-
在全球范围内,乳腺癌是女性癌症死亡的主要原因,2018年约有210万女性疑似患有乳腺癌,占女性癌症的25%[1]。在我国,乳腺癌在女性肿瘤中发病率居首位,死亡率居第5位,近几十年来乳腺癌负担迅速增长[2]。目前,雌激素敏感的乳腺癌患者主要以内分泌治疗为主,然而,缺乏激素受体的乳腺癌细胞通常使用化疗药物,如紫杉醇和阿霉素[3]。但是,化疗药物对肿瘤细胞和正常细胞均表现出毒性反应,这限制了其临床应用。此外,细胞毒等抗肿瘤药物表现出的细胞耐药性进一步限制其应用。因此,迫切需要寻找毒性较小、效果较好的治疗药物。
五味子乙素(schisandrin B, Sch B)是从五味子中提取的主要活性成分[4]。据报道[5],Sch B可通过抑制NF-κB激活及MAPK/ Erk/p38/c-Jnk信号通路激活而有效减轻炎症反应,NASSER等[6]发现,Sch B可通过抑制PI3K/AKT和STA3/JAK2信号通路磷酸化,从而降低细胞内ROS的产生发挥抗前列腺癌作用,Wang等[7]发现,Sch B可通过TGF-b信号通路靶向miR-101-5p抑制大鼠肝纤维化。Dai等[8]发现,Sch B可通过STAT3的磷酸化和核转位发挥抗乳腺癌活性,但是Sch B 如何影响乳腺癌细胞增殖凋亡能力及具体机制尚不清楚。本研究以Sch B为研究对象,探讨其对人乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞凋亡的影响及其作用机制。
-
人乳腺癌细胞株MDA-MB-231(中科院细胞库,目录号:SCSP-5043);甘草查尔酮A(纯度≥98%,批号76296-75-6,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司);CCK-8试剂盒、Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡试剂盒、JC-1荧光探针、DCFH-DA荧光探针、Hoechst 33342 染色剂、PBS(大连美仑生物);1640培养基、胎牛血清( FBS) (美国HyClone公司);ECL发光液、BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(美国Thermo公司);Bcl-2、Bax、CHOP、GPR78、ATF4、PERK、p-PERK、p-eIF2α、eIF2α、β-actin、二抗(美国 Cell Signaling Technology公司)。
-
人乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清、100 μg/ml链霉素及100 U/ml青霉素的L-15培养基中,置于37 ℃、5% CO2的饱和湿度培养箱培养,细胞2~3 d可传代培养。Sch B药物处理时,首先取生长状态良好的对数期细胞进行实验,细胞分为对照组和药物组,根据细胞存活率检测结果计算IC50,药物组分为Sch B低剂量组剂量(1/2倍IC50),Sch B中剂量组(1倍IC50),Sch B高剂量组(2倍IC50)。
-
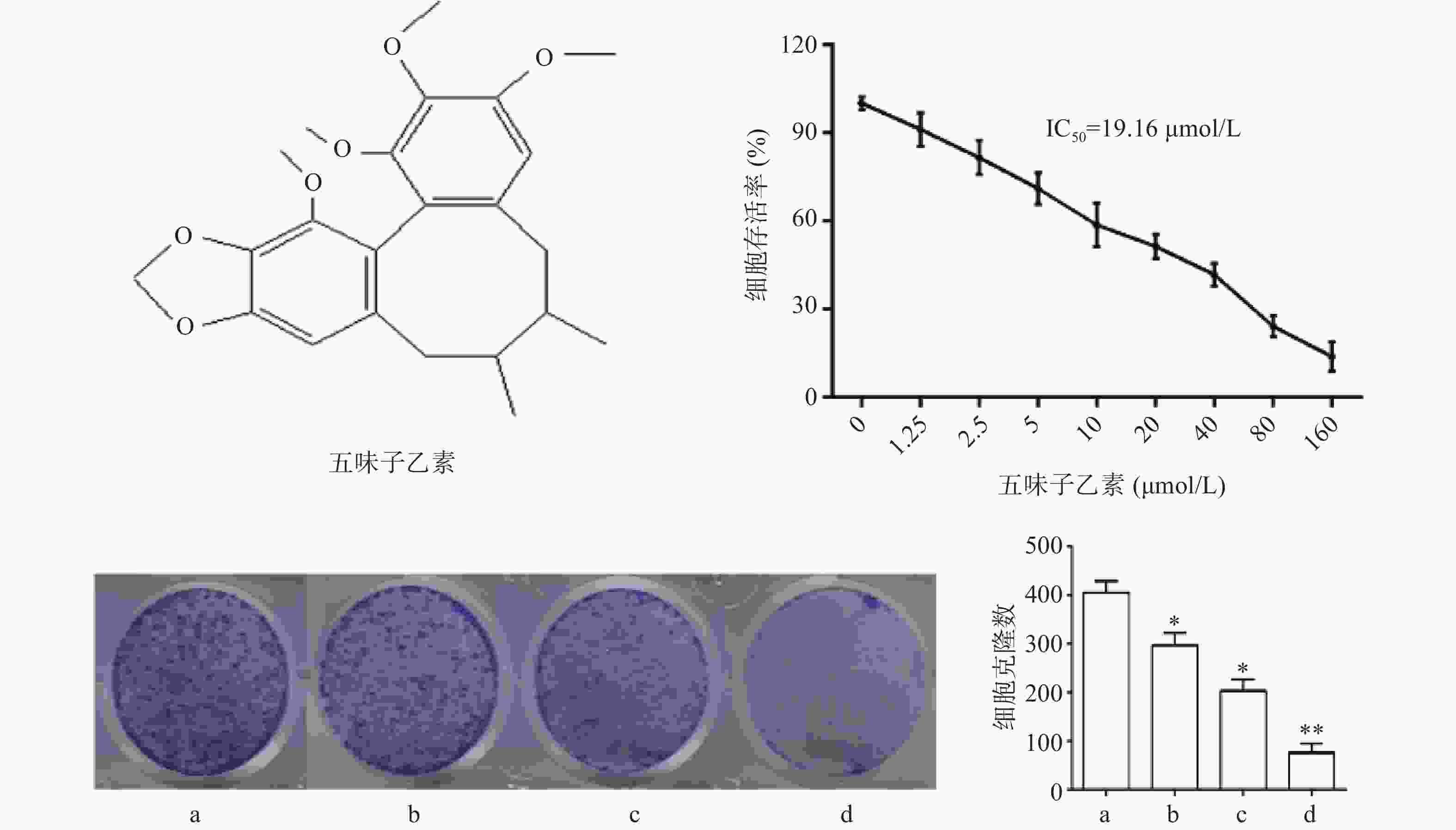
取状态良好的对数期MDA-MB-231细胞,以8×103/100 μl细胞密度接种于96孔板,于37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱培养过夜。将细胞分为空白组(含培养基,不含细胞)、对照组(含培养基,含细胞,不含药物)和药物处理组,药物处理组分别以终浓度为1.25、2.5、5、10、20、40、80、160 μmol/L的Sch B处理细胞24 h,每组3个复孔。24 h后每孔加入CCK-8溶液(10 μl), 于培养箱继续培养1 h,用酶标仪在450 nm处测定吸光度(OD)值,计算细胞存活率,并计算药物IC50值。
细胞存活率=[(OD药物−OD空白)/(OD对照−OD空白)]×100%
细胞克隆形成分析:取生长良好的对数期MDA-MB-231细胞,消化成单细胞悬液,以每孔3×103个细胞接种于6孔板,轻轻摇动使细胞分散均匀,过夜贴壁。分为对照组和药物组,对照组加等体积的培养基,药物组分别加以终浓度为(10、20、40 μmol/L)Sch B培养基,置培养箱中培养14 d。然后用PBS清洗2次,室温下用4%多聚甲醛固定15 min,1%结晶紫染色10 min。显微镜观察克隆形成情况,观察3个视野中克隆数量。
-
将生长良好的对数期MDA-MB-231细胞,以每孔2.5×105个/ml细胞密度接种于6孔板,置培养箱过夜培养。待细胞贴壁后,分别将终浓度为10、20、40 μmol/L的Sch B处理24 h。用不含EDTA胰酶消化细胞,PBS洗涤2次,结合缓冲液(100 μl)重悬细胞,转入流式管,然后再分别加入Annexin V-FITC(5 μl)和PI染液(5 μl),室温孵育15 min(避光),最后加入结合缓冲液(400 μl)混匀,流式仪上机检测,Flow Jo软件处理数据。
-
将生长良好的对数期MDA-MB-231细胞,以1×105个/ml细胞密度接种于12孔板,置培养箱过夜培养。待细胞贴壁后,分别将终浓度为10、20、40 μmol/L的Sch B处理24 h。DCFH-DA染液用PBS 1∶1000稀释成工作液,每孔加入200 μl工作液,37 ℃培养箱中避光孵育30 min,PBS洗涤2次,倒置荧光显微镜拍照,Image J软件检测荧光强度。
-
将生长良好的对数期MDA-MB-231细胞,以2.5×105个/ml细胞密度接种于6孔板,于培养箱过夜培养。待细胞贴壁后,将细胞依次分为对照组和药物组,对照组细胞加等体积培养基,药物组分别加终浓度为10、20、40 μmol/L的Sch B及加或者不加活性氧(ROS)清除剂(NAC)5 mmol/L, 内质网应激抑制剂4-PBA 2 mmol/L处理24 h。用RIPA(含PMSF蛋白酶抑制剂)裂解液提取蛋白,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,加入5×上样缓冲液金属浴(100 ℃)使蛋白变性。20 μg蛋白样品经PAGE凝胶电泳后转至PVDF膜,5%脱脂牛奶封闭1 h,孵育一抗(4 ℃冰箱过夜),1×TBST洗涤3次,二抗室温孵育2 h,采用ECL显影液显色,凝胶成像系统拍照,Image J软件分析。
-
数据采用GraphPad软件进行分析,以
$ \bar{x}\pm s $ 表示。组间比较采用t检验和单因素方差分析,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。 -
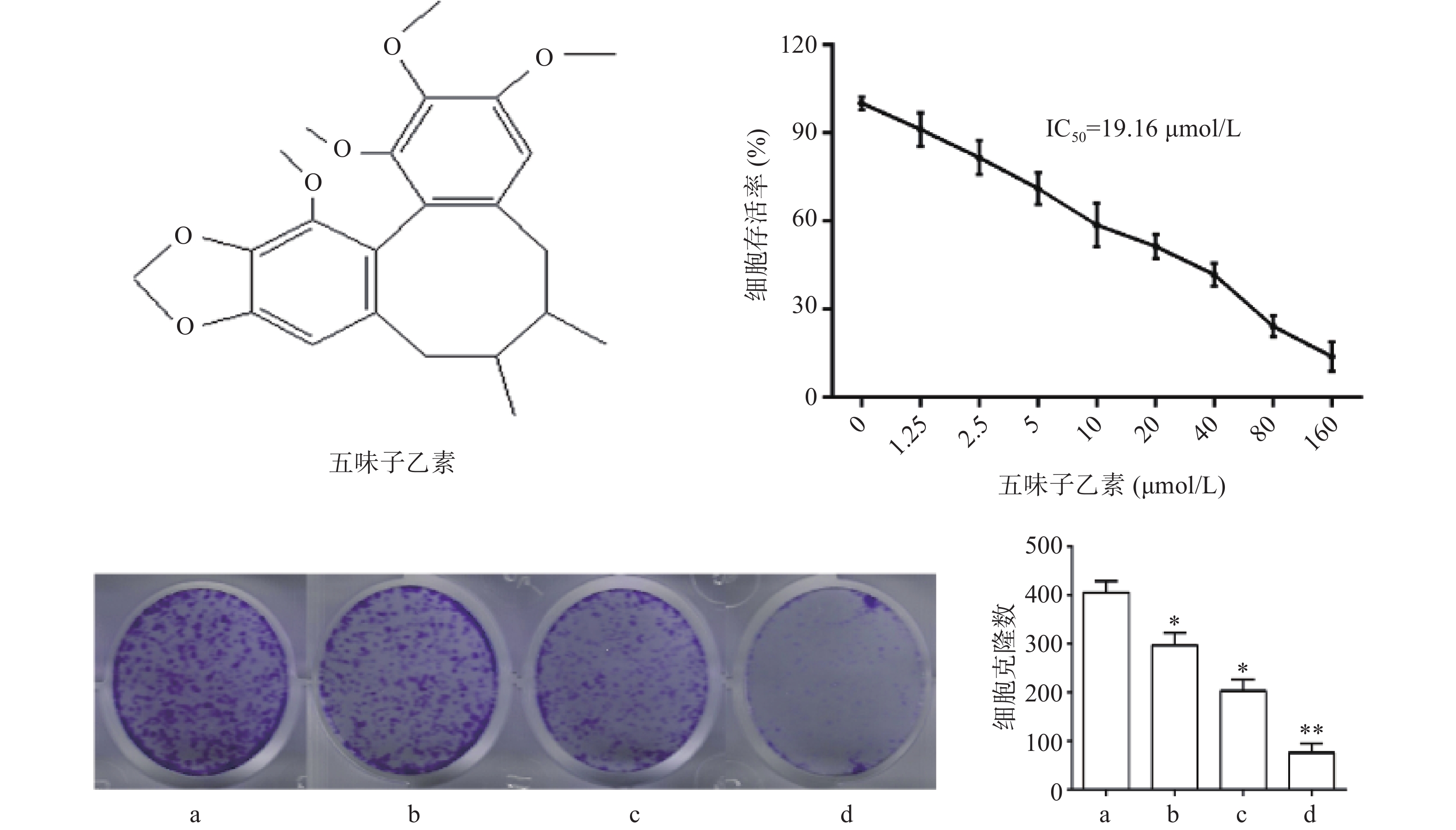
图1结果显示,与对照组比较,随着药物浓度增大,细胞存活率下降,其IC50为19.16 μmol/L,故选择1/2倍IC50(10 μmol/L),1倍IC50(20 μmol/L),2倍IC50(40 μmol/L)3个剂量进行后续实验。细胞克隆实验结果显示,随着药物浓度增大,细胞克隆形成显著被抑制,且呈现剂量依赖关系,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
-
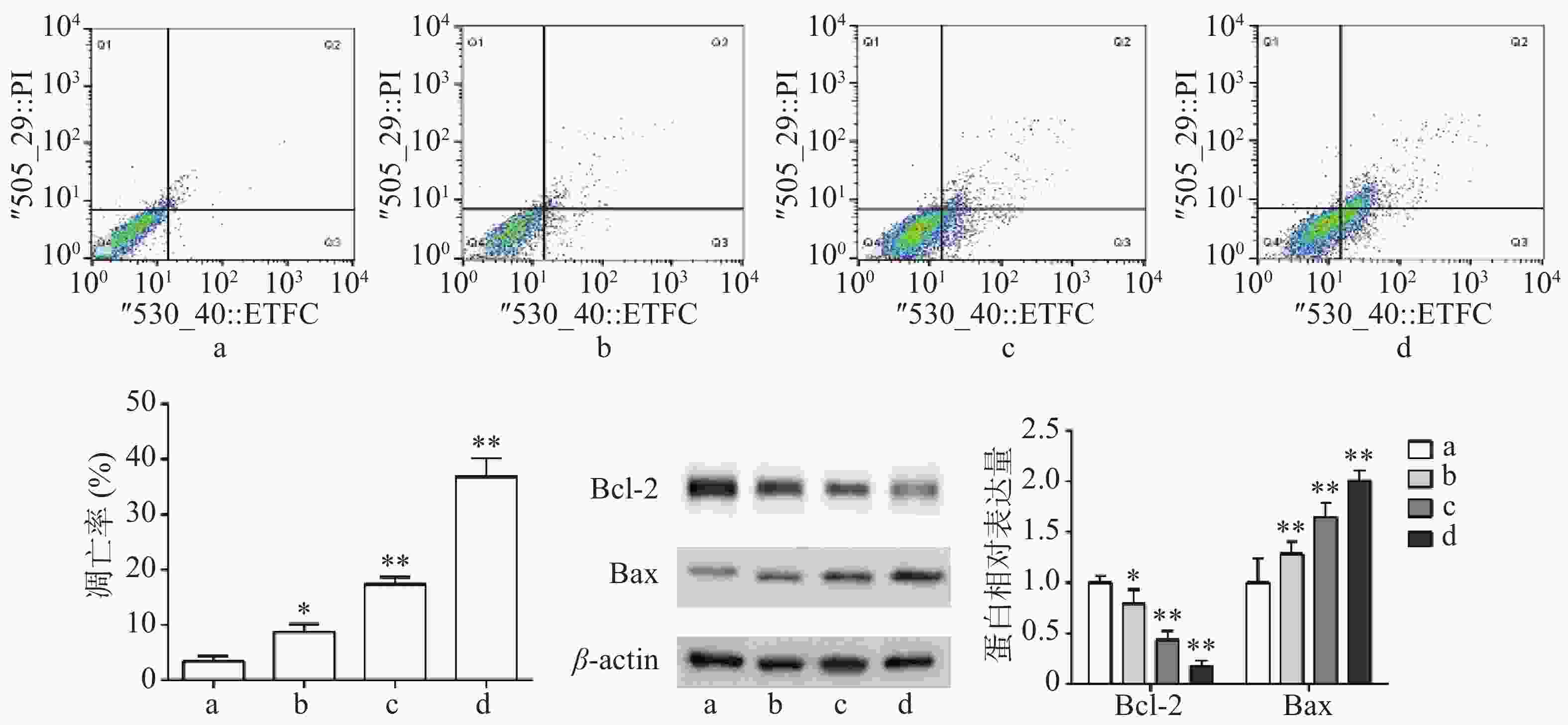
流式细胞术检测结果显示,与对照组比较,Sch B(10、20、40 μmol/L)均可诱导细胞凋亡,且呈剂量依赖,具有统计意义(P<0.05)。Western blot法检测结果显示,与对照组比较,Sch B(10、20、40 μmol/L)使抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的表达显著降低,促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达显著升高( P<0.05),结果见图2。
-
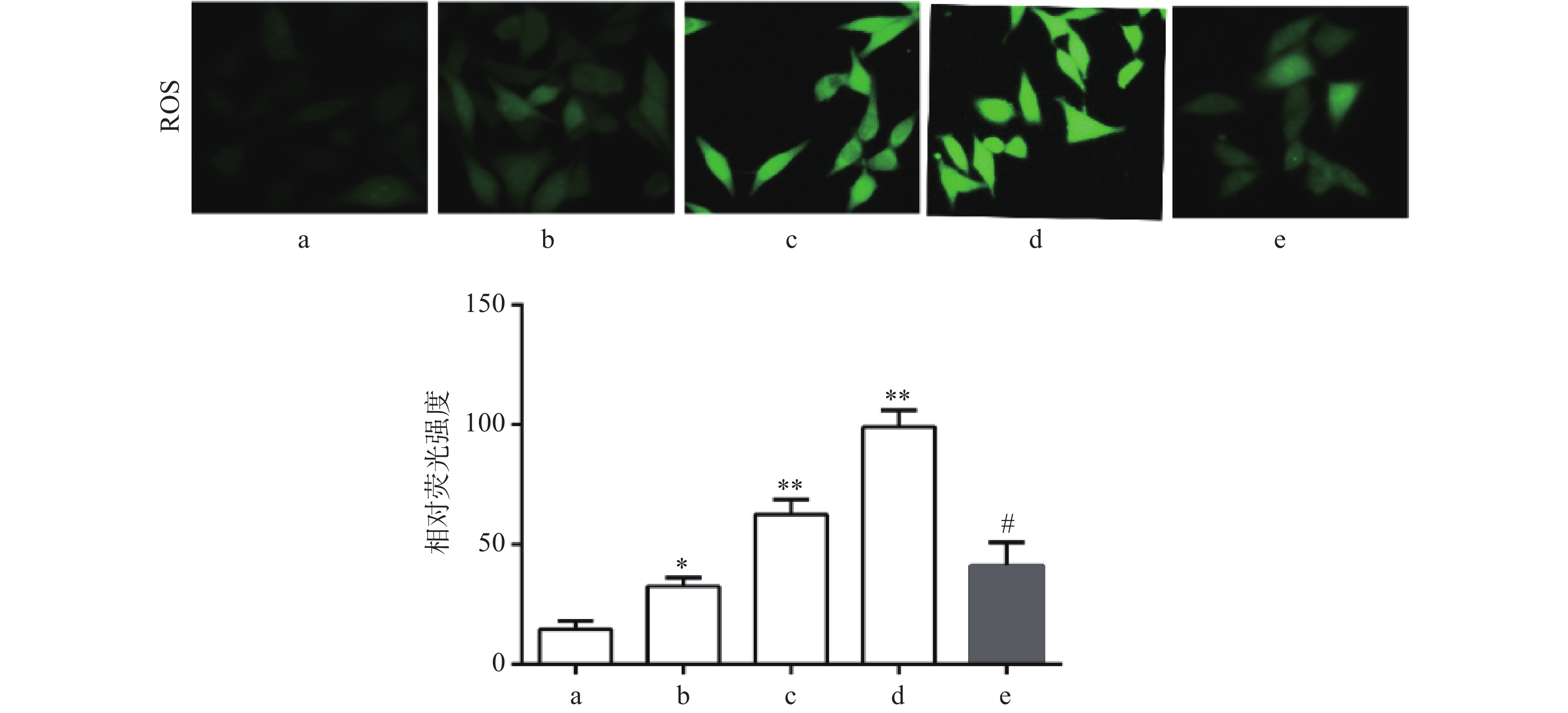
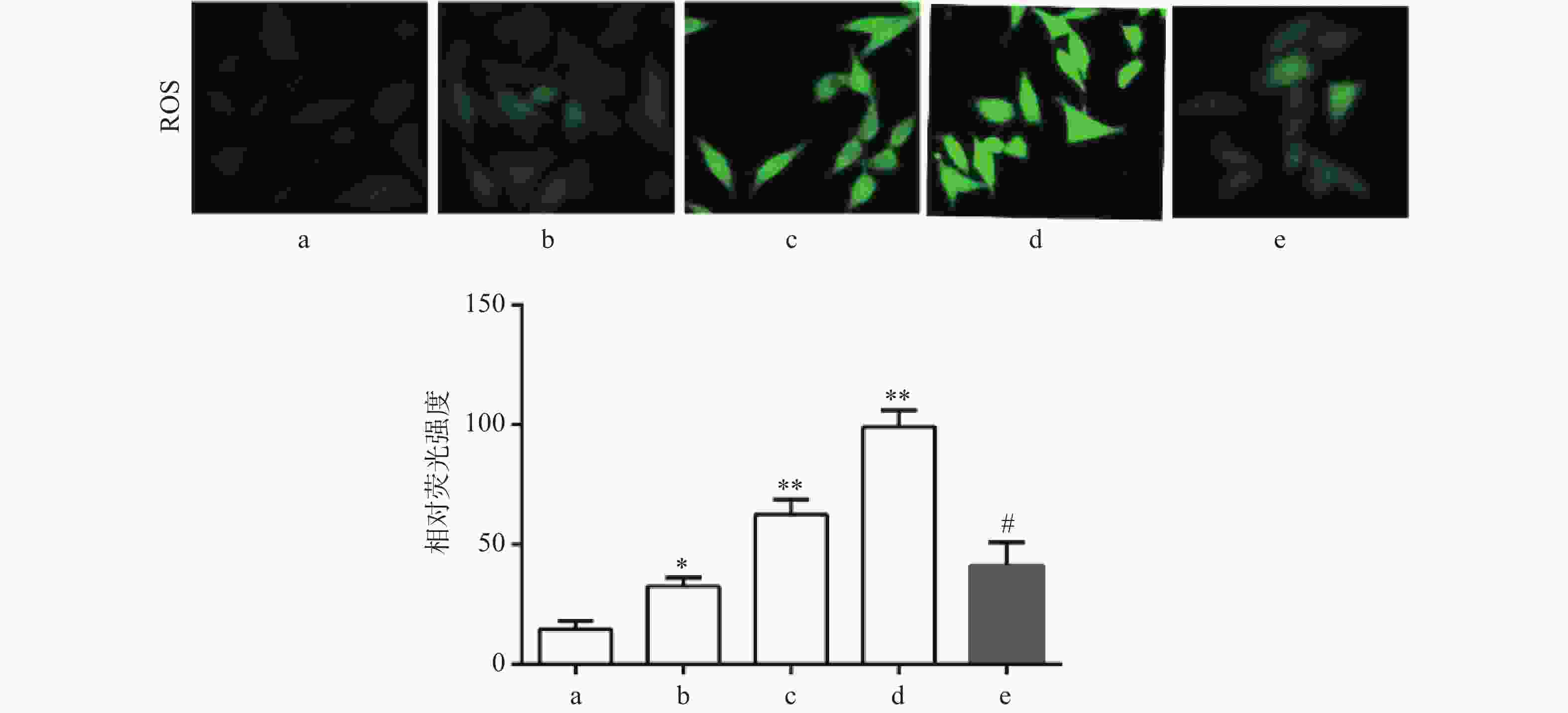
DCF-DA染色结果显示,与对照组比较,Sch B(10、20、40 μmol/L)组绿色荧光逐渐增强,显示细胞内ROS水平增高,且呈剂量依赖,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),活性氧清除剂NAC(5 mmol/L)预处理2 h可显著抑制由Sch B导致的细胞内ROS增多(P<0.05),结果见图3。
-
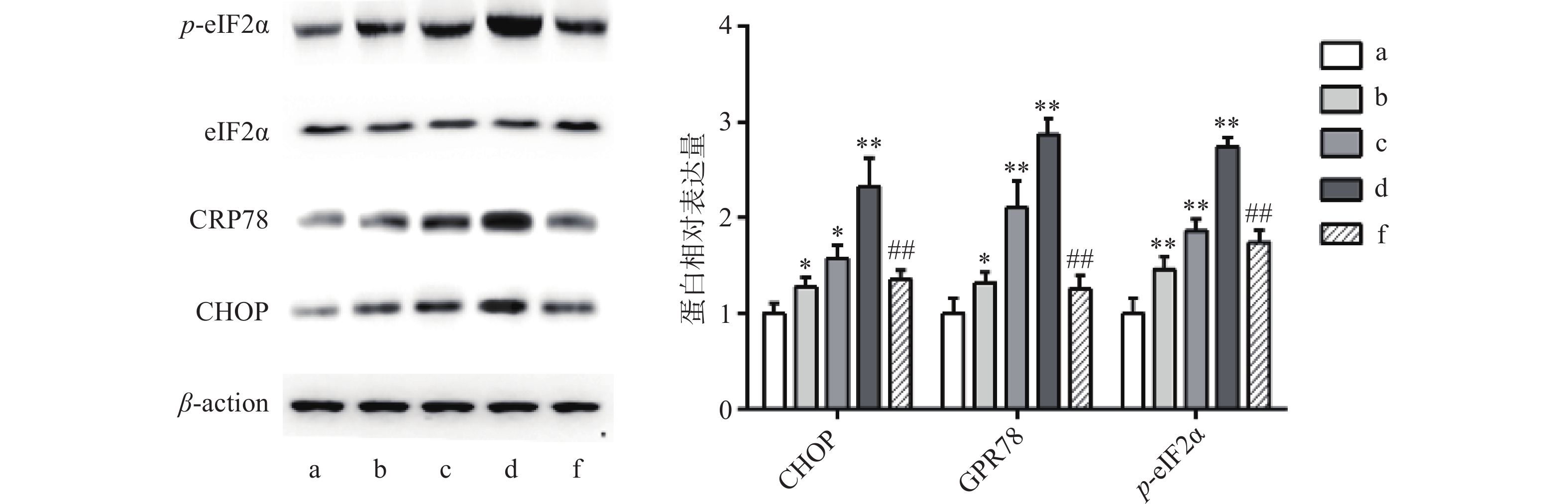
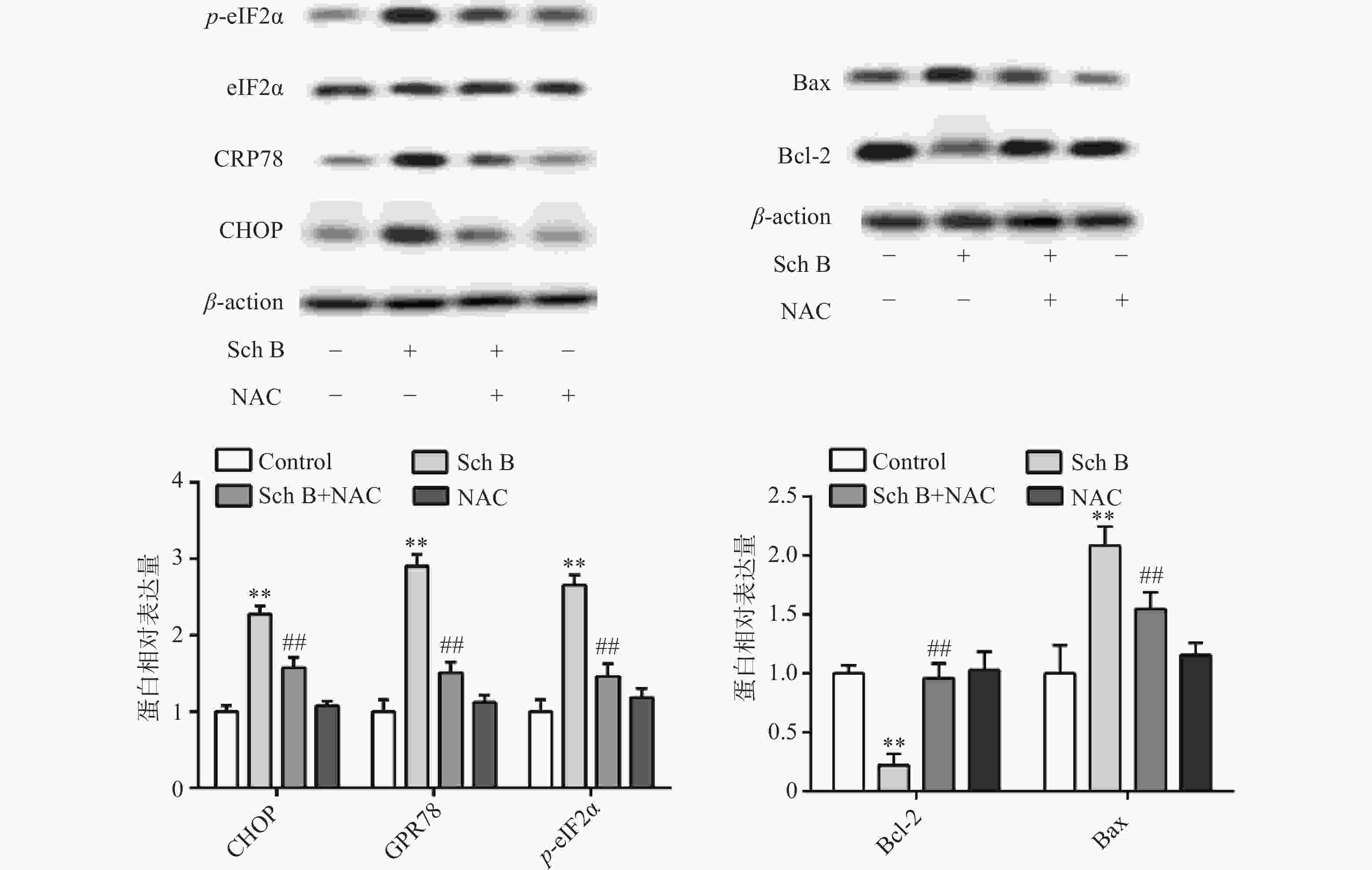
异常内质网应激可引起细胞凋亡,Western blot 法检测结果显示,与对照组比较,Sch B(10、20、40 μmol/L)分别使内质网应激相关蛋白CHOP,GPR78,p-eIF2α表达增多且呈剂量依赖,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),内质网应激抑制剂4-PBA(2 mmol/L)预处理2 h,可显著抑制由Sch B引起的内质网应激,使内质网应激相关蛋白CHOP、GPR78、p-eIF2α表达降低(P<0.05),结果见图4。
-
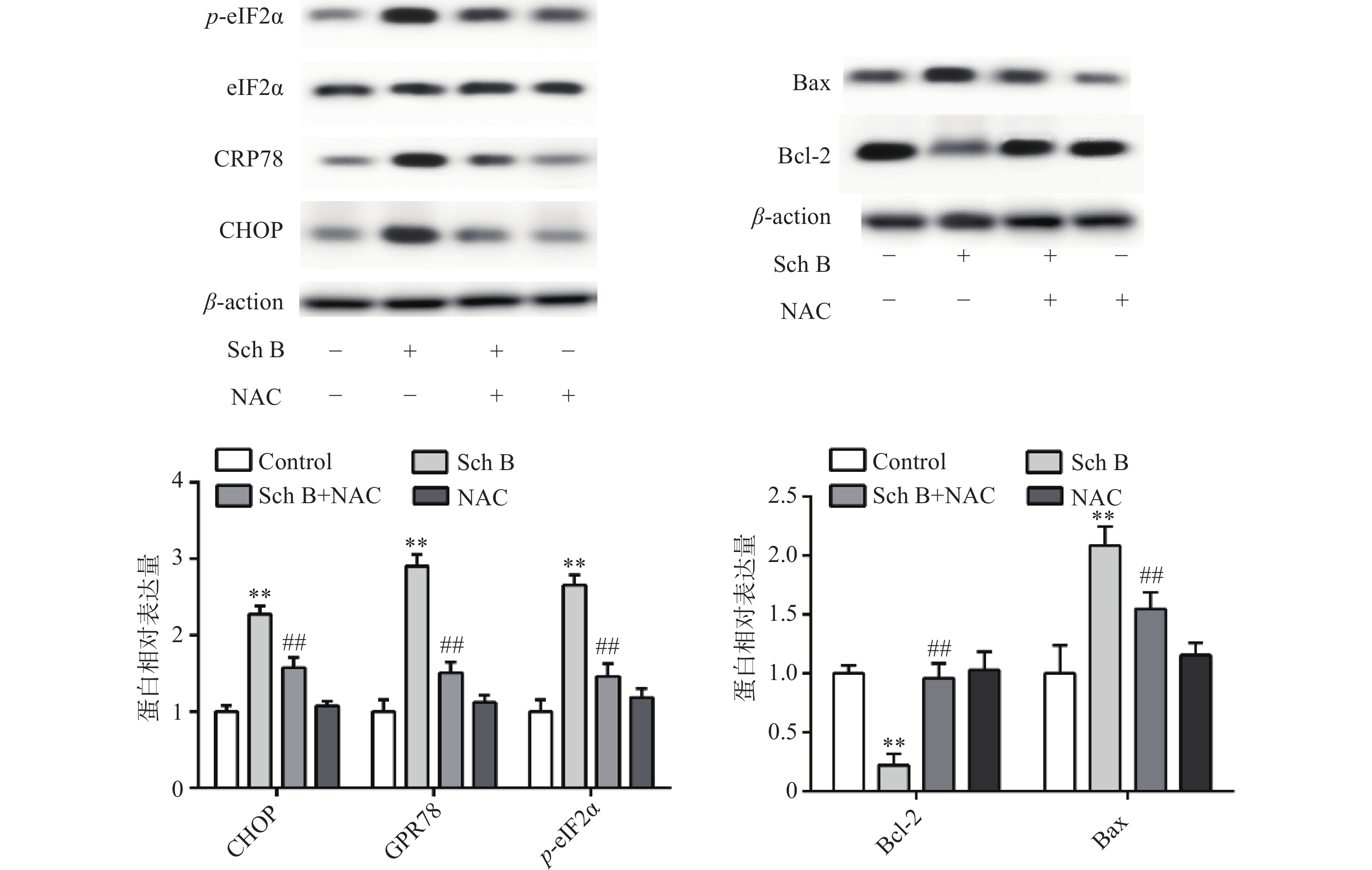
上述结果表明Sch B可以使细胞内ROS升高,Sch B也可以使内质网应激诱导细胞凋亡。为了验证ROS升高与内质网应激之间的联系,MDA-MB-231用ROS清除剂NAC(5 mmol/L)预处理2 h,结果显示,NAC可逆转由Sch B引起的内质网应激,使内质网应激相关蛋白CHOP,GPR78,p-eIF2α显著降低(P<0.05),进一步实验证明, 5 mmol/L NAC可逆转由Sch B引起的细胞凋亡,使抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的表达显著升高,促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达显著降低(P<0.05),结果见图5。
-
乳腺癌是临床上特别常见的恶性肿瘤,每年的发病率和死亡率都在增加,其发生发展是一个复杂的病理过程,是不受控制的细胞增殖和抵抗凋亡的结果[9]。尽管癌症研究领域取得了相当大的进展,但由于对化疗耐药和高复发率,乳腺癌的总体生存率仍然不令人满意,因此,大量的研究都集中在发现新的有效的治疗乳腺癌的候选药物中[10]。从植物中提取的天然化合物具有更有效和更少的副作用被认为是抗癌药物的重要来源。
ROS在细胞存活和死亡中起着关键作用。在正常生理条件下,适当水平的ROS有助于细胞存活。然而,过量的ROS会导致细胞损伤和凋亡细胞死亡[11]。ROS作为不良刺激之一,可引起内质网功能障碍,诱导内质网应激,称为ROS介导的内质网应激[12]。在本研究中,MDA-MB-231细胞在与Sch B孵育前先经ROS清除剂NAC预处理。凋亡减轻,ROS生成减少,CHOP,GPR78和p-eIF2a表达下调,内质网应激减轻。这说明Sch B诱导的MDA-MB-231细胞内质网应激依赖性凋亡中,ROS是不可或缺的。
内质网是真核细胞中传导和提供蛋白质折叠环境的细胞器,因为它对刺激的敏感性会导致某种情况发生成为内质网应激,内质网应激被认为是应对内质网稳态失衡的各种细胞生物学生理和病理事件的一种高度保守的细胞防御机制,如抗癌药物诱导的细胞凋亡通路[13]。GPR78是调节内质网应激的关键因子,GPR78的激活增加了真核启动子2 alpha (eIF2α) 51位丝氨酸的磷酸化,从而抑制蛋白的合成,磷酸化的eIF2α促进活化转录因子4 (ATF4)和C/EBP同源蛋白(CHOP) 的表达,CHOP是调节Bcl-2家族蛋白表达的关键促凋亡转录因子[14]。我们发现,Sch B可引起乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞内质网应激,CHOP,GPR78和 p-eIF2α蛋白水平呈剂量依赖性增加,当使用内质网抑制剂4-PBA后,内质网应激减轻。
综述所述,Sch B可诱导乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞凋亡,其机制可能与增加细胞内ROS水平,使p-eIF2α蛋白激活,GPR78和CHOP表达增多,引发细胞内质网应激有关。本研究可为乳腺癌的辅助治疗提供一定的实验依据。
Schisandrin B induces apoptosis of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through ROS mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202106123
- Received Date: 2021-06-24
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-10-18
- Available Online: 2021-12-27
- Publish Date: 2021-11-25
-
Key words:
- schisandrin B /
- breast cancer /
- reactive oxygen species /
- endoplasmic reticulum stress /
- apoptosis
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Weiting, YIN Xueqin, XIA Jine, ZHANG Xiayan. Schisandrin B induces apoptosis of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through ROS mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2021, 39(6): 499-503, 533. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202106123 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: