-
菊花为菊科植物菊花的干燥头状花序,是一种常见的药食两用的花卉,具有清热、明目、疏风、解毒之功效[1-2]。根据经典的记载,中国栽培菊花历史已有3000多年。汉朝《神农本草经》记载:“菊花久服能轻身延年”。现代药理学研究表明,菊花具有抗菌、抗病毒、抗氧化、抗炎以及保肝等作用[3-12],因此,常作为保健饮品服用。安徽黄山是菊花的重要产地,拥有黄山金丝皇菊、黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊等多个品种,其中皇菊的黄酮含量极高,富含多种氨基酸、维生素和微量硒元素,具有重要的药用价值;而道地黄山贡菊更是菊花中的上等品,“白边黄芯绿屁股”,处于四大药菊之首。本研究主要对以上四种菊化品种进行研究,对比其抗氧化及抗炎活性,为菊花抗氧化和抗炎品种的开发提供参考和借鉴。
-
4种菊花(黄山金丝皇菊、黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊)来源于黄山市产品质量检验研究院;总抗氧化能力检测试剂盒(ABTS法)、总抗氧化能力检测试剂盒(FRAP法)、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼试剂盒(DPPH法)购自Solarbio;双报告基因检测试剂盒购自Promega;LPS购自美国Sigma公司;SD大鼠,雄性,体重180~220g,购自上海斯莱克实验动物中心。
-
4种不同菊花经粉碎机粉碎并过60目筛,各取100 g,加入1000 ml去离子水浸泡12 h,然后加热回流提取2 h,过滤去除滤渣,滤液用旋转蒸发仪(60 ℃)蒸发去除溶剂,然后经真空干燥彻底去除水分[13]。由于4种菊花水提物得率基本一致(约17%),因此后续用相同质量的水提物表征同等质量的菊花。
-
将等体积的ABTS溶液和氧化剂溶液混合配置成ABTS工作母液,室温避光存放24 h。使用前,把ABTS工作液用PBS稀释30~50倍,要求ABTS工作液的吸光度减去相应的PBS空白对照后,A734为0.7±0.05,对应的A405在1.4左右。称取菊花粗提物粉末100 mg,用适量蒸馏水充分溶解。同时,用蒸馏水将10 mmol/L Trolox标准溶液稀释成0.15、0.3、0.6、0.9、1.2和1.5 mmol/L。于96孔板的每个检测孔中加入200 μl ABTS工作液,空白对照孔中加入10 μl蒸馏水;标准曲线检测孔中加入10 μl各浓度Trolox标准溶液;样品检测孔中加入10 μl样品溶液,轻轻混匀。室温孵育2~6 min后测定A734。根据标准曲线计算样品的总抗氧化能力[14]。
-
将TPTZ稀释液与TPTZ溶液充分混匀再加入检测缓冲液,从而配制成FRAP工作液。称取菊花粗提物粉末100 mg,用适量蒸馏水充分溶解。称取27.8 mg本试剂盒提供的 FeSO4•7H2O,溶解并定容到1 ml,此时浓度即为100 mmol/L。取适量100 mmol/L FeSO4溶液用蒸馏水稀释至0.15、0.3、 0.6、 0.9、 1.2和1.5 mmol/L。于96孔板的每个检测孔中加入180 μl FRAP工作液,空白对照孔中加入5 μl蒸馏水;标准曲线检测孔中加入5 μl各浓度FeSO4标准溶液;样品检测孔中加入5 μl样品溶液,轻轻混匀。室温孵育2~6 min后测定A593。根据标准曲线计算样品的总抗氧化能力[14]。
-
称取菊花粗提物粉末100 mg,用适量蒸馏水充分溶解。同时,用蒸馏水将10 mmol/L Trolox标准溶液稀释成0.15、0.3、0.6、0.9、1.2和1.5 mmol/L。于96孔板的每个检测孔中加入190 μl DPPH工作液,空白对照孔中加入10 μl蒸馏水;标准曲线检测孔中加入10 μl各浓度Trolox标准溶液;样品检测孔中加入10 μl样品溶液,混匀后室温避光静置30 min,测定A515。根据标准曲线计算样品的总抗氧化能力[14]。
-
Raw264.7细胞以适当密度接种于96孔板,实验分别设置空白组、LPS刺激组和不同药物浓度处理组,每组分别设置3个复孔。细胞过夜贴壁,利用转染试剂共转染报告基因质粒pNF-κB-Luc 和pRL-SV40,转染6 h后换液。转染24 h后加药,药物孵育2 h后加入LPS(终浓度1 μg/ml)刺激6 h,双报告基因法检测NF-κB转录活性。
-
取SD大鼠48只,随机分为6组,分别为空白组、模型组、菊花水提物给药组(2 g/ kg,相当于菊花11.76 g/kg)。各组大鼠连续灌胃给药3 d,模型组给予相同体积的生理盐水,第4天于每只大鼠右后足垫皮下注射1.0%角叉菜胶100 μl,致炎后灌胃给予相应药物,分别在致炎前和致炎后1、2、4 h,测量大鼠致炎侧足容积,计算足趾肿胀率和肿胀抑制率[15-16]。按下式计算小鼠足趾肿胀率和抑制率:肿胀率=(致炎后足趾体积-致炎前足趾体积)/致炎前足趾体积×100%, 抑制率= (模型组足趾肿胀率-给药组足趾肿胀率)/模型组足趾肿胀率×100%。
-
数据以(
$\bar x $ ±s)表示,单因素方差分析(One way ANOVA)比较各组差异,以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。 -
ABTS、FRAP和DPPH线性方程以及相关系数见表1。
项目 方程 相关系数 ABTS Y=0.662 4X+0.715 3 r=0.999 5 FRAP Y=0.298 5X+0.060 r=0.999 4 DPPH Y=0.459 8X−0.023 8 r=0.998 9 从表1可以看出,ABTS、FRAP以及DPPH测定方法具有很好的线性。
-
ABTS法检测菊花水提物总抗氧化能力,结果显示,4种菊花的抗氧化能力存在明显差异,其中,黄山金丝皇菊抗氧化能力最强,为(0.481±0.052) mmol/g(总抗氧化能力用TEAC标准溶液表示),其次是黄山皇菊,为(0.402±0.043) mmol/g,然后依次是黄山贡菊(0.369±0.031)mmol/g和黄山黄菊(0.287±0.014)mmol/g。FRAP和DPPH检测以上四种菊花水提物抗氧化能力,结果与ABTS法类似,黄山金丝皇菊抗氧化能力最强,其次依次是黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。综上,可以得出结论:黄山金丝皇菊水提物抗氧化能力最强,其次是黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊(表2)。
名称/抗氧化
能力FRAP(mmol FeSO4/g) ABTS(mmol Trolox/g) DPPH(mmol Trolox/g) 黄山金丝皇菊 0.504±0.049 0.481±0.052 0.359±0.025 黄山皇菊 0.421±0.036 0.402±0.043 0.305±0.033 黄山贡菊 0.347±0.028## 0.369±0.031 0.277±0.041# 黄山黄菊 0.270±0.017###,** 0.287±0.014## 0.208±0.019##,* *P<0.05,**P<0.01,与黄山皇菊比较;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,###P<0.001,与黄山金丝皇菊比较。 -
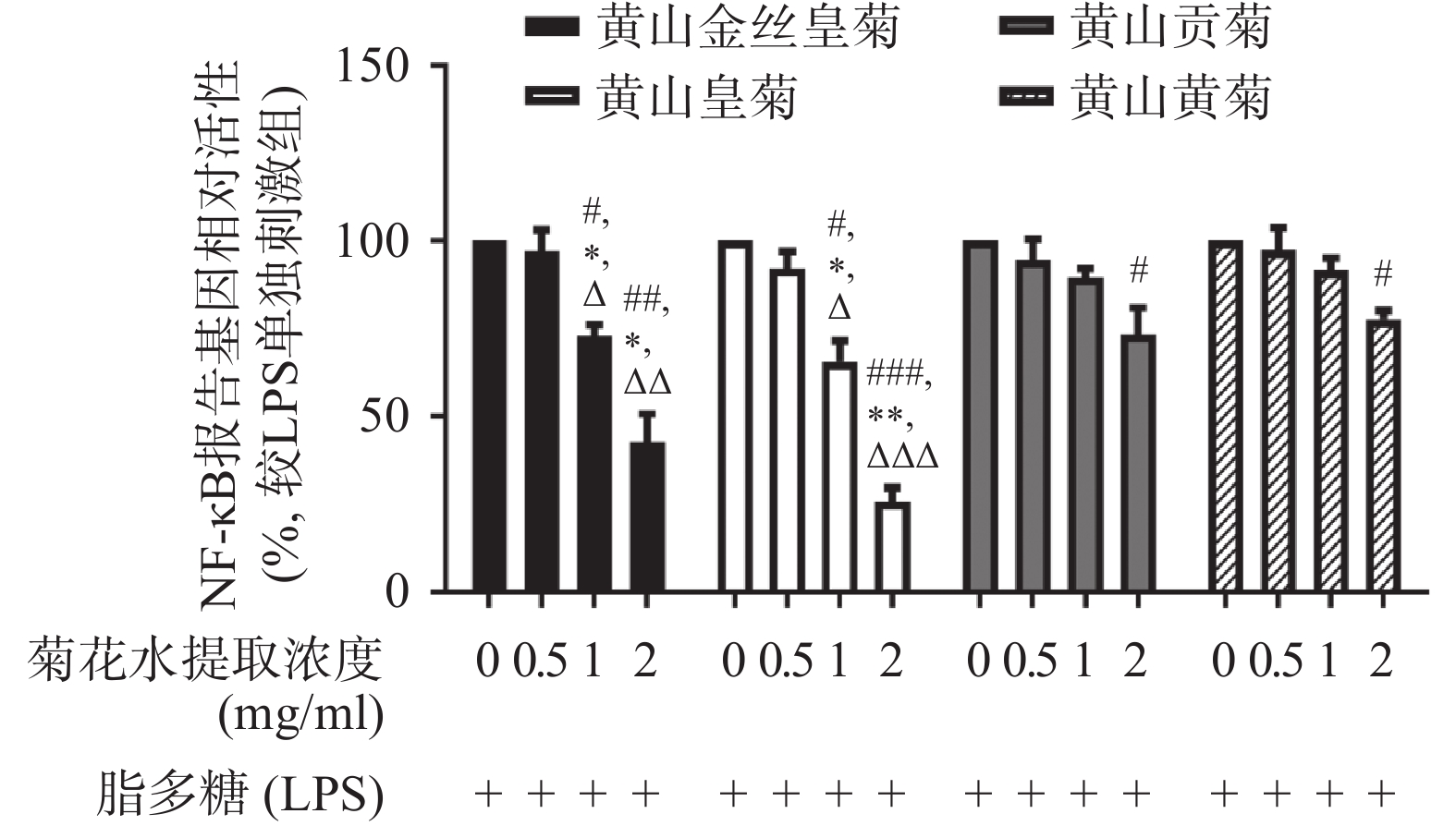
利用双报告基因的方法检测4种菊花水提物对Raw264.7细胞 NF-κB转录活性的影响,结果显示4种菊花水提物均能够一定程度的抑制LPS诱导的NF-κB的转录活性。相同作用浓度下,黄山皇菊NF-κB抑制活性最强,其次依次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。结果表明黄山皇菊抗炎作用最强,其次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊(图1)。
-
为了进一步确认4种菊花提取物的抗炎活性,我们构建了角叉菜胶致大鼠足肿胀模型。大鼠足趾肿胀率和肿胀抑制率如表3所示,1 h时间点,给予菊花水提物处理的各组大鼠足趾肿胀均低于模型对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。2 h时间点,黄山皇菊和黄山金丝皇菊对足趾肿胀仍然具有抑制作用,而黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊抑制作用消失; 组间比较,黄山皇菊足趾肿胀抑制作用优于黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊(P<0.05)。4 h时间点,各组对足趾肿胀的抑制作用消失。综上结果表明,黄山皇菊的抗炎活性最好,其次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊,该结论与NF-κB报告基因结果一致。
组别 1 h 2 h 4 h 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 肿胀率(%) 抑制率(%) 模型组 41.6±
4.5− 52.5±
10.7− 45.1±
8.2− 黄山金丝皇菊 31.5±
5.9#24.3 42.3±
7.1#19.5 44.9±
8.80.5 黄山皇菊 28.9±
5.9##30.6 38.9±
7.8#,*,ΔΔ26.0 46.4±
10.0−2.8 黄山贡菊 31.8±
6.3#23.7 50.0±
11.74.8 46.4±
8.3−2.8 黄山黄菊 33.3±
6.2#20.1 51.0±
7.32.9 44.9±
8.80.6 *P<0.05,与黄山贡菊比较;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,与模型组比较;ΔΔP<0.01,与黄山黄菊比较。 -
本研究采用ABTS、FRAP和DPPH 这3种方法测定了4种黄山菊花水提物的抗氧化活性,并通过报告基因法和大鼠足肿胀模型评估了其抗炎活性。结果表明,4种菊花表现出不同的抗氧化活性和抗炎活性,其中黄山金丝皇菊的抗氧化能力最强,其次是黄山皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊;而黄山皇菊的抗炎活性最强,其次是黄山金丝皇菊、黄山贡菊和黄山黄菊。菊花中黄酮类化合物具有清除自由基和超氧阴离子的能力,其抗氧化能力与黄酮类化合物含量有关;而菊花中的抗炎成分相对复杂,包含多糖、黄酮类化合物(如木犀草素、槲皮素及黄芩苷等)、有机酸(如绿原酸)和挥发油等,4种不同菊花在抗炎及抗氧化方面的活性差异可能与上述成分的差异有关[2,17-18]。尽管不同菊花品种在抗氧化和抗炎活性方面存在差异,但是均表现出良好的药用及食用价值,人们在日常生活中可以根据使用目的的不同进行选择,如考虑通过饮用菊花茶起到抗氧化目的,可以优先选用金丝皇菊,而如果考虑菊花抗炎作用,则可以考虑黄山皇菊。综之,4种黄山道地菊花提取物均表现出一定的抗氧化活性及抗炎活性,常饮之有保健功效。
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of four kinds of Huangshan chrysanthemum
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202211024
- Received Date: 2022-11-09
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-02-24
- Publish Date: 2023-05-25
-
Key words:
- antioxidation /
- anti-inflammation /
- chrysanthemum /
- feet swelling
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Lin, FANG Yu, YU Wenwu, HONG Ze. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of four kinds of Huangshan chrysanthemum[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(5): 325-328. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.2097-2024.202211024 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: