓度为80 µmol/ L,持续作用48 h时,其抑制效率最高,推测与细胞增殖相关的细胞周期蛋白D1(CD1)和周期蛋白依赖性激酶1(CDK1)重组蛋白表达水平的下调有关。据报道,黄芩素通过降低CDK1和CD1以及上调Bax / Bcl-2的比例,阻碍了S期分裂和半胱天冬酶(caspase)-3酶原的活化,抑制非小细胞肺癌H460细胞生长并诱导凋亡[7]。此外,还发现黄芩素可以抑制细胞EMT和Notch信号通路,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的侵袭。
-
黄芩素还可以作为肺癌常规化疗药物的增敏剂,Lu等[8]研究发现黄芩素可通过下调miR-424-3p,并靶向作用于PTEN / PI3K / Akt信号途径,来抑制A549和H460细胞的生长和增加顺铂的敏感性。该小组在后期的细胞毒性实验中证实,BE仅对A549和H460细胞呈剂量依赖性,而对正常人支气管上皮细胞毒性较小。Lu等[9]研究表明黄芩素和抗肿瘤药多西他赛联用时,可增加微管的稳定性并阻断细胞周期的进程,从而协同抑制A549细胞和Lewis肺癌细胞的增殖,最终诱导细胞凋亡,并评估其具有较好的安全性和有效性。因此,黄芩素作为一种新型的单用和协同抗肿瘤药时,具有较好的发展前景。
1.1. 通过靶向Src/Id1途径抑制肺癌细胞生长
1.2. 抑制调节细胞周期的蛋白表达诱导肺癌细胞凋亡
1.3. 为常规化疗药物的增敏剂
-
磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(PI3K)/Akt,也称为蛋白激酶B(PKB),是信号通路的关键分子[10]。PI3K/Akt信号通路参与多种生物过程,例如恶性肿瘤细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡、血管生成、侵入和转移等,同时诱导肝癌细胞凋亡的药物也可能会干扰PI3K / Akt信号通路。BE可通过上调p21和p27的表达,抑制PI3K/Akt通路,阻滞S期和G2/M期的细胞周期,从而抑制Bel-7402细胞的增殖[11]。另一项研究表明,黄芩素可调控PI3K/Akt信号通路,与LY294002联合用药,诱导SMMC-7721细胞凋亡,是治疗包括肝癌在内的多种癌症的有效途径。阻断程序性细胞死亡蛋白配体1(programmed death ligand1, PD-L1)/ 程序性细胞死亡蛋白1(programmed cell death protein-1, PD-1)途径以防止肿瘤细胞的免疫逃逸是治疗包括肝癌(HCC)在内的多种癌症的有效方法。Ke等[12]发现BE对肝癌细胞除了具有直接的细胞毒性外,还可通过降低信号和激活因子3(STAT3)的活性,进一步下调干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)诱导的PD-L1表达来增强T细胞的免疫应答,以杀死肿瘤细胞。
长非编码RNA已被证实是癌症的治疗靶标,该种编码的过度表达可增强黄芩素在体外抑制肝癌细胞的增殖、诱导细胞凋亡和迁移,在体内具有抑制肿瘤生长等作用。此外,长非编码RNA还可抑制IκBα磷酸化、NF-κB核易位和活性,增强了黄芩素对NF-κB信号传导的影响。对调节NF-κB信号传导在体内外的抗肝癌作用具有显著效果,所以长非编码RNA和黄芩素联合用药可能是肝癌的潜在治疗策略[13]。
-
CD24是一种小的糖基化黏蛋白样细胞表面蛋白,通过糖基磷脂酰肌醇(GPI)锚固附着在细胞膜上。在血液系统恶性肿瘤包括各种实体瘤中都可以观察到CD24的上调,例如神经胶质瘤、乳腺癌、小细胞肺癌、肝癌、卵巢癌和前列腺癌等[14]。研究表明,黄芩素可通过下调CD24中的mRNA的表达来抑制肝癌细胞的生长和存活[15]。
人类早期肝损伤,原发性和转移性肝肿瘤以及肿瘤衍生的细胞系的遗传分析证据明确表明,c-Myc失调是肝癌发生和发展的关键改变。Myc位的染色体畸变是晚期人类肝癌中最常见的异常基因,由于c-Myc是细胞周期进程,细胞凋亡和细胞转化的关键调节剂,靶向该基因的药物可能会获得更有效的抗癌作用并改善HCC的治疗。Han等[15]通过高通量筛选了14种植物提取物的抗肝癌能力,结果证实黄芩素是c-Myc表达的最有效抑制剂,可显著降低c-Myc在HCC细胞中的表达,从而诱导HCC细胞凋亡。
-
自噬是一种高度受控的过程,可响应癌细胞中的饥饿,代谢应激和细胞毒性等各种类型的刺激[12]。研究发现黄芩素可触发肝癌细胞的保护性自噬,AKT / mTOR途径被称为自噬的关键调节因子,在HepG2细胞中被黄芩素抑制[16]。另一项研究表明,黄芩素通过人肝癌细胞SMMC-7721和Bel-7402的内质网应激诱导自噬[17]。
2.1. 调控信号通路诱导肝癌细胞凋亡
2.2. 通过调节因子的表达促进肝癌的增殖和凋亡
2.3. 通过触发肝癌细胞的自噬抑制肝癌细胞增殖
-
基质金属蛋白酶2(MMP-2)和基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)是乳腺癌细胞侵袭和迁移的关键蛋白酶。黄芩素可通过抑制MMP-2和MMP-9的活性(通过抑制Akt途径)来显著抑制细胞迁移和侵袭,这两种酶是乳腺癌细胞的重要因子[18]。Wang等[19]证实了这一点,BE可通过抑制MMP-2和MMP-9的激活和表达来介导MDA-MB-231细胞的侵袭性。MDA-MB-231细胞中的MAPK/MMP信号传导有助于潜在的侵袭机制,这表明MAPK信号传导是高度侵袭性乳腺癌细胞的潜在标志和治疗靶标。Chen等[20]发现BE可明显抑制17β-雌二醇(E2)和GPR30激动剂(G-1)诱导的乳腺癌细胞侵袭以及基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)的表达和激活。Gao等[21]报道了黄芩素通过抑制组织特异性核机制结合蛋白1(special AT-rich binding protein1,SATB1)的表达来抑制MDA-MB-231细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭性。SATB1在许多实体肿瘤中高表达,被认为是抗肿瘤药物的重要靶分子之一。
-
上皮-间质转化(EMT)是乳腺癌细胞在迁移和侵袭过程中发挥作用的关键步骤。Chung等[22]报道了黄芩素可抑制乳腺癌上皮细胞的上皮-间质转化从而起到抗乳腺癌作用。另外一项研究表明,黄芩素不仅可直接作用于乳腺癌细胞还可通过调节乳腺癌巨噬细胞的极化和上皮-间质转化(EMT)来抑制乳腺癌细胞生长,为BE用于乳腺癌以及其他癌症的治疗提供了新的见解[23]。Ma等[24]的研究则表明黄芩素可通过下调SATB1和Wnt/β-catenin途径来抑制EMT,进一步抑制体内外人乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞的转移,也有研究指出,黄芩素可通过下调MDA-MB-231乳腺癌细胞中的Cyr61和LOXL-2的表达来抑制EMT[25]。
3.1. 抑制乳腺癌细胞的侵袭和转移
3.2. 抑制乳腺癌细胞的上皮-间质转化(EMT)
-
细胞衰老是一个正常的二倍体细胞停止分裂和生长停滞,但仍能存活、代谢并具有独特的转录谱和基因调控特征的生物学过程。对衰老细胞产生的分子机制及其分子调控的进一步了解,将为设计新的癌症疫苗或治疗方法开辟新的途径。丝裂原激活的蛋白激酶(MAPK)通路与许多生理效应有关,包括细胞凋亡,细胞增殖和衰老。MAPK信号通路在调节细胞周期再进入和致癌性RAS诱导的衰老中起重要作用[26]。黄芩素可诱导人结肠癌细胞特异性MAPK p38和ERK1/2信号通路的选择性调控,从而可控制肿瘤细胞周期阻滞、凋亡和衰老的分子过程。核因子E2相关因子(nuclear factor erythroid-derived factor2-related factor,Nrf2)与抗氧化反应元件(antioxidant responsive element,ARE)结合构成Nrf2/ARE通路。可启动下游多个抗氧化、抗肿瘤、抗炎蛋白、解毒酶等的表达,是机体抵御各种氧化应激的重要保护通路。Havermann等[19]发现,黄芩素通过激活Hct116人结肠癌细胞中Nrf2/ARE通路和秀丽隐杆线虫中SKN-1基因的应激反应而发挥抗肿瘤作用。Wang等[27]则证明钌-黄芩素复合物可通过激活p-53依赖性细胞凋亡,调节AKT/mTOR和WNT/β-catenin的信号通路发挥化学治疗作用,并能通过诱导细胞凋亡来减少大鼠结肠组织中的ACF多样性和增生性病变。Su等[28]研究发现黄芩素使孕酮诱导的蜕膜蛋白DEPP和DNA损伤诱导45(Gadd45a)的表达上调,通过在Gadd45a和JNK/p38之间形成正反馈环,促进MAPK的激活,可明显引起人结肠癌细胞的凋亡。总的来说,这些发现确定了黄芩素是一种具有较好发展前景的治疗结肠癌的抗肿瘤药。
4.1. 调控信号通路诱导结肠癌细胞衰老和凋亡
-
据相关研究报道,黄芩素通过活化caspase依赖的线粒体途径并抑制Akt磷酸化,从而诱导T24膀胱癌细胞凋亡。更具体地说,黄芩素通过阻断G1/S期的细胞周期进程来抑制T24细胞的生长,并通过激活caspase-9和caspase-3、下调B淋巴细胞瘤2基因(B-cell lymphoma-2, Bcl-2)的表达和上调Bcl2-associated X的蛋白(Bax)的表达来诱导膀胱癌细胞的凋亡[29]。黄芩素还可通过下调miRNA-106来抑制JNK和MEK / ERK通路,从而抑制T24细胞的增殖和迁移,并诱导其凋亡。这项研究为黄芩素在膀胱癌的治疗中提供了新的调节机制,有助于确定膀胱癌治疗的新靶标。
-
活性氧(ROS)作为一类具有高度生物活性的分子,在肿瘤中得到了广泛的研究。癌细胞通常比正常细胞表现出更高水平的ROS,这主要是由于它们的代谢增加、致癌基因激活和线粒体功能障碍。过量的活性氧浓度会导致各种类型的细胞死亡。最近一项研究表明,黄芩素可刺激膀胱癌5637细胞内ROS的生成,并且ROS的产生与凋亡细胞线粒体功能紊乱呈正相关[30]。
5.1. 诱导T24膀胱癌细胞的凋亡
5.2. 促进活性氧的产生从而诱导膀胱癌细胞凋亡
-
黄芩是我国重要的中药材,在中国及其亚洲其他国家都有广泛的应用。通过其活性成分和对不同类型癌症的抗肿瘤机制的研究进展,将为癌症治疗提供新的潜在策略。本文综述了黄芩素的多种作用机制,包括阻断细胞周期,诱导凋亡,抑制肿瘤细胞的侵袭和转移,增强化学治疗剂的作用,触发自噬细胞死亡等。近年来,黄芩素的临床前研究取得了令人鼓舞的进展,但仍需要进一步研究以改善其生物学作用。我们有理由相信黄芩素可能会被开发为一种新型的抗癌药,可以单独使用或与化学治疗药联合使用,从而改善癌症患者的用药多样性,减少癌症患者的痛苦和提高癌症患者的生存周期。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: