-
白血病是一类由造血干细胞恶性增殖引起的以出血、贫血、感染、不同程度的肝、脾、淋巴结肿大等为症状的造血系统恶性肿瘤[1]。目前,化疗是白血病治疗的重要手段,但复发率高、预后差、易产生耐药性等情况使得其对白血病的治疗效果大大折扣[2-3]。因此,寻找低毒、高效的治疗药物来提高疗效并降低复发率是治疗白血病的关键[4-5]。中医古籍中无白血病病名,但据其临床特点,应归属于“急劳”“热劳”“髓劳”“血证”“髓枯”“虚劳”等范畴[6],由正虚邪实导致形成本虚标实之证。中药有可改善症状、减低化疗后毒副反应等特点,在白血病的治疗方面具有独特优势[7]。
定清片是上海中医药大学附属岳阳中西医结合医院(本院)血液科黄振翘教授、周永明教授在“扶正祛邪”理论指导下,经多年潜心研究,逐步改良而成的一种治疗白血病的有效制剂,由雄黄、黄芩、人工牛黄、栀子、陈皮、冰片等12味药组成[8]。方中诸药配伍,共奏益气养阴、清解邪毒之功,使标本得治、虚实共调。定清片在临床使用中取得了很好的疗效,在临床上定清片联合化疗治疗急性髓系白血病患者的西医疗效总有效率为80.0%,中医证候疗效总有效率为93.34%,缓解率66.7%,高于化疗治疗,还可显著改善患者临床症状,减轻化疗引起的常见毒副反应[9-10]。实验表明,定清片在体外能抑制人白血病HL-60细胞增殖,其作用机制可能与影响细胞周期和诱导细胞凋亡相关[11],但其具体作用机制尚不明晰,需要进一步研究。
本研究利用网络药理学及分子对接技术,探讨定清片治疗白血病的活性成分和作用靶点,以期阐明其可能的作用机制,为定清片用于白血病的临床治疗提供理论依据。
-
本研究通过检索TCMSP数据库(https://old.tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php),以OB≥30%,DL≥0.18[12] 作为筛选条件选出定清片的有效成分及对应的靶点信息。对于TCMSP数据库没有的中药,通过HERB数据库(http://herb.ac.cn/)筛选成分,在Pubchem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)中下载有效成分的2 D结构,并在SwissTargetPrediction数据库(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/)中输入有效成分的2 D结构进行检索,以“Probability>0.1”为条件对靶点进行筛选。最后利用UniProt数据库(https://www.uniprot.org/)将筛选到的靶点转换为对应的标准基因名。
-
在OMIM(https://www.omim.org/)、DisGeNET (https://www.disgenet.org/)和GeneCards(http://www.genecards.org/)数据库,以关键词“Leukemia”进行检索,获取白血病相关疾病靶点,在Venny2.1在线平台导入药物与疾病靶点,绘制药物-疾病共有靶点韦恩图,获得定清片治疗白血病的潜在靶点。
-
将药物、活性成分、疾病靶点导入Cytoscape 3.7.2软件,构建“药物-成分-疾病靶点” 网络图。
-
将共有靶点导入 String 数据库(https://cn.string-db.org),种属选择“homo sapiens”,设置置信度为0.4,隐藏游离节点,其他参数保持默认设置,输出后将结果导入Cytoscape软件构建PPI网络,应用MCODE插件,识别密集连接的网络特征,进一步筛选核心靶点群落。
-
将物种设置为“homo sapiens”,利用DAVID数据库(https://david-d.ncifcrf.gov/), 进行基因本体论(GO)功能富集分析和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)通路富集分析。富集结果以P<0.05为标准进行筛选,通过微生信在线软件(http://www.Bioinformatics.com.cn/)进行数据可视化处理。
-
用RCSB PDB数据库(https://www.rcsb.org/)下载核心靶点的蛋白结构,借助Pymol软件去除蛋白的水分子和小分子配体。通过Pubchem数据库获取成分的3 D结构,运用OpenBabel-3.1.1软件将小分子结构转换为mol 2格式。再通过AutoDock vina软件对小分子配体和蛋白受体进行预处理并进行分子对接,得到靶点蛋白和化合物对接的最低结合能,运用Pymol软件将对接结果进行可视化。
-
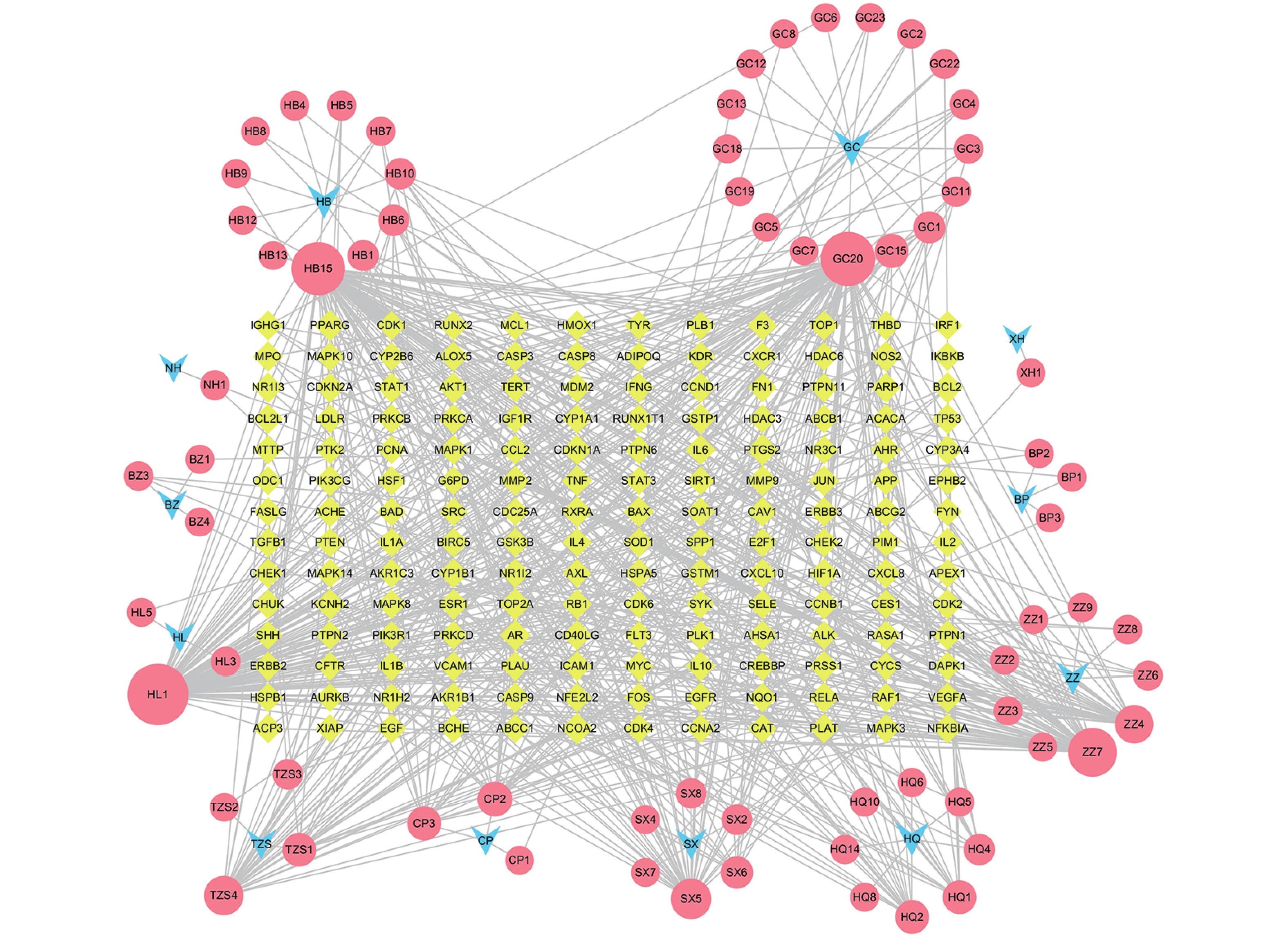
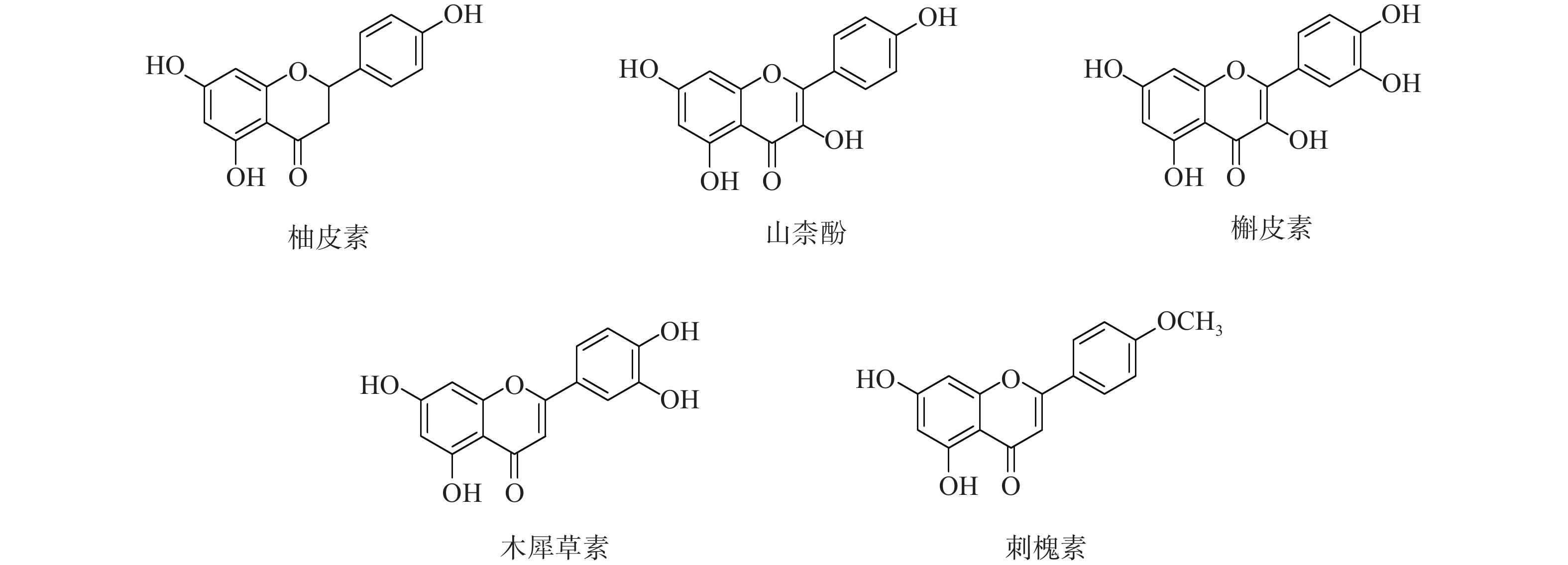
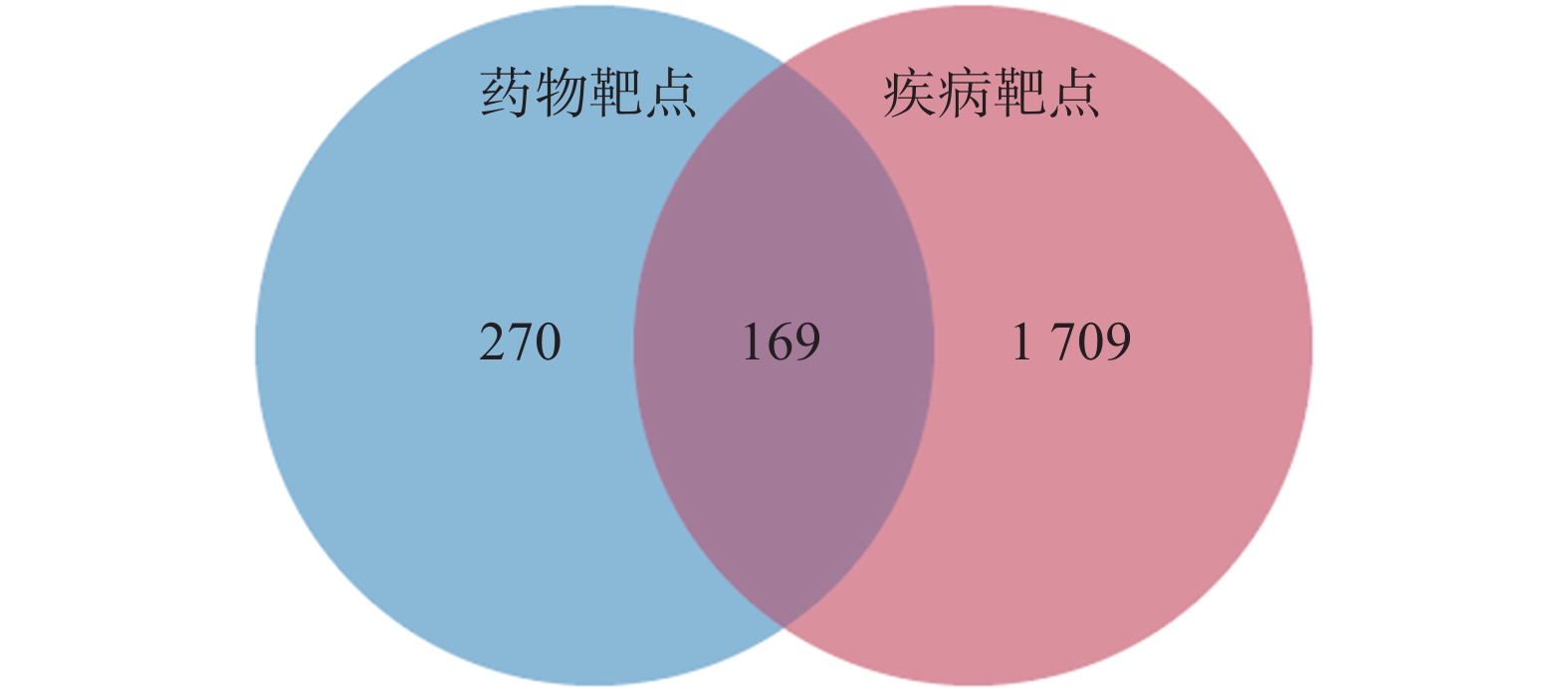
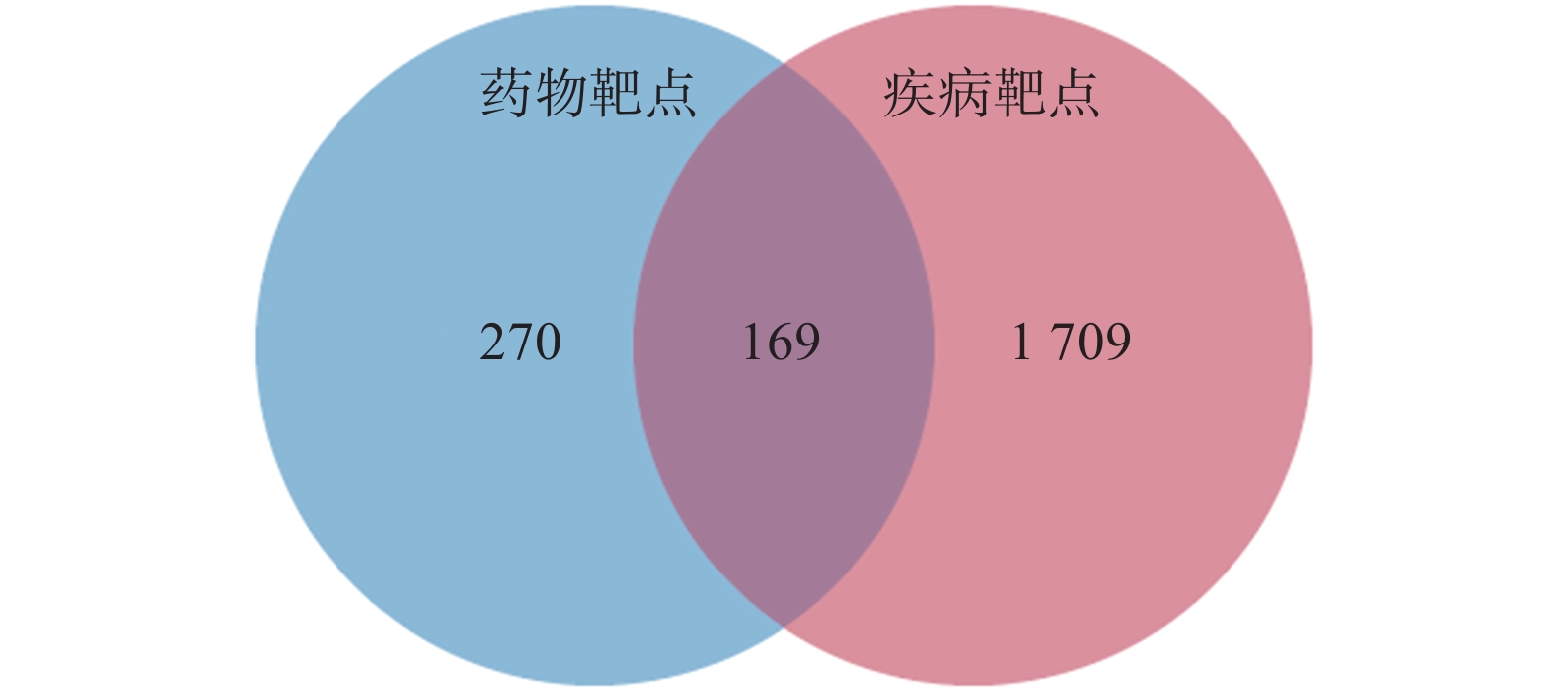
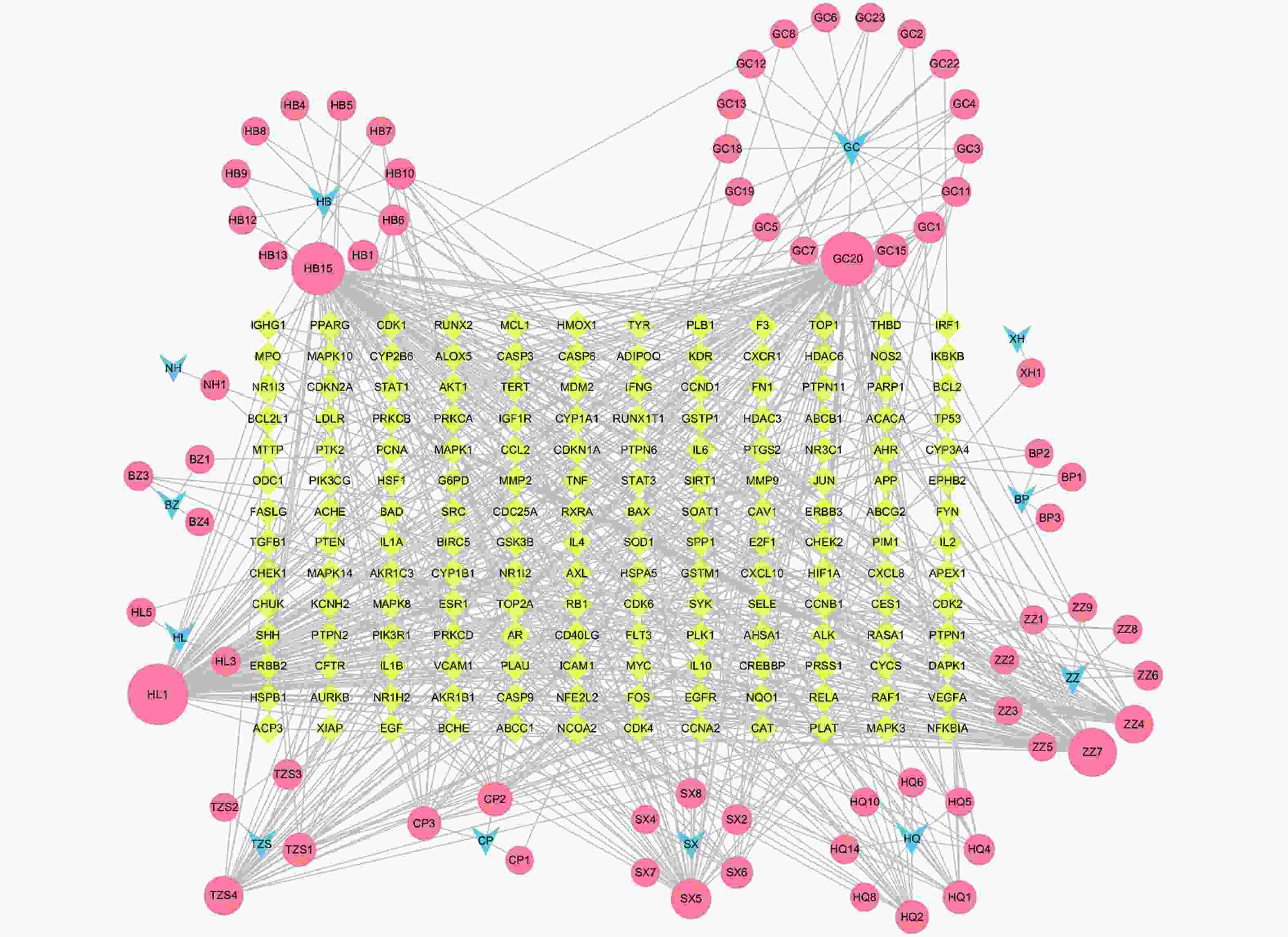
定清片由12味药组成,通过数据库搜集共获得82个活性成分及439个作用靶点。通过疾病数据库得到白血病相关靶点1 878个,将疾病靶点与活性成分靶点进行交集,绘制韦恩图(图1),得到169个共有靶点。将这169个共有靶点导入Cytoscape中,删除与靶点无交集的孤立成分后绘制“药物-成分-靶点-疾病”网络图(图2),共获得249个节点、712条边。根据网络的拓扑分析,筛选出度值较大的活性成分有槲皮素(97)、桑黄素(78)、山柰酚(75)、木犀草素(61)、川陈皮素(33)、汉黄芩素(20)和柚皮素(17)等,这些度值较大的化合物可能是定清片治疗白血病的潜在活性成分。
-
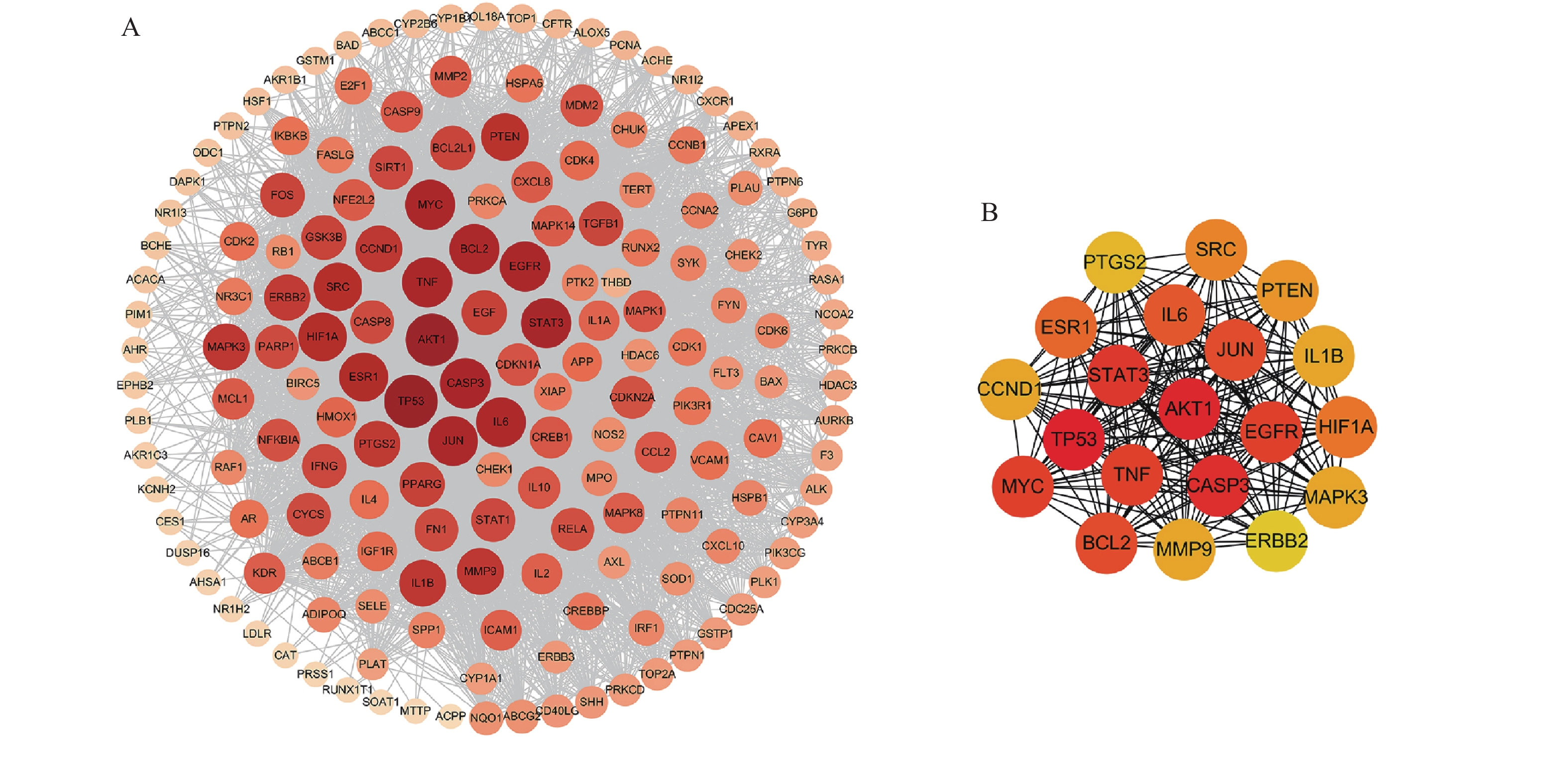
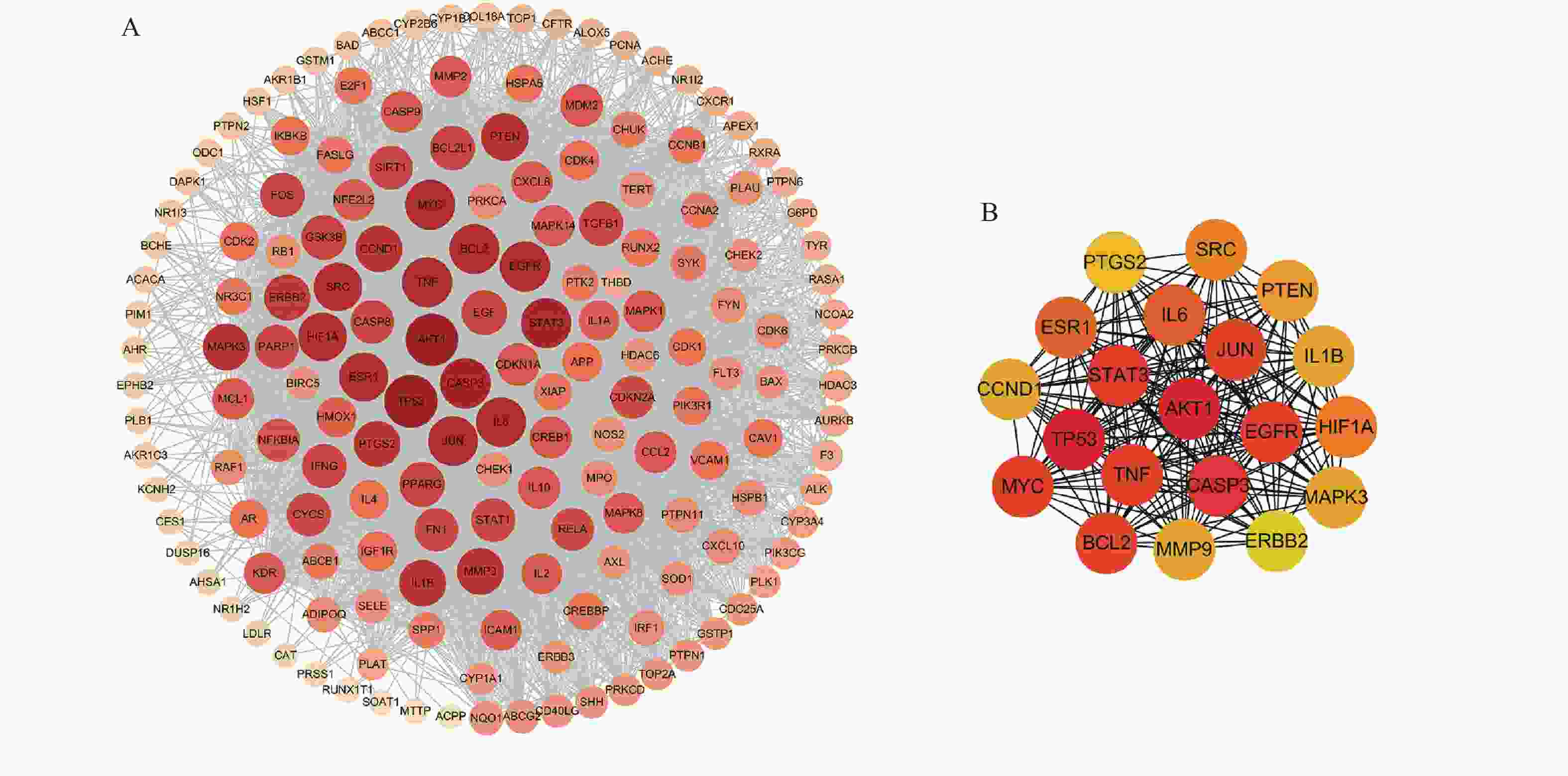
将169个共有靶点导入STRING数据库,将得到的文件导入Cytoscape软件进行可视化处理(图3A),获得PPI网络图。通过分析可知网路中共有162个节点(靶点蛋白)、1 817条边(蛋白相互作用),颜色由深变浅代表度值由大变小。按照度值大小排名靠前的靶点有TP53、AKT1、CASP3、STAT3、TNF、MYC、EGFR、JUN、BCL2等,选取度值最高的靶点绘制核心靶点PPI网络图(图3B),这些可能是定清片治疗白血病的关键靶点。
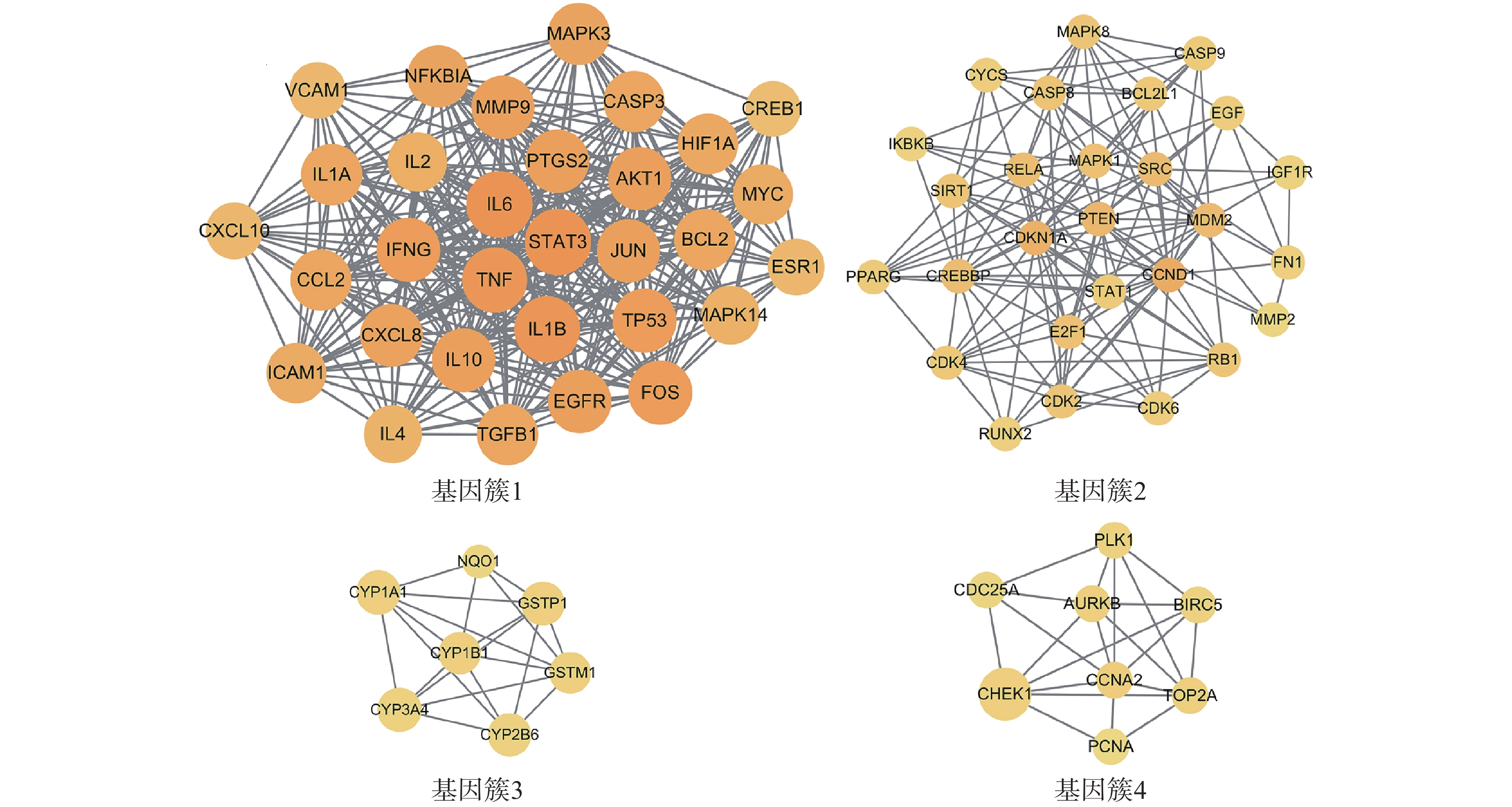
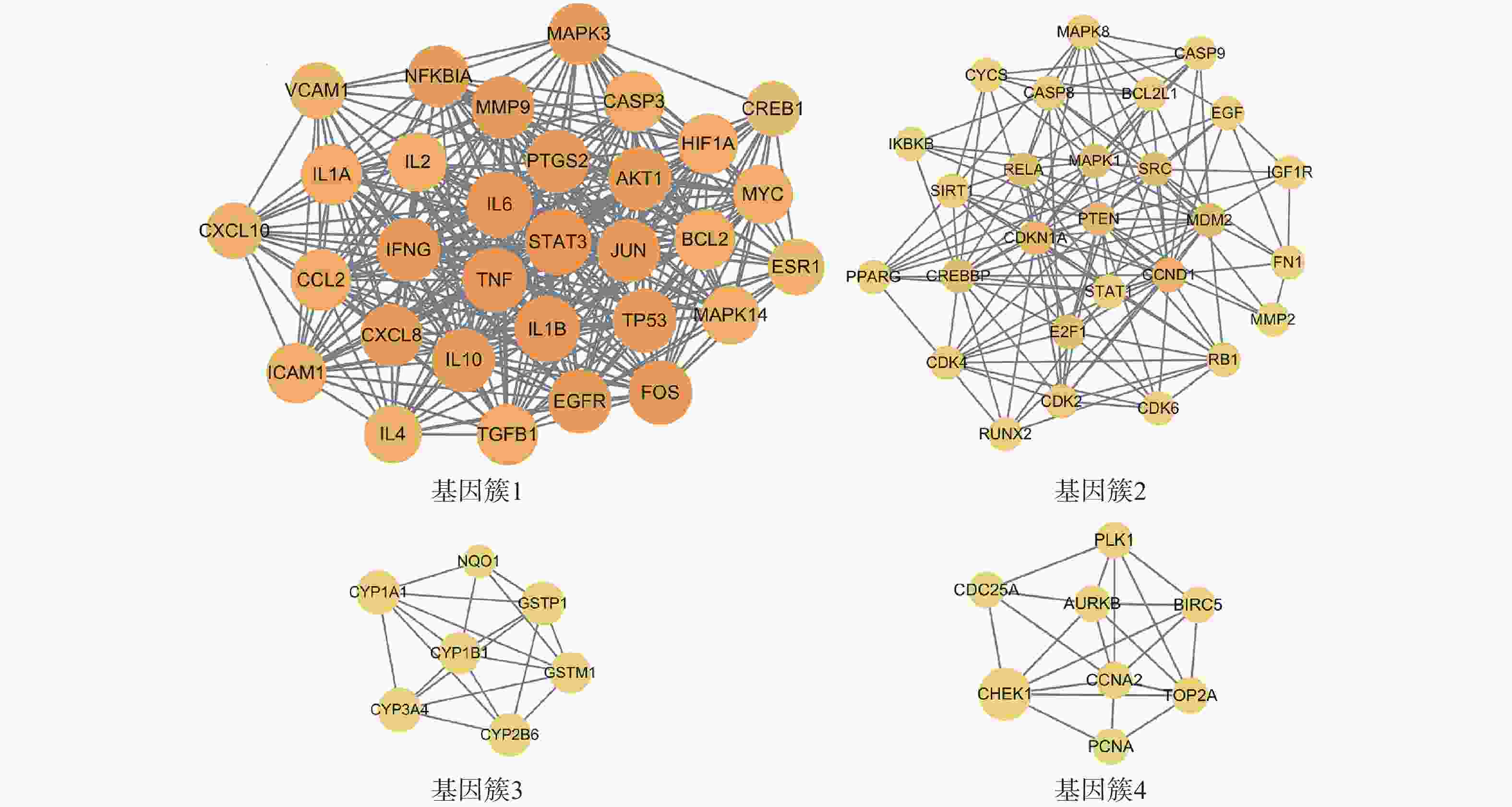
为进一步探究靶点间的集落关系,对PPI网络开展MCODE子簇分析,得到评分最高的4个基因簇(图4)。其中基因簇1包含31个靶点,2含27个,3含7个,4含8个。评分最高的基因簇1中包含了31个关键靶点,有FOS、IL-2、EGFR、TP53、ICAM1、MAPK3、MAPK14、IFNG、TGFB1、MYC、NFKBIA、HIF1A、CREB1、ESR1、BCL2、TNF、IL-10、AKT1、IL-6、IL-1B、MMP9、CCL2、JUN、CXCL10、PTGS2、IL-4、VCAM1、STAT3、IL-1A、CASP3、CXCL8。
-
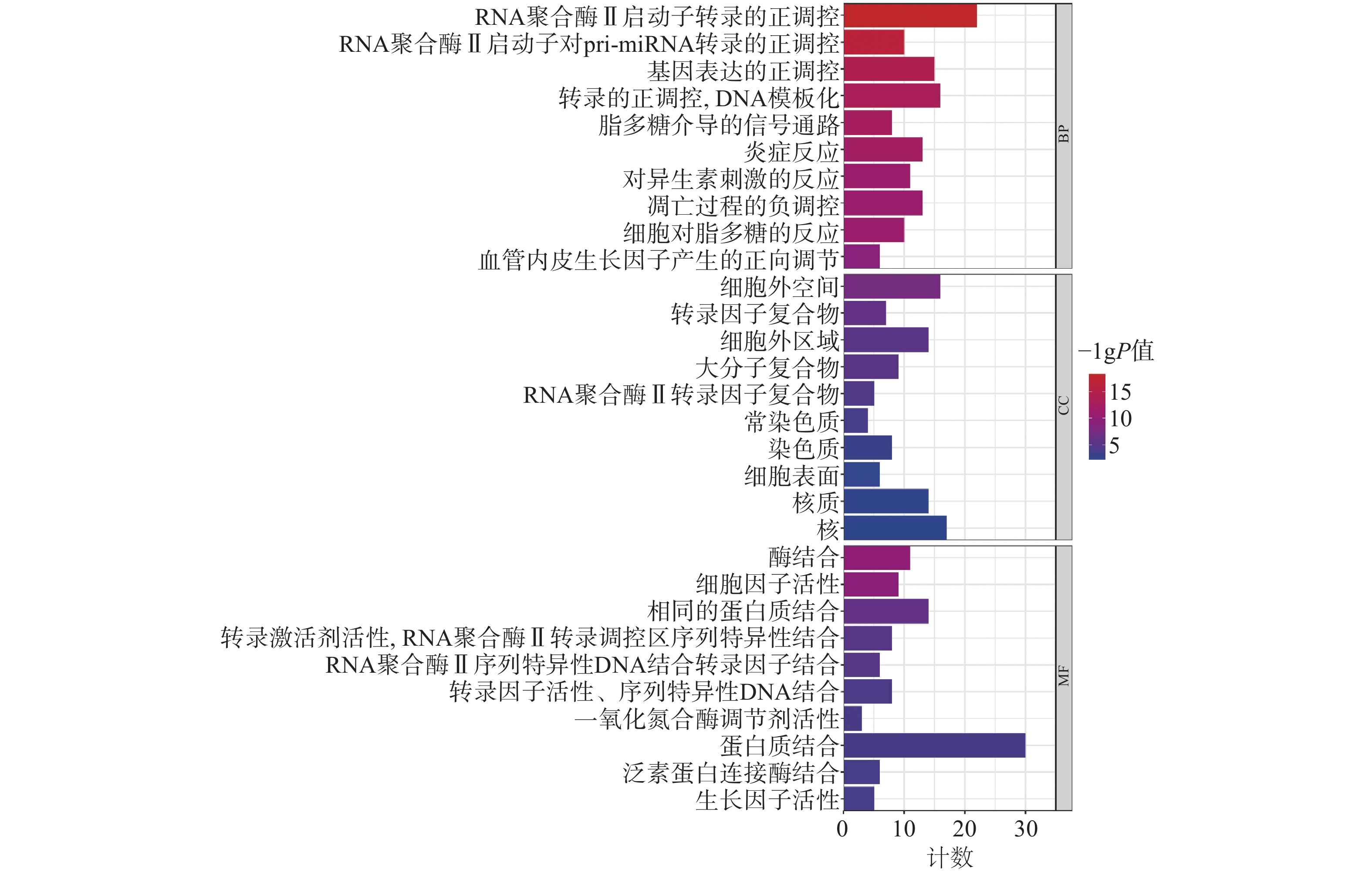
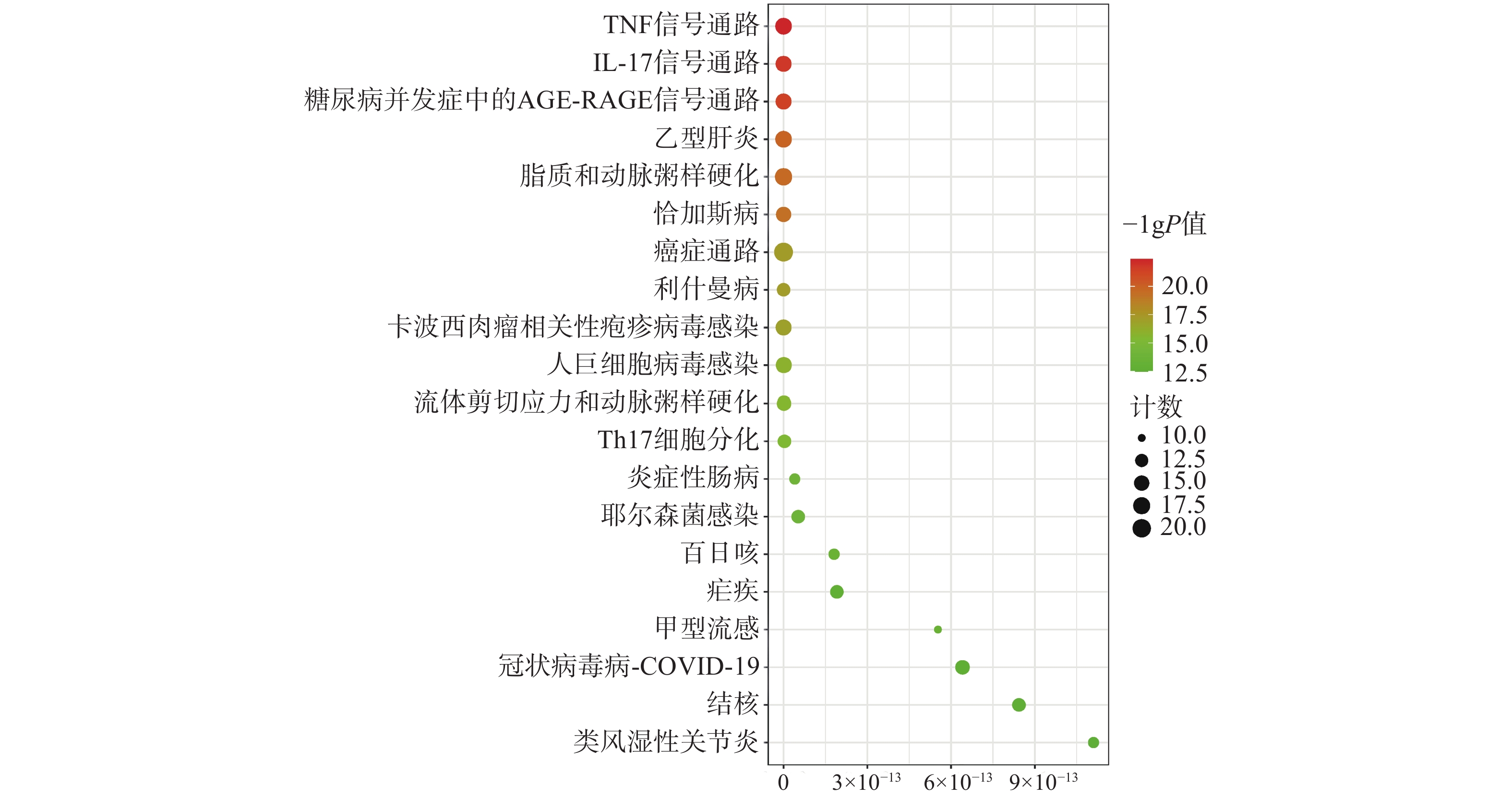
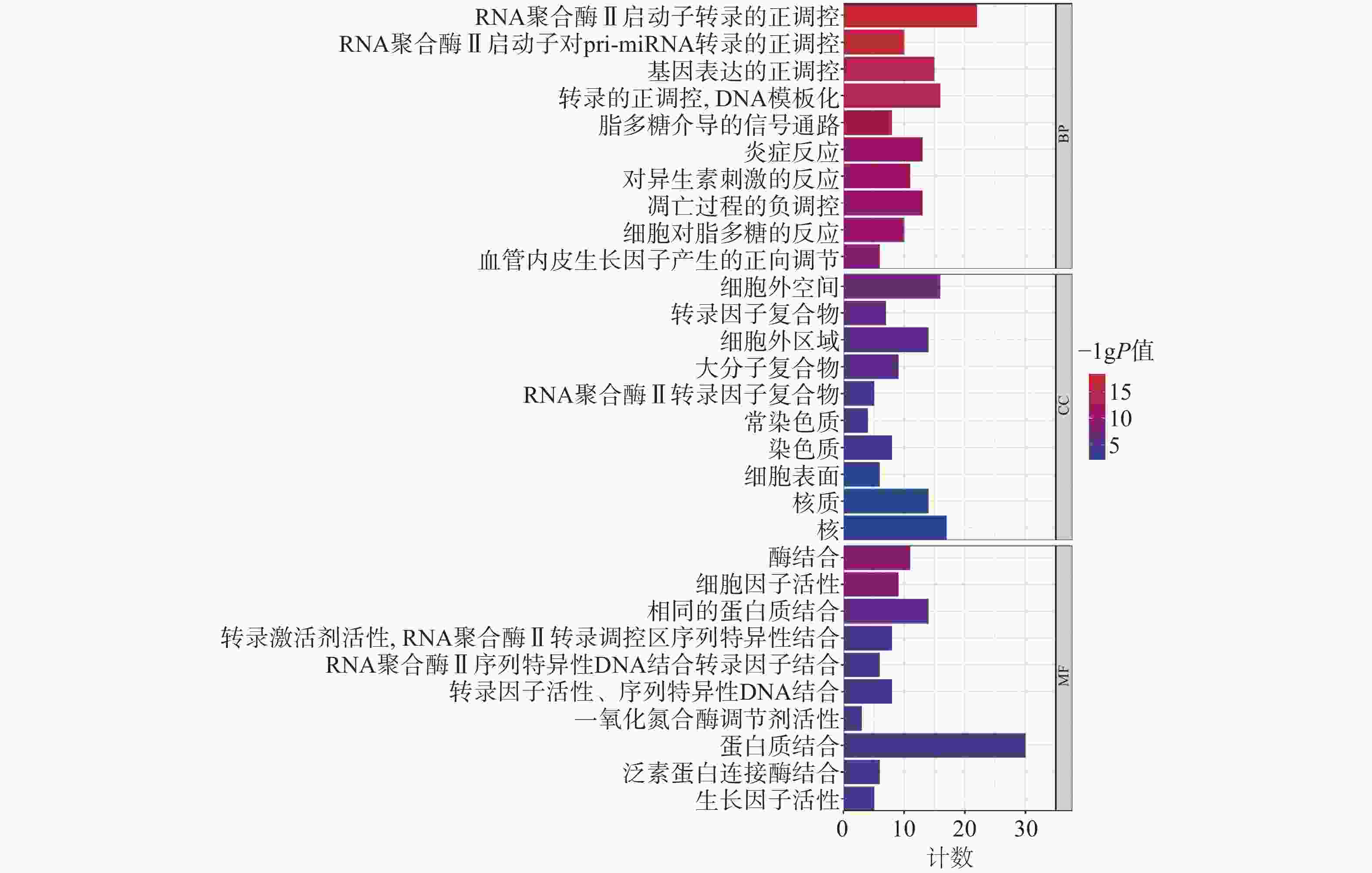
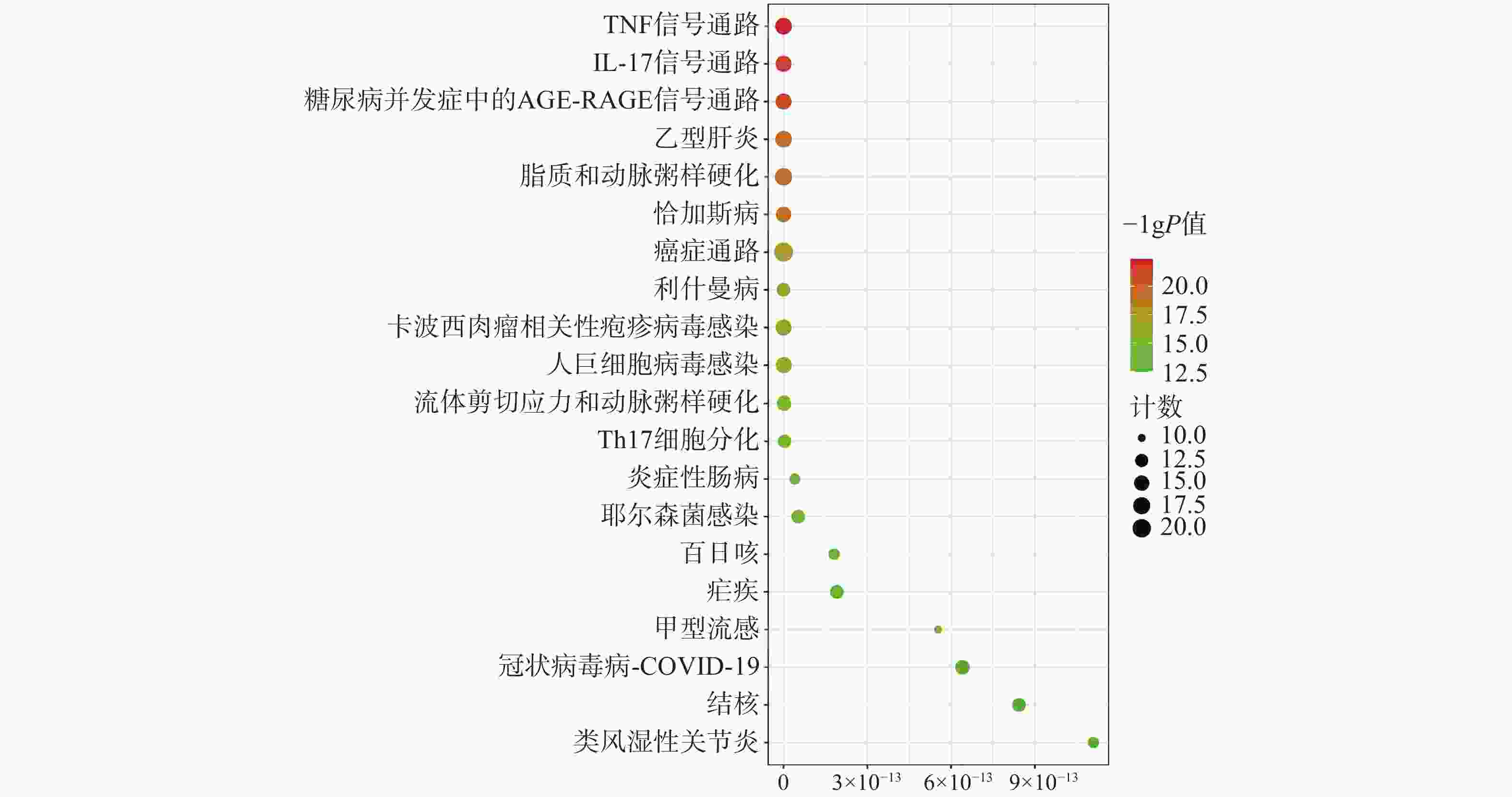
为聚焦核心靶点的相互作用,对基因簇1中的31个关键靶点进行GO和KEGG通路富集分析,最终得到GO富集条目431条。其中,生物过程(BP)368条,细胞组成(CC)19条,分子功能(MF)44条。通过GO富集分析发现,BP主要包括RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的正调控、基因表达的正调控、炎症反应、细胞凋亡过程的负调控等;CC主要包括细胞外间隙、转录因子复合物、大分子复合物等;MF主要包括酶的结合、细胞因子活性、相同蛋白质结合等(图5)。KEGG信号通路有138个条目,相关通路主要有TNF信号通路、IL-17信号通路、糖尿病并发症中的AGE-RAGE信号通路、脂质和动脉粥样硬化和癌症信号通路等(图6)。
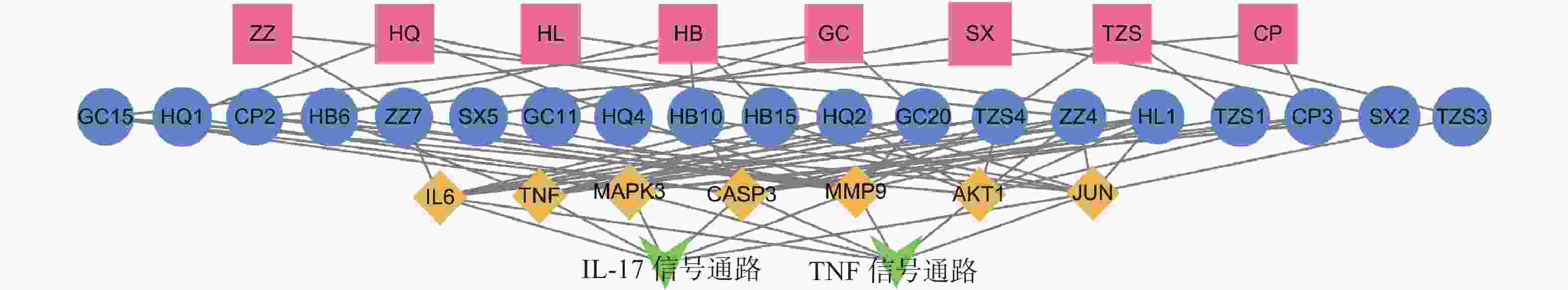
为进一步探究其作用机制,以KEGG分析获得的TNF、IL-17信号通路为重点研究对象,探讨药物、活性成分、核心靶点的关系。通过分析发现,信号通路中包含的核心靶点有7个,分别为AKT1、CASP3、MMP9、TNF、JUN、IL-6、MAPK3。这7个核心靶点与定清片中相关活性成分对应,构建活性成分-关键靶点-通路网络(图7),包括36个节点和75条边。核心靶点对应得到的13个活性成分为:槲皮素、山柰酚、木犀草素、柚皮素、刺槐素、β-谷甾醇、汉黄芩素、吴茱萸次碱、川陈皮素、桑黄素、睾酮、黄芩素、芒柄花素等。这些成分存在于黄连、太子参、黄芩、黄柏等8味药材中,通过调控核心靶点参与了TNF与IL-17信号通路的调节,可能在定清片治疗白血病的过程中发挥重要作用。
-
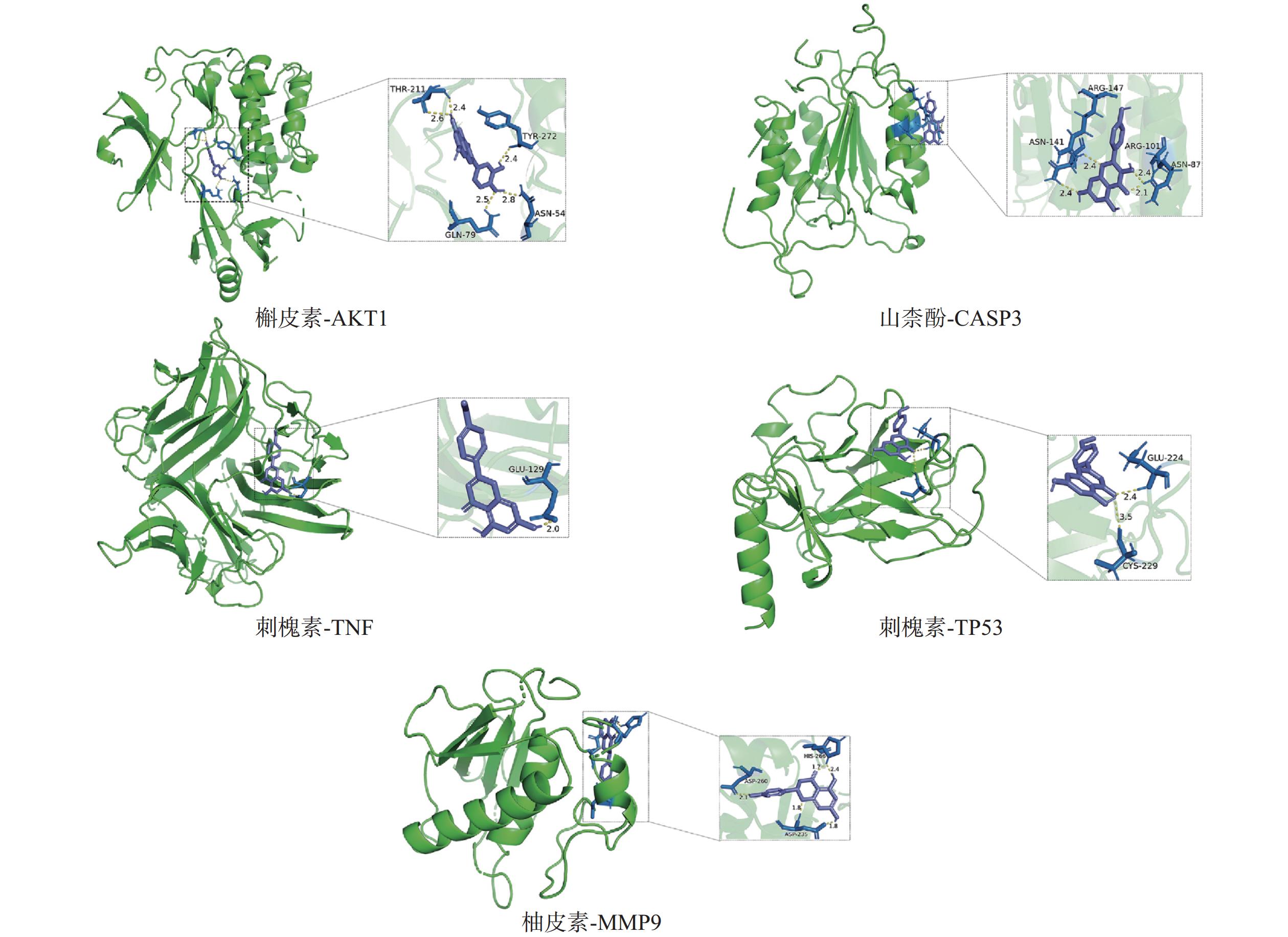
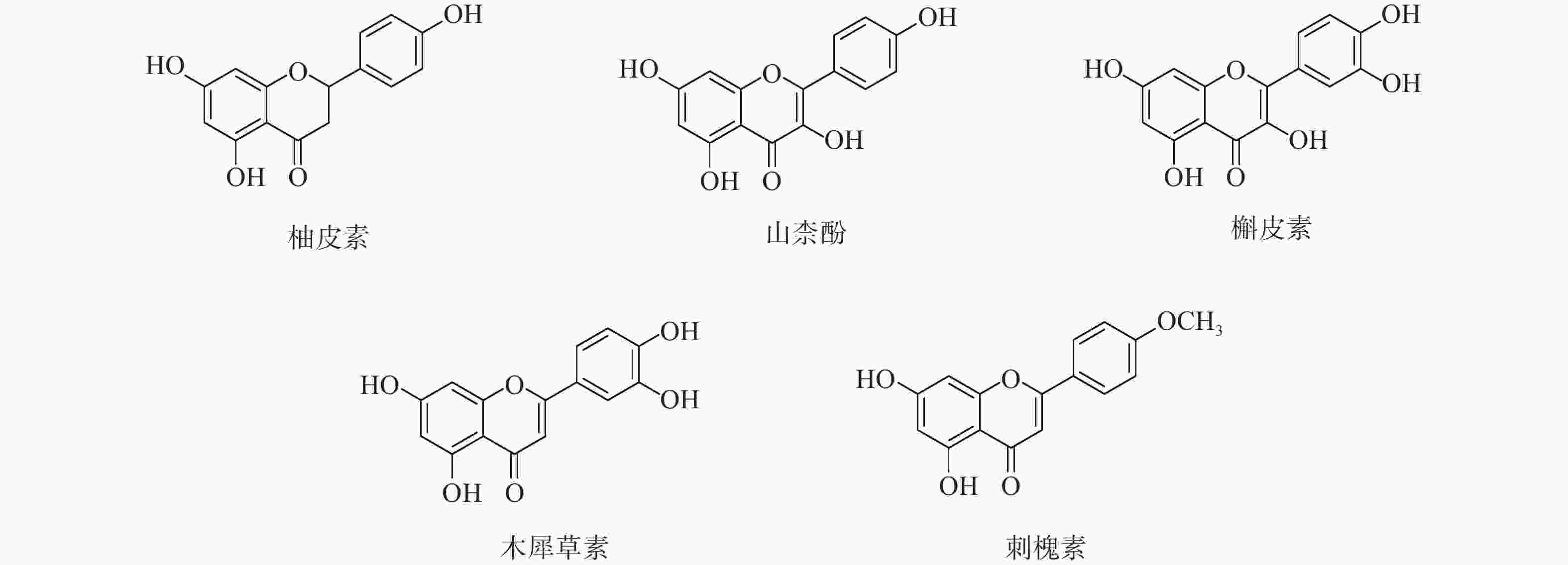
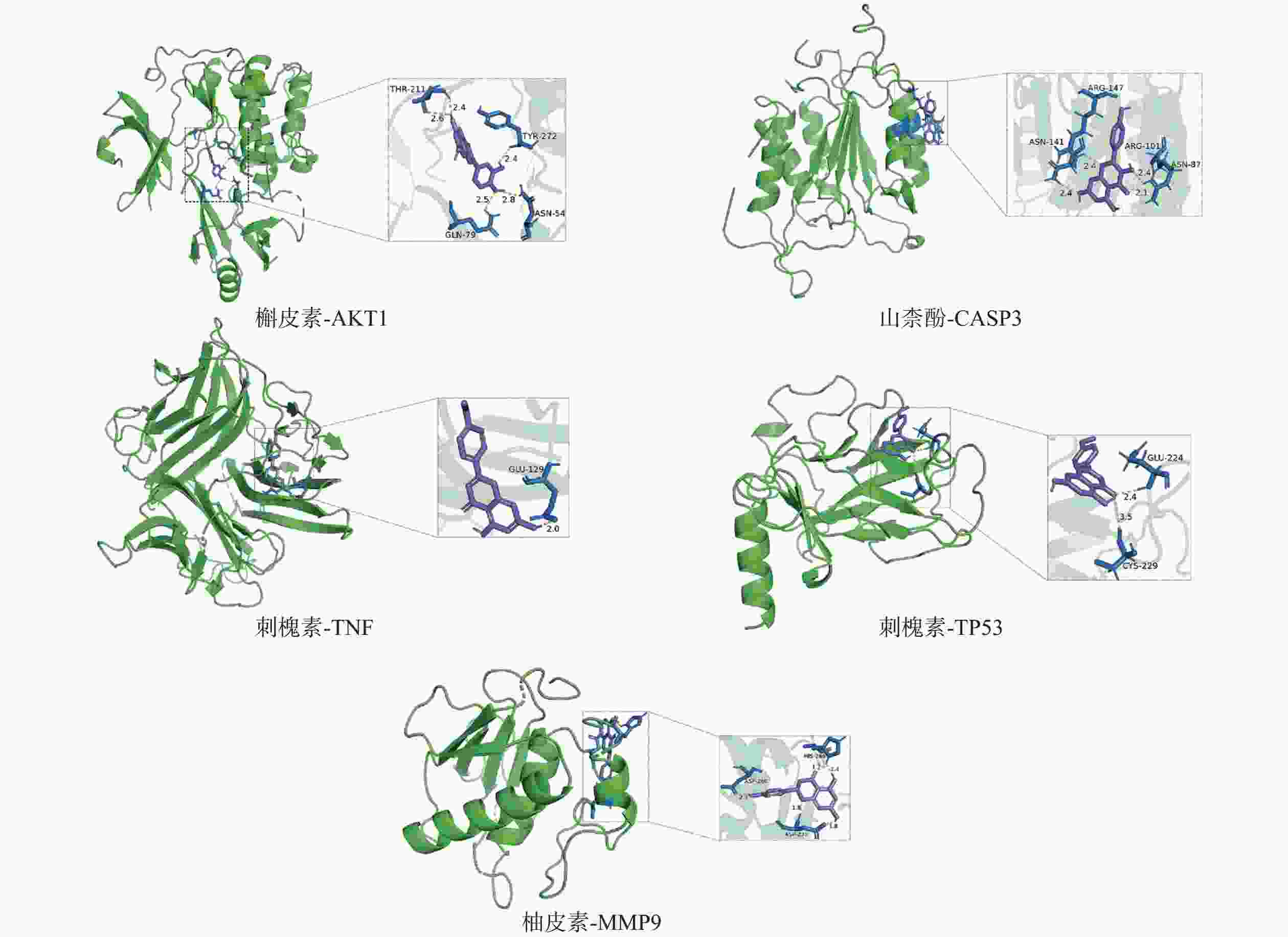
采用分子对接技术,选择药物-疾病共有靶点和基因簇1的“药物-成分-靶点-通路”网络图中节点度值最高的核心靶点蛋白,包括TP53、AKT1以及MMP9、CASP3和TNF,与排名靠前的活性成分槲皮素、山柰酚、木犀草素、刺槐素和柚皮素(图8)进行分子对接分析。化合物与靶点的结合能越低,表明其可能有更好的相互作用。从表1的结合能结果可知,定清片中的活性成分与核心靶点蛋白有一定的相互作用,例如槲皮素,与多个靶点的结合能均小于−20.93 kJ/mol,被认为可能有较好的结合性,其中与AKT1的结合能最低(−41.03 kJ/mol),表明其与AKT1的结合能力最强,槲皮素可能与蛋白上的TYR-272、ASN54、GLN79、THR211残基通过氢键等相互作用(图9),其他活性成分均与对应的大分子蛋白上的关键残基存在相互作用,对接可视化结果见图9。这些结果提示,定清片中的多种化合物成分与白血病的相关核心靶点有良好的亲和性。
活性成分 结合能(kJ / mol) MMP9 TNF TP53 AKT1 CASP3 槲皮素 −24.28 −24.70 −31.40 −41.03 −31.40 刺槐素 −25.96 −27.21 −33.08 −25.96 −29.73 木犀草素 −25.54 −23.86 −30.14 −26.38 −28.47 山柰酚 −25.12 −26.38 −33.91 −27.63 −31.82 柚皮素 −27.63 −26.80 −30.98 −25.96 −30.14 -
定清片是本院黄振翘教授和周永明教授通过多年临床实践拟定的经验方,对白血病的疗效得到了普遍认可。其由12味中药组成,每味药物中又有许多不同的化合物。且其对白血病治疗的作用机制尚未阐明。
白血病的发病机制涉及多种因素,不同的药物治疗针对不同的通路和机制发挥作用[13]。本研究通过网络药理学分析,筛选出可能在定清片防治白血病的作用机制中具有重要作用的5个核心靶点。其中,肿瘤抑制基因TP53是人类癌症中最常见的突变基因之一,也是包括血液系统恶性肿瘤在内的许多恶性肿瘤研究的重要预后指标。其编码产生的p53蛋白与细胞周期的调控、细胞凋亡和衰老等重要的生物学功能息息相关,通过抑制细胞的生长,预防癌症的发展[14-15]。在分子对接实验中,刺槐素与p53蛋白有较好的亲和性。已有研究表明,刺槐素能通过结合RARγ,靶向调控AKT-p53信号通路,诱导癌细胞凋亡[16];但其是否能直接作用于p53从而调控下游生物学功能尚需实验证实。丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶1(AKT1)在细胞存活、细胞周期、侵袭和代谢的调节中发挥作用。研究表明,包括白血病在内的多种癌症都伴有AKT信号的失调,在急性白血病中经常发现AKT的持续激活和磷酸化水平的显著升高。AKT1与PI3K、PTEN和mTOR等构成的重要信号通路对维持细胞存活和凋亡之间的平衡具有重要作用[17],且AKT1会影响来自胸腺的调节性T细胞的增殖能力[18]。研究发现,定清片中的槲皮素与多个核心靶点均有较好的亲和力,其与AKT的相互作用可能最强。已有多项研究表明,槲皮素可用于白血病的治疗,是一种有应用前景的抗肿瘤药物。槲皮素可通过调节CaMKKβ/AMPK/mTOR信号通路诱导HL-60细胞凋亡和自噬[19],还能克服癌细胞的耐药性[20]。但槲皮素治疗白血病是否与AKT通路有关,有待进一步研究。在药物-靶点网络中显示与白血病靶点密切相关的化合物,如木犀草素、山柰酚和柚皮素等,都可能是定清片治疗白血病的关键化合物。
聚类分析结果显示,定清片治疗白血病的作用机制可能与TNF信号通路和IL-17信号通路有关。TNF参与白血病发生发展的所有过程,包括细胞转化、增殖、血管生成和髓外浸润等,并且在急性髓性白血病患者外周血中,调节性T细胞的增殖依赖于TNF受体通路[21]。而对慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)、免疫功能紊乱和肿瘤细胞生存期延长是病情进展的重要诱因之一。在CLL早期,存在机体Th细胞免疫系统失衡,其中Th2细胞活化、嗜酸性粒细胞聚集,促进慢性炎症的发生,致使IL-17水平升高,最终导致CLL进展,预后欠佳[22]。IL-17诱导炎性细胞因子(如TNF-α和IL-6)和趋化因子(CXCL1、CXCL2)的持续产生,从而促进急性髓性白血病(AML)的发生发展[23]。在B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病中,Th17细胞分泌的IL-17A水平明显升高,其通过激活Akt 信号通路显著促进细胞的增殖,提高柔红霉素的耐药性[24]。这些研究均表明,TNF信号通路和IL-17信号通路在白血病的发生发展中有重要作用,药物对这些通路发挥调控作用可能是其治疗白血病和改善耐药性的作用机制。
综上所述,本研究基于网络药理学方法,对定清片中的12味药材进行有效成分和作用靶点的筛选,构建了药物成分-疾病-靶点网络图,并通过对关键子网络核心靶点的富集分析,探索其治疗白血病的主要通路。定清片中的主要有效成分如山柰酚、槲皮素、木犀草素、柚皮素、刺槐素等,可能通过与核心靶点TP53、AKT1、MMP9、CASP3和TNF等的相互作用,调控TNF、IL-17等信号通路,从而发挥对白血病的治疗作用。本研究围绕中药复方多种药物成分、多靶点的基本分析策略,验证了“定清片”的有效性和科学性,为其在临床的推广应用提供了一定的理论依据。
Mechanism of effective ingredients of Dingqing tablets in the treatment of leukemia based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202401073
- Received Date: 2024-01-31
- Rev Recd Date: 2024-06-20
- Available Online: 2024-11-19
- Publish Date: 2024-11-25
-
Key words:
- Dingqing tablets /
- leukemia /
- network pharmacology /
- molecular docking /
- mechanism
Abstract:
| Citation: | CHEN Jing, HE Ruihua, WENG Yue, XU Yi, LIU Jing, HUANG Jin. Mechanism of effective ingredients of Dingqing tablets in the treatment of leukemia based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2024, 42(11): 479-486. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202401073 |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: