-
冻伤是由寒冷、潮湿或大风引起的,会导致周围组织的损伤、丧失和残疾,尤其是手、脚、鼻子、脸颊和耳朵[1]。冻伤可引起微血管收缩,红细胞聚集,小动脉口径减小,硬度增大,毛细血管通透性升高,从而增加血液黏度,增大血流阻力,引起局部组织血流量减少,最终导致微循环障碍,使组织细胞由于缺血缺氧而坏死[2-3],临床早期主要通过血管阻塞症状和软组织缺血边界来判断冻伤程度[4-5]。因此,课题组着手研发一种由肌醇烟酸酯(IN)和肝素钠组成的冻伤膏,直接涂在易冻伤的四肢上,用于预防和治疗冻伤,降低冻伤程度。该冻疮膏对早期冻伤、皲裂、湿疹及软组织损伤均有很好的治疗效果[6]。其中,IN是一种外周血管扩张剂,温和持久,能选择性扩张病变部位及冷刺激敏感部位的血管,具有溶栓抗凝、缓解血管痉挛、改善小血管循环、降低毛细血管脆性的作用[7]。此外,它还具有止痒、止痛、消肿的作用。在此处方中,肌醇烟酸酯还可缓解长期使用肝素钠引起的局部血肿血栓和皮肤过敏,有效减少全身凝血功能障碍的副作用。
分析药物在体内血药浓度随时间变化的动态过程,是传统药动学的研究方法。然而,对于经皮给药,药物入血浓度往往很低,难以定量。故本研究采用活体分时采样法,直接在大鼠皮肤上涂药,在不同时间点测定皮肤组织匀浆中的药物浓度。目前,已有研究对人或大鼠血浆中肌醇烟酸酯进行药代动力学研究[8-9],但是,没有可用于定量分析大鼠皮肤组织匀浆样品中肌醇烟酸酯的含量。因此,本研究旨在建立一种快速、灵敏、重现性好、经济简便的HPLC法,定量分析大鼠皮肤中肌醇烟酸酯,用于大鼠经皮给药肝素钠肌醇烟酸酯乳膏后肌醇烟酸酯的药动学研究。
-
W501型高效液相色谱仪(Waters);KQ3200型超声波清洗器(昆山市超声仪器有限公司,功率150 W,频率40 kHz);FLUKO MODE组织匀浆器(上海弗鲁克流体机械制造有限公司);XW-80A微型旋涡混合器(上海沪西分析仪器厂有限公司);离心机(ABBOTT LABORATORIES Germany);剃须刀(上海飞科电器有限公司);AUW120D型电子分析天平(SHIMADZU公司)。
-
肌醇烟酸酯(天津中瑞药业有限公司,纯度:99.5%);甲苯咪唑对照品(中国食品药品检定研究院;纯度:99.9%);肝素钠肌醇烟酸酯乳膏(北部战区总医院药剂科自制,批号:
20150108 );盐酸(分析纯,天津市凯信化学工业有限公司);乙腈(色谱纯,Sigma公司);甲醇(色谱纯,Sigma公司);四氢呋喃(色谱纯,Sigma公司);水为纯化水;其他试剂均为分析纯。 -
SD清洁级雄性大鼠(体重230~250 g):由辽宁长生生物技术有限公司提供,许可证号:SCXK(辽)2010-0001。
-
Kromasil ODS C18 色谱柱(4.6 mm× 250 mm,5 μm);流动相为甲醇-水-四氢呋喃(35∶55∶10,V/V/V);检测波长为262 nm;流速1.0 ml/min;柱温25 ℃;进样量20 μl。
-
精密称取肌醇烟酸酯对照品12.5 mg(现用现配),置于10 ml量瓶中,加入适量0.5 mol/L盐酸水溶液,超声溶解,0.5 mol/L盐酸水稀释至刻度,即得浓度为1 250 μg/ml的对照品储备液。精密量取对照品储备液适量,置于10 ml量瓶中,分别用0.5 mol/L盐酸水稀释成系列溶液,即得到浓度为5.00、10.00、20.00、50.00、100.00、200.00和400.00 μg/ml的系列对照品溶液。同法配制浓度分别为10.00、50.00、300.00 μg/ml的低、中、高对照品溶液。
-
精密吸取低、中、高对照品溶液各50 μl,分别加入到1 ml空白皮肤匀浆液中,分别得到浓度为0.50、2.50和15.00 μg/ml的质控样品(QC)。
-
取甲苯咪唑对照品适量,精密称定,加2%盐酸甲醇溶液超声溶解并定量稀释制成浓度为12 μg/ml的内标溶液。
-
根据非临床药动学研究技术指导原则及《中国药典》生物样品定量分析方法验证指导原则的有关要求[10-11],对定量研究方法进行方法学验证。
-
取72只健康SD大鼠,雄性,体重(230~250)g,于实验条件下饲养5 d(22±2) ℃,相对湿度(50±10)%。试验开始前1 d,用电动理发器对腹部皮肤进行脱毛(4 cm×4 cm,不要损伤皮肤),禁食不禁水。其中6只大鼠作为空白组,涂抹空白乳膏基质。其余大鼠将临床3倍用量的肝素钠肌醇烟酸酯乳膏均匀涂抹于腹部脱毛处皮肤,剂量为0.2 g/只,于给药后0.25、0.5、l、2、3、4、6、8、10、12、24 h各时间点分别取6只大鼠,给药皮肤表面用生理盐水反复擦拭,以棉签擦干,剥离剪取固定面积的皮肤,去除附着的肌肉,备用。皮肤样品的处理:精密称取皮肤样品0.07 g,加入1 ml 甲醇-0.5mol/L盐酸(50:50,V/V),组织匀浆机研磨后超声处理20 min,离心10 min(转速为10 000 r/min),取300 μl上清液,加入50 μl内标溶液,再加入1 ml乙腈,涡旋混匀1 min,离心10 min(转速为10 000 r/min),取上清液,空气流吹干,加200 μl流动相涡旋1 min复溶,离心5 min(转速为10 000 r/min),取上清液,20 μl进样。
-
采用DAS 2.0药动学软件处理,以统计矩方法计算药动学参数。
-
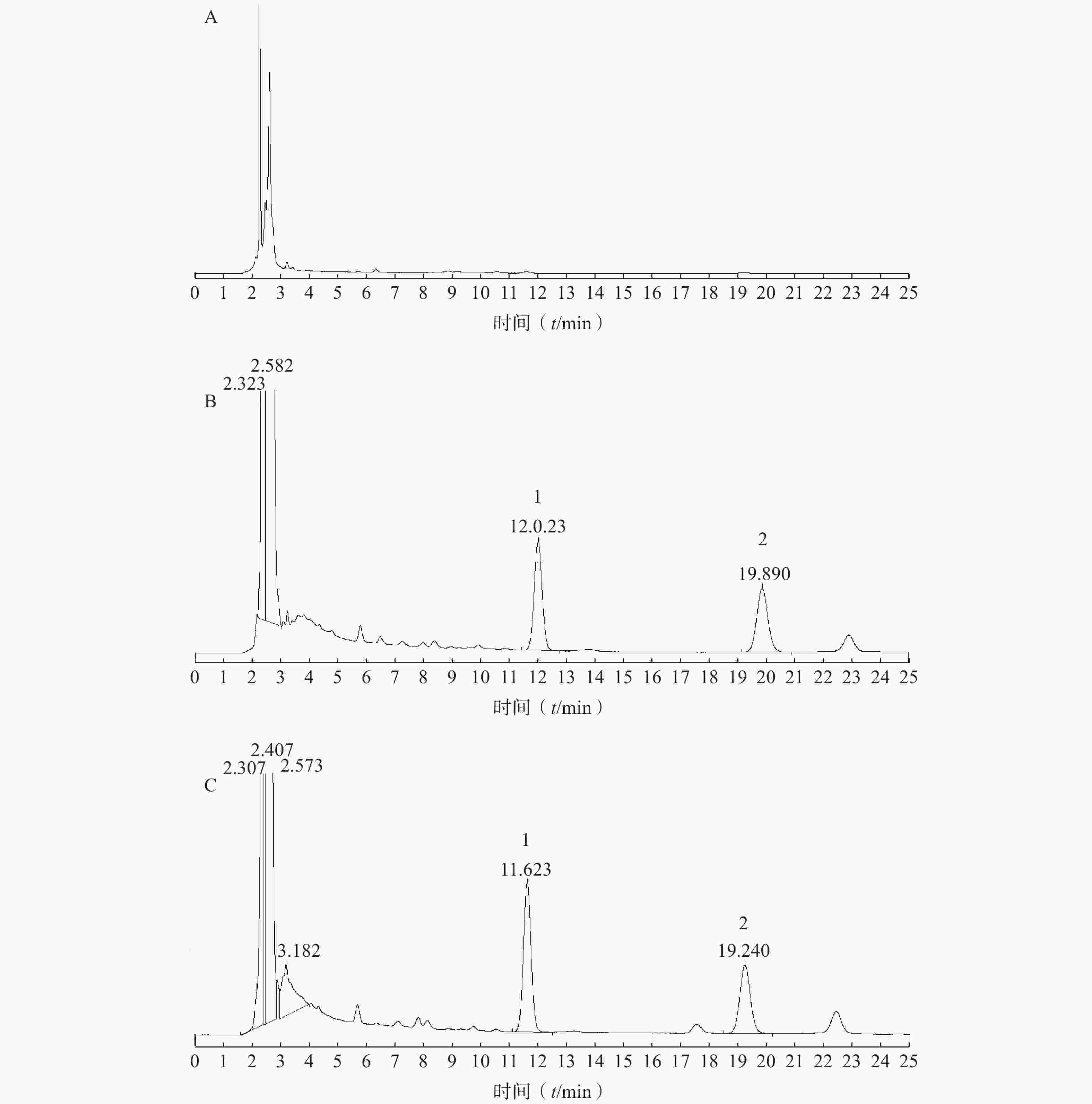
取涂抹空白乳膏基质的大鼠皮肤和给药后大鼠皮肤经处理后,分别进样20 μl,记录色谱图,考察是否有内源性物质干扰肌醇烟酸酯的测定。结果见图1。由实验结果可知,在此色谱条件下,皮肤中内源性物质和空白乳膏基质不干扰肌醇烟酸酯和内标的定量测定。
-
精密吸取系列对照品溶液各50 μl,分别加入到1 ml空白皮肤匀浆液中,分别得到待测物浓度为0.25、0.50、1.00,2.50,5.00,10.00和20.00 μg/ml的系列溶液,按“2.4”项下操作后进样分析,记录峰面积,以肌醇烟酸酯的浓度(X)为横坐标,以肌醇烟酸酯(A)与内标物(B)的峰面积比值(Y)为纵坐标,进行线性回归计算,得回归方程为Y=0.172X+0.002(r=0.999 9),线性范围0.25~20.00 μg/ml,定量下限为0.25 μg/ml(S/N≥10)。
-
取低、中、高不同浓度的QC样品及定量下限,按“2.4”项下方法操作。每个浓度配制6份样品,配制3个分析批,连续测定3 d。计算定量下限和QC样品的日间和日内的准确度RE%和精密度RSD%,见表1,该方法的精密度和准确度均符合生物样品分析要求。
质量浓度
(ρB/μg·ml−1)日内精密度 日间精密度 实测浓度
(ρB/μg·ml−1)RSD
(%)RE
(%)实测浓度
(ρB/μg·ml−1)RSD
(%)RE
(%)0.25 0.24±0.020 8.20 −3.44 0.24±0.025 10.38 −3.18 0.5 0.50±0.042 8.53 −0.87 0.51±0.039 7.65 1.61 2.5 2.37±0.068 2.85 −5.25 2.33±0.12 5.15 −7.00 15 14.67±0.66 4.49 −2.22 13.99±0.85 6.07 −6.73 -
取低、中、高不同浓度的QC样品,按“2.4”项下方法操作,记录峰面积(A1)。另外,将1 ml空白皮肤匀浆液按“2.4”项下方法操作,提取后,加入3种不同浓度的QC样品各50 μl,空气流吹干,加200 μl流动相涡旋1 min复溶,离心(10 000 r/min,5 min),取上清液,20 μl进样,记录峰面积(A2)。将两者相比,即得QC样品的提取回收率。结果见表2。肌醇烟酸酯的平均提取回收率为96.18%,甲苯咪唑的平均提取回收率为90.65%,RSD均<15%,表明该提取方法具有较好的稳定性和重现性。
成分 质量浓度
(ρB/μg·ml−1)回收率( % ) mean±SD RSD( % ) 肌醇烟酸酯 0.5 94.26±4.11 4.36 2.5 96.76±5.02 5.19 15 97.52±2.20 2.26 甲苯咪唑 1.70 90.65±3.17 4.35 -
取低、高不同浓度的QC样品,按照“2.4”项下皮肤样品的处理方法操作,分别考察低、高2个浓度的QC样品在室温下放置12 h、−4 ℃放置12 h、反复冻融3次(−20 ℃)和冷冻贮存2周(−80 ℃)的稳定性。数据结果见表3。结果表明,各生物样品在上述条件下稳定性均良好。
稳定性条件 质量浓度
(ρB/μg·ml−1)实测值
(ρB/μg·ml−1)RSD
(%)室温下放置12 h 0.5 0.47±0.037 7.94 15 14.56±0.63 4.36 −4 ℃乙腈中放置12 h 0.5 0.46±0.034 7.40 15 16.71±0.50 3.03 −20 ℃反复冻融3次 0.5 0.50±0.019 3.75 15 16.73±0.16 0.96 −80 ℃冷冻贮存2周 0.5 0.47±0.038 8.24 15 13.21±0.75 5.69 -
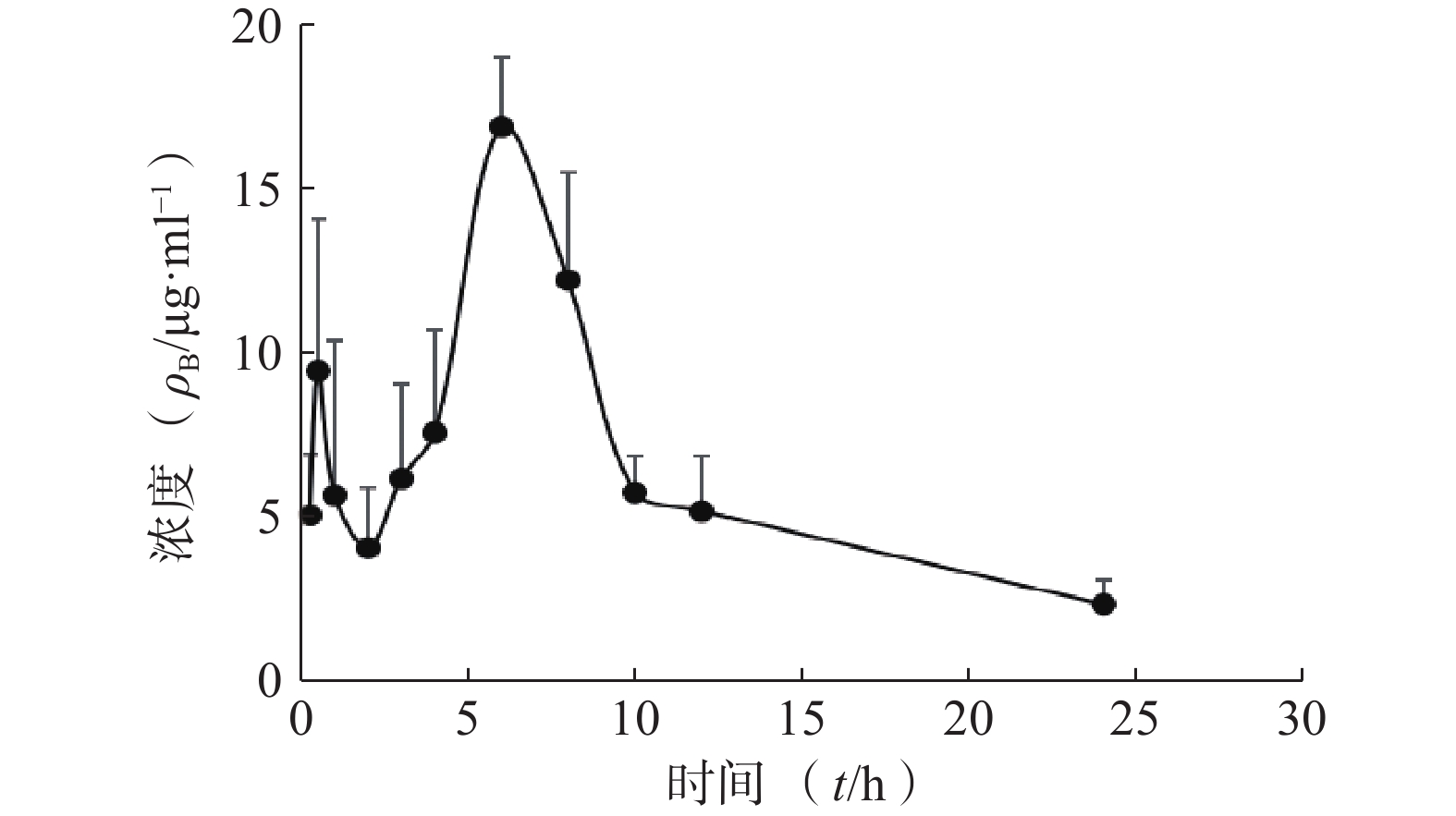
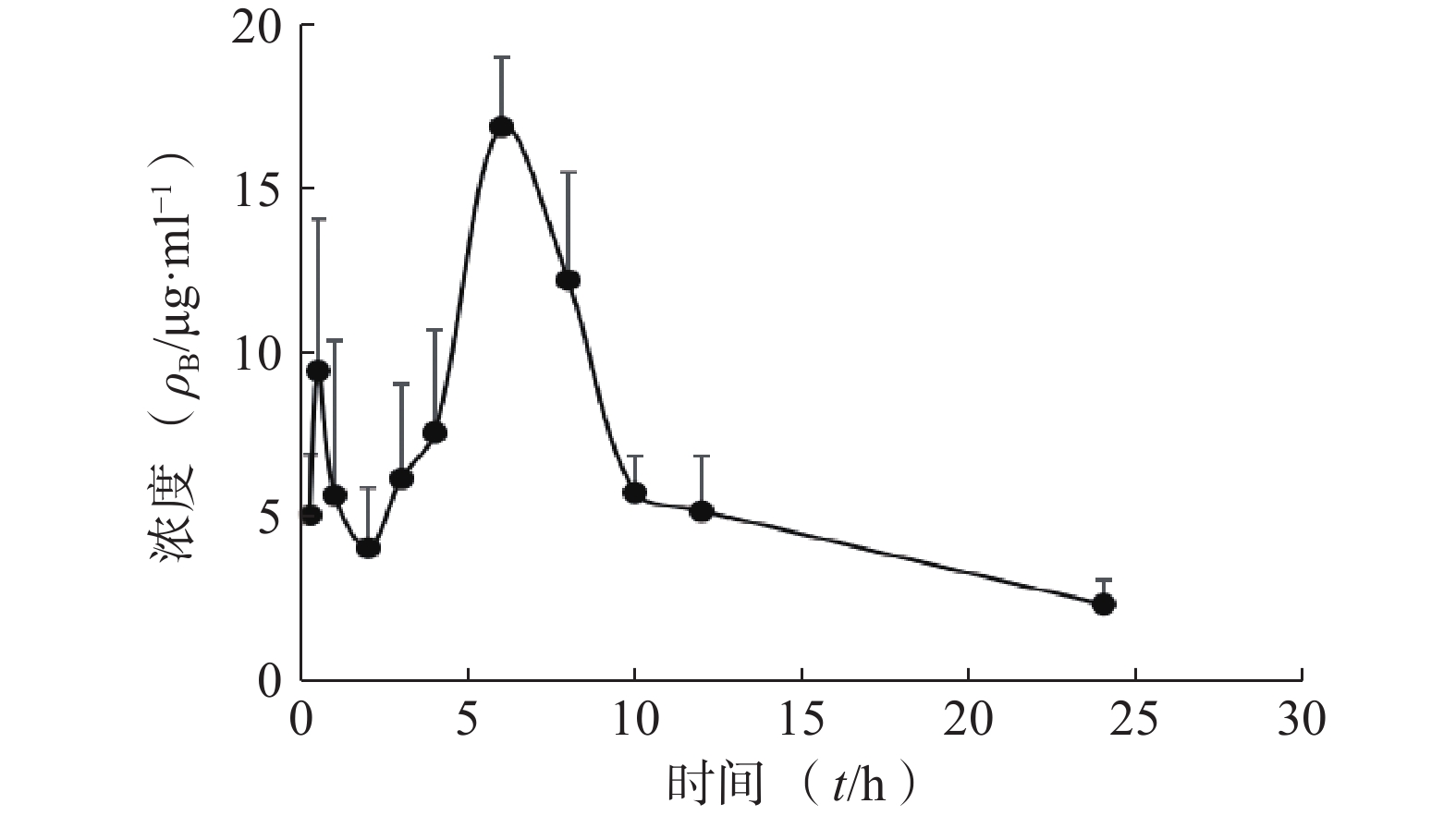
采用DAS 2.0软件,以非房室模型分析待测物的药动学数据。皮肤中药物浓度数据以(mean±SD)表示,绘制了平均药物浓度时间曲线,各时间点含药浓度的计算分别伴随行标曲及QC。将给药后不同时间血药浓度和时间数据用DAS 2.0药动学软件处理,以统计矩方法计算药动学参数。详见图2和表4。
统计矩参数 单位 肌醇烟酸酯参数值 t1/2 h 4.555±2.054 Tmax h 6±0 Cmax mg/L 16.929±2.153 AUC0-t mg·h /L 150.665±16.568 AUC0-∞ mg·h /L 161.074±23.917 MRT(0−t) h 9.044±0.618 MRT(0−∞) h 10.444±1.91 CLz/F L/(h·kg) 0.19±0.03 Vz/F L/(h·kg) 1.19±0.437 -
本实验采用在体给药分时取样法,在不同时间点取皮制备成匀浆测定皮肤中药物浓度。该方法线性关系良好、所测匀浆样品的精密度、准确度等方法学均符合生物样品定量分析要求,其专属性强、灵敏度高、简便、快速高效,可以用于大鼠皮肤中IN的含量测定,对IN在体皮肤浓度测定以及相关药理研究有一定的参考价值。由上述结果可知,IN能迅速渗透进入皮肤,并能长时间蓄积在皮肤局部,有利于IN在病变部位长时间发挥药效。HPLC分析方法快速、准确、回收率高、重现性好,可成功的用于测定GJR中IN在皮肤中的含量,表明在体给药分时取样法能较好地反映药物在大鼠体内的经皮代谢过程,适用于临床前外用药物的皮肤药动学筛选与评价,为临床用药方案的确定提供参考。
Skin pharmacokinetics of inositol nicotinate in heparin sodium inositol nicotinate cream
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202404006
- Received Date: 2024-04-02
- Rev Recd Date: 2024-07-10
- Available Online: 2025-01-16
- Publish Date: 2025-01-25
Abstract:
| Citation: | CUI Yaling, WU Qiong, MA Liangyu, HU Bei, YAO Dong, XU Zihua. Skin pharmacokinetics of inositol nicotinate in heparin sodium inositol nicotinate cream[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2025, 43(1): 6-9, 21. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202404006 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: