-
麻黄碱是中药麻黄的主要有效成分,但它也可以引起中枢神经系统毒副作用。麻黄碱属于小分子生物碱,能够通过血脑屏障对神经细胞产生直接毒性作用 [1-4]。然而,有关麻黄碱神经毒性的作用机制并不完全清楚。脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)已被证实参与学习、记忆等多种中枢神经系统的活动[5]。突触后致密蛋白是突触后膜胞质面聚集的一层均匀而致密的蛋白,其中PSD95是主要成分之一[6]。而synapsin1是维持突触前膜功能的重要成分之一[7]。BNDF、PSD95和synapsin1与神经元结构完整性和功能的完备性密切相关。本研究以PC12细胞为研究对象,考察麻黄碱的细胞毒性,同时检测BDNF、PSD95和synapsin1表达水平的变化,初步探讨麻黄碱引起细胞毒性的可能机制。
-
盐酸麻黄碱(批号:D03150702,赤峰艾克制药科技有限公司);BDNF抗体(批号:ab108319)、PSD95抗体(批号:ab18258)、synapsin1抗体(批号:ab64581)均购自英国Abcam公司。
-
PC12细胞购自中科院细胞库。
-
电子天平(德国Sartorious公司);孵育箱(Thermo公司);酶标仪(BioTek公司);Western blot设备(美国Bio-Rad公司)。
-
将培养瓶里的PC12细胞接种到96孔板上,每孔接种6000个细胞,用含1%FBS(胎牛血清)的RPMI 1640培养12 h后,吸弃原培养基,加入RPMI 1640基础培养基,1 h后分别加入不同浓度的麻黄碱,使其终浓度分别为0.25、0.5、1、2、4、8、16、20 mmol,继续培养24 h后,加入终浓度为0.5 mg/ml的MTT,继续孵育4 h,吸弃培养液,每孔加入150 μl的DMSO(二甲基亚砜),轻微震荡10 min,在酶标仪检测570 nm处的光密度(OD)值。
-
将培养瓶的PC12细胞接种到12孔板中,用含1%FBS的RPMI 1640培养12 h后,吸弃原培养基,加入RPMI 1640基础培养基1 h后分别加入不同浓度的麻黄碱,使其终浓度分别为10、500、1000 μmol,继续培养24 h后,在倒置显微镜下明场视野观察细胞形态变化。
-
将6孔板每孔接种105个PC12细胞,用含1%FBS的RPMI1640培养12 h,换上基础培养基RPMI1640,1h后分别加入不同浓度的麻黄碱,其终浓度分别为1、10、100、500、1000 μmol,继续培养24 h后,迅速将培养基吸弃,置于−30℃冷冻数小时,然后在冰上每孔加相应量的RIPA(含1%磷酸酶抑制剂和1%蛋白酶抑制剂)裂解液,4℃震荡30 min,将细胞裂解液收集到相应离心管里,4℃低温高速(12000 r/min)离心10 min。取出上清,蛋白浓度检测(BCA)试剂盒测定蛋白浓度后,加入相应量的5×的上样缓冲液和适量的RIPA裂解液,95℃加热10 min制样。制胶上样,样品80 V电泳结束后,400 mA电流90 min转移至PVDF(聚偏氟乙烯膜)后,5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭2 h,按分子量切出相应条带,分别孵育相应一抗过夜,洗涤后室温孵育相应二抗2 h,漂洗后,增强化学发光(ECL)法显影。
-
实验数据以
$ \bar x \pm s $ 表示。应用SPSS 20.0统计软件,采用单向方差分析法处理试验结果。首先进行Levene方差齐性检验,方差齐性且整体比较组间有显著性差异时,采用LSD法进行多重比较,方差分析不显著时不进行多重比较;若方差不齐,则作Welch检验,方差分析有显著性差异时,采用Dunnett’s T3法进行多重比较,方差分析不显著时不进行多重比较。 -
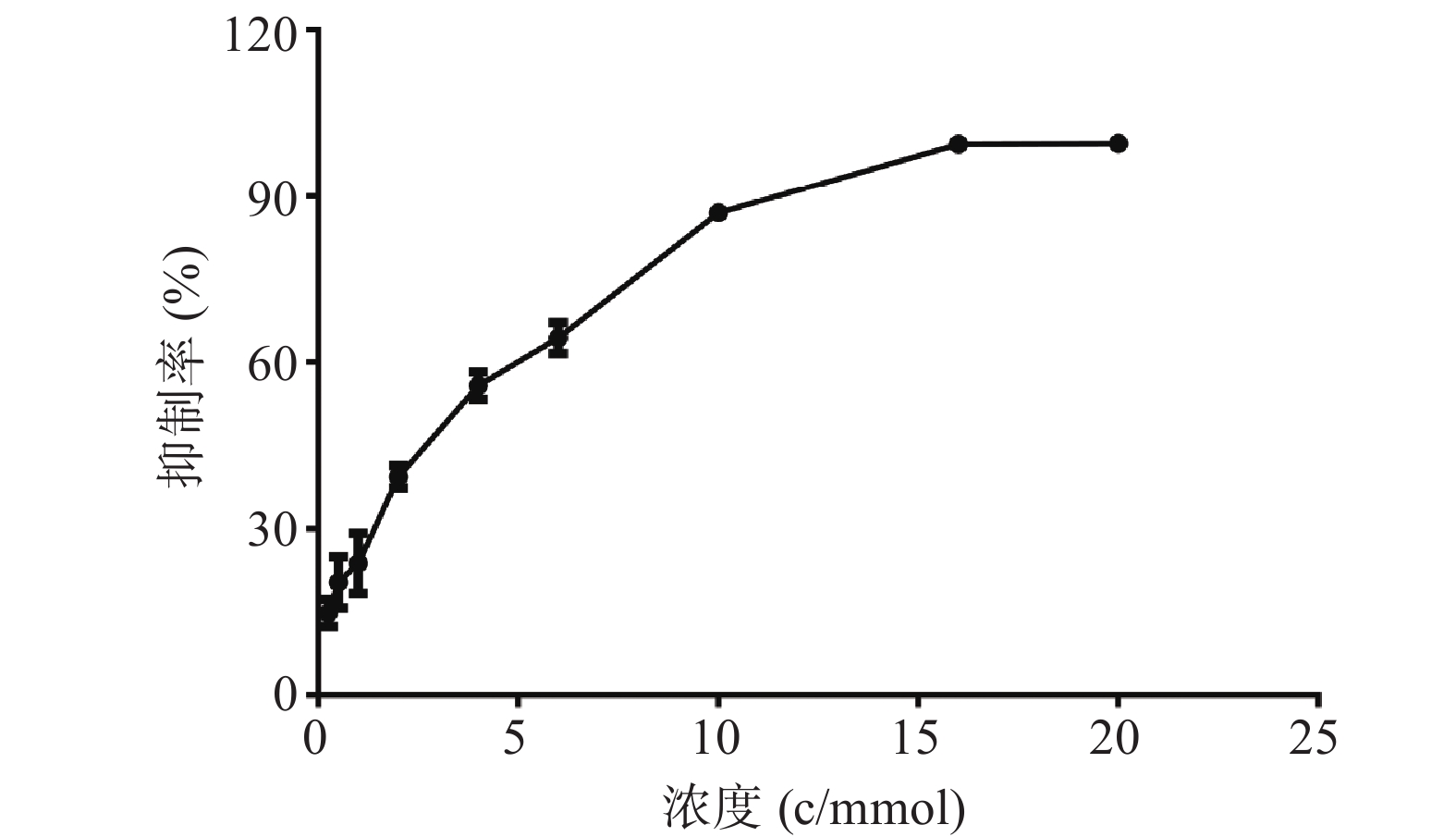
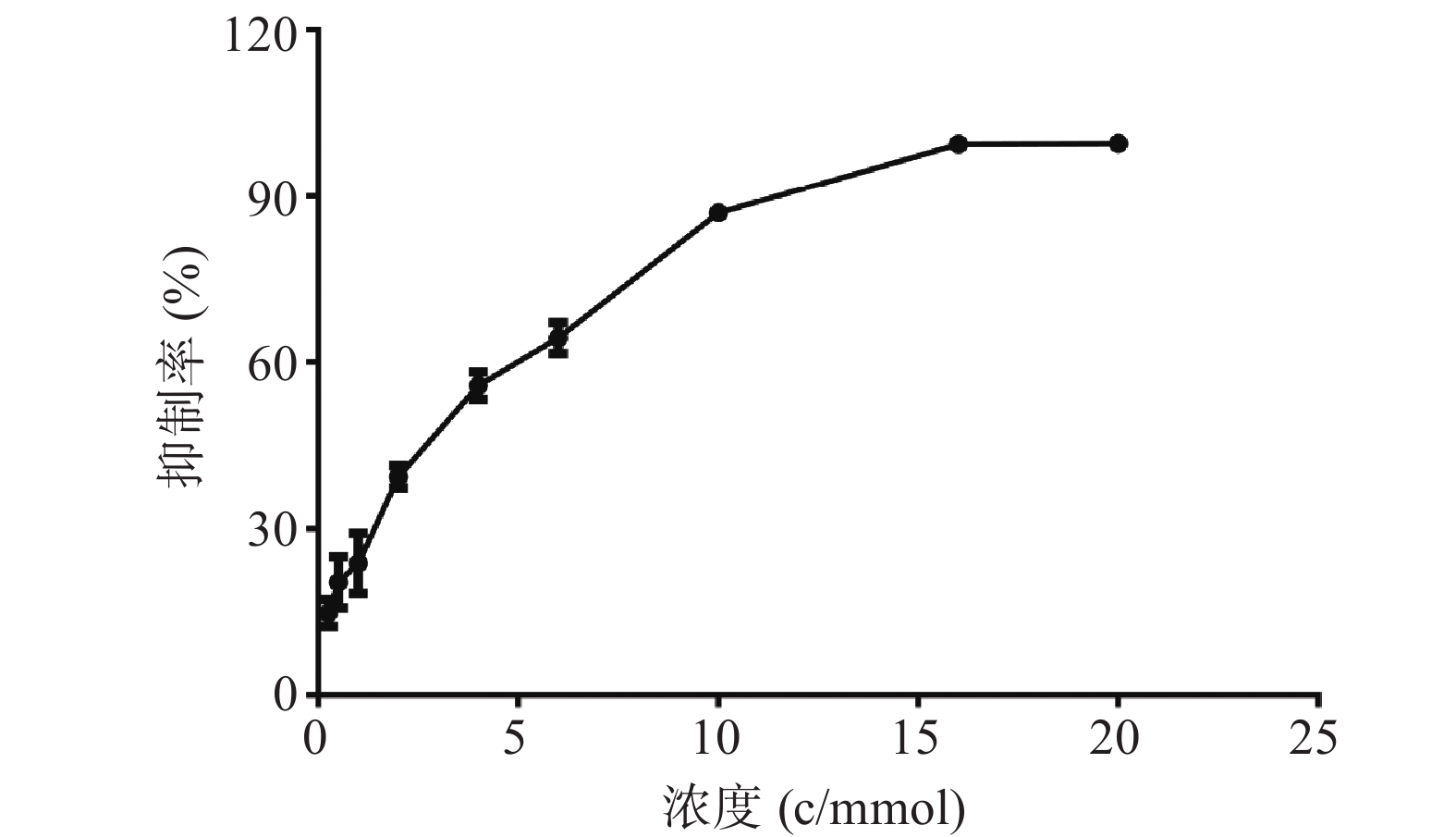
MTT结果如图1所示,麻黄碱在一定范围内对PC12细胞有一定的毒性,经拟合计算在PC12细胞中麻黄碱的IC25值为0.536 mmol,IC50值为2.8 mmol。
-
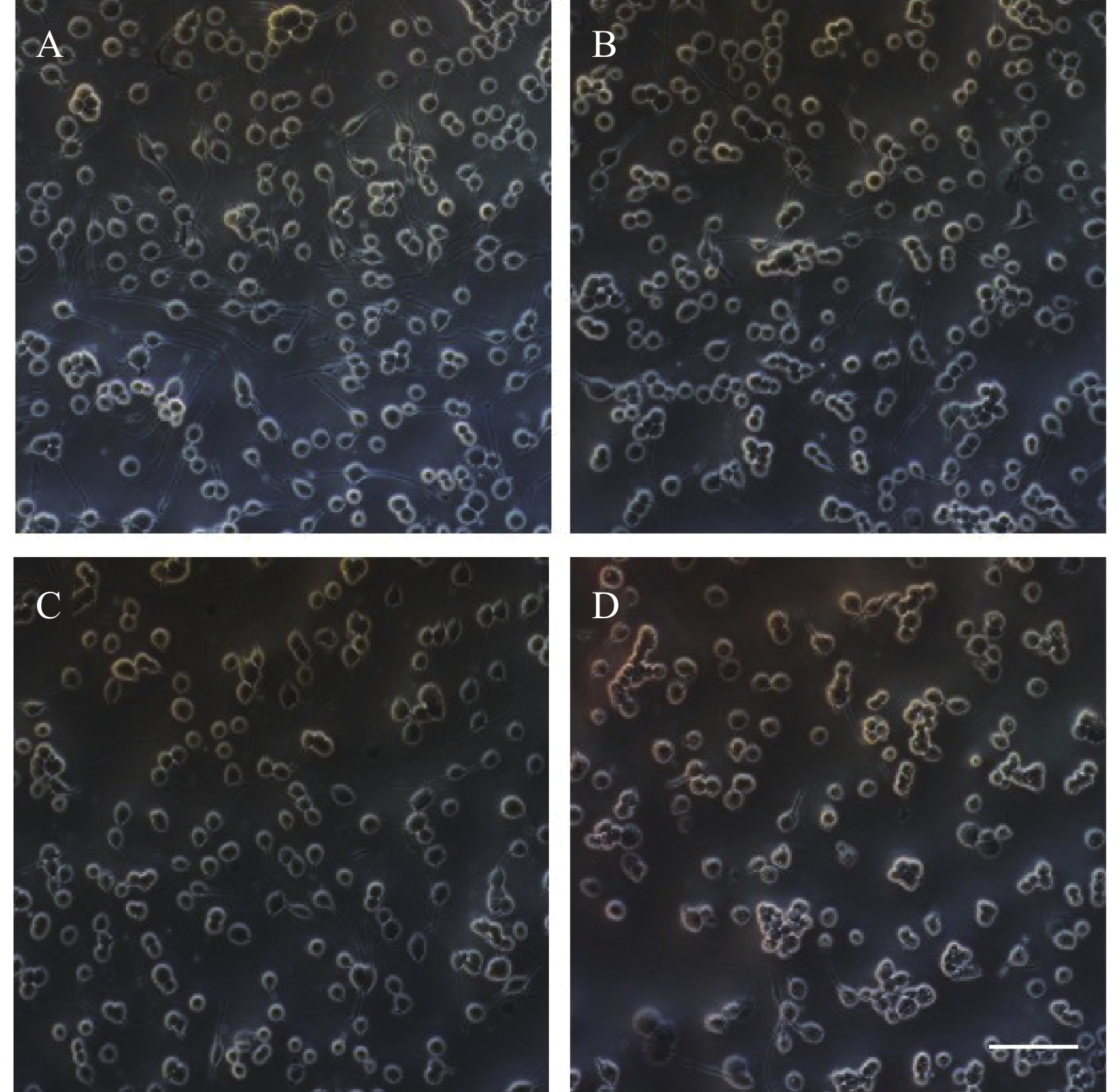
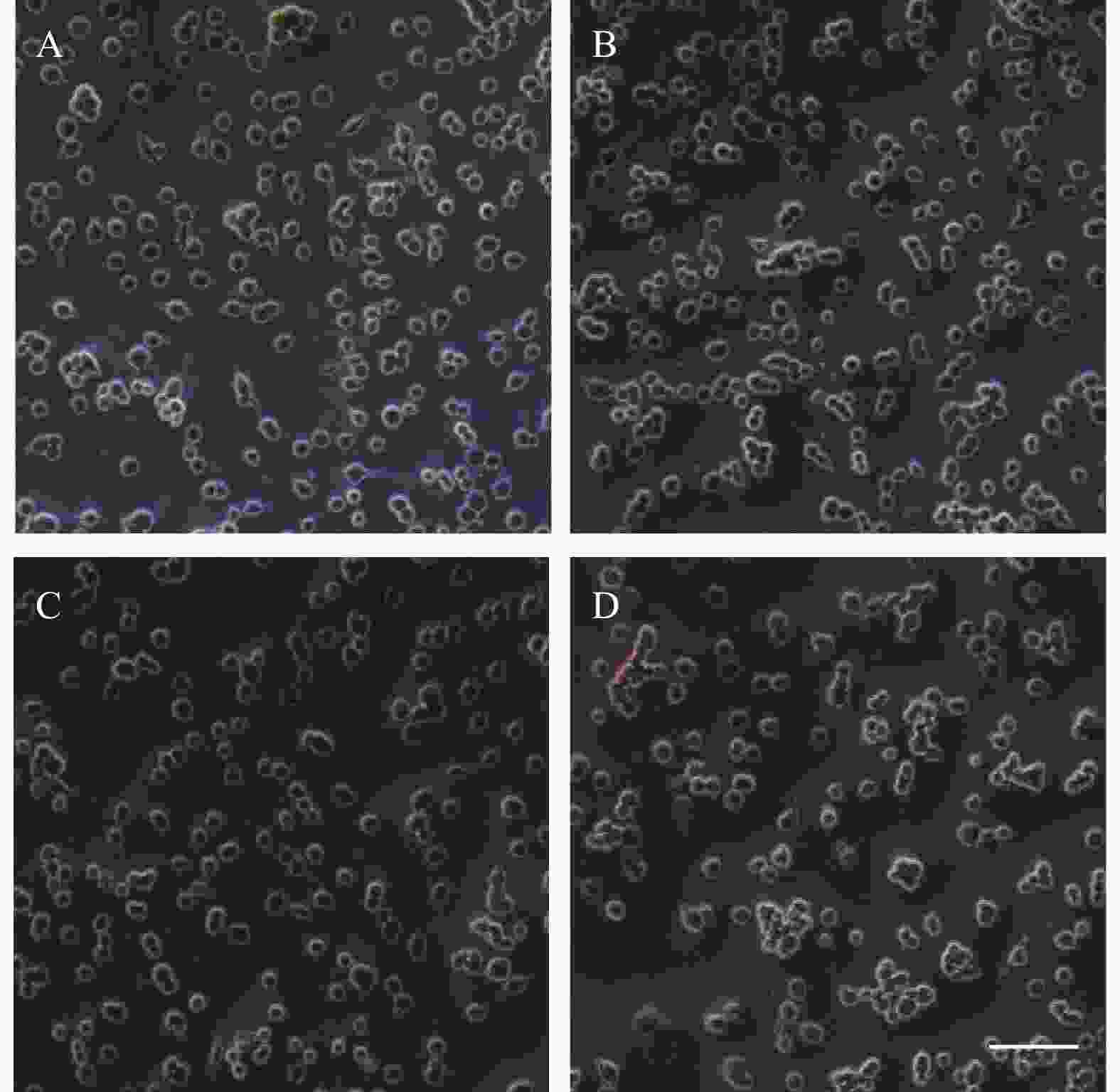
PC12细胞形态学变化如图2所示,在20倍镜下观察,随着麻黄碱浓度的升高细胞数量与空白对照组相比逐渐减少,细胞突触数量也随之减少。1000 μmol浓度处理条件下,轴突长度显著减短,细胞体边缘模糊,细胞体积显著变小。
-
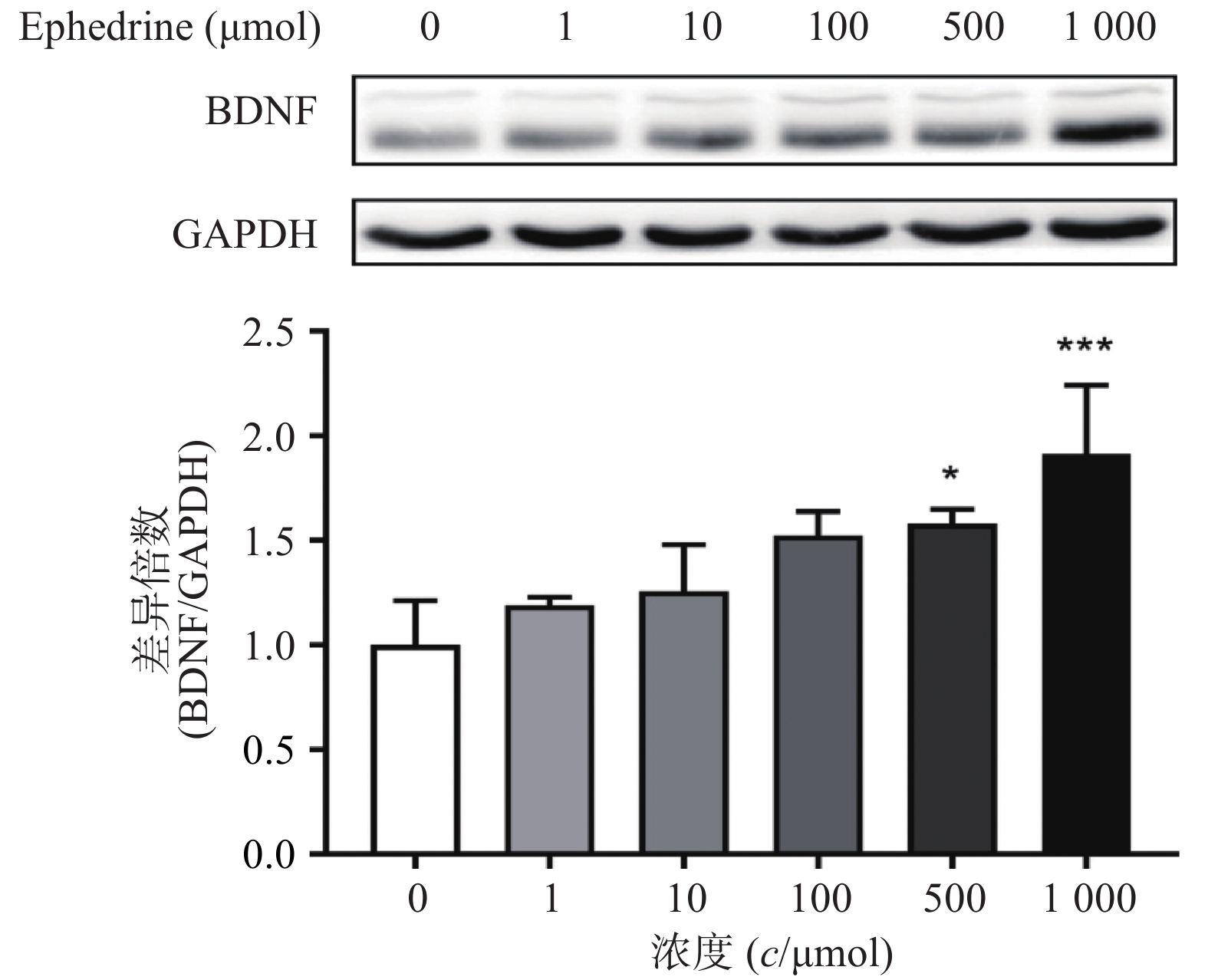
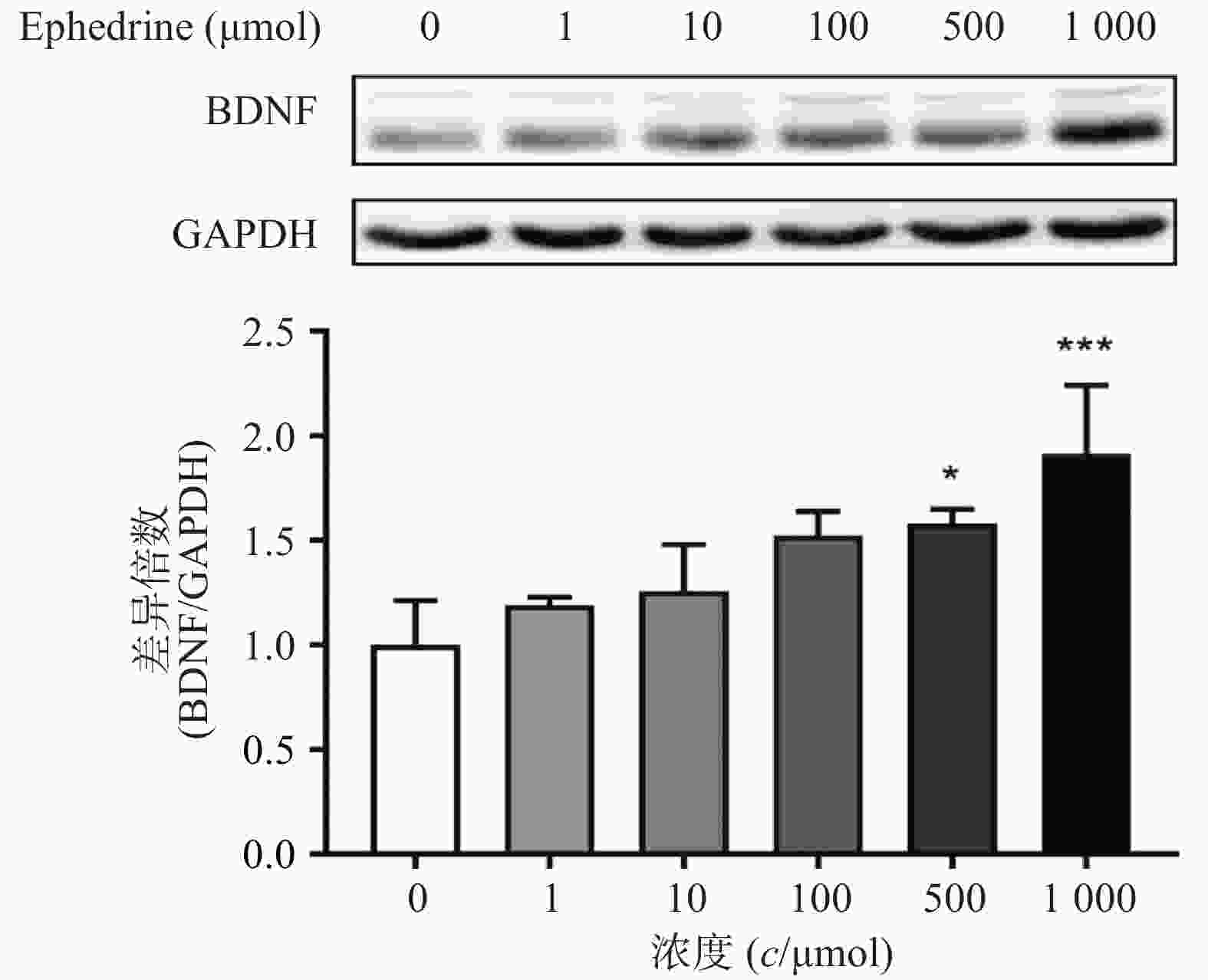
图3结果显示,随着麻黄碱剂量的增加,PC12细胞中BDNF的蛋白表达量增加。当麻黄碱浓度为500 μmol时,BDNF的表达量约为空白对照组的1.58倍,有统计学差异(P<0.05);而当麻黄碱浓度高达 1000 μmol时,BNDF为对照组的1.91倍(P<0.001)。说明该浓度范围内麻黄碱可以浓度依赖性的引起PC12细胞中BDNF表达升高。
-
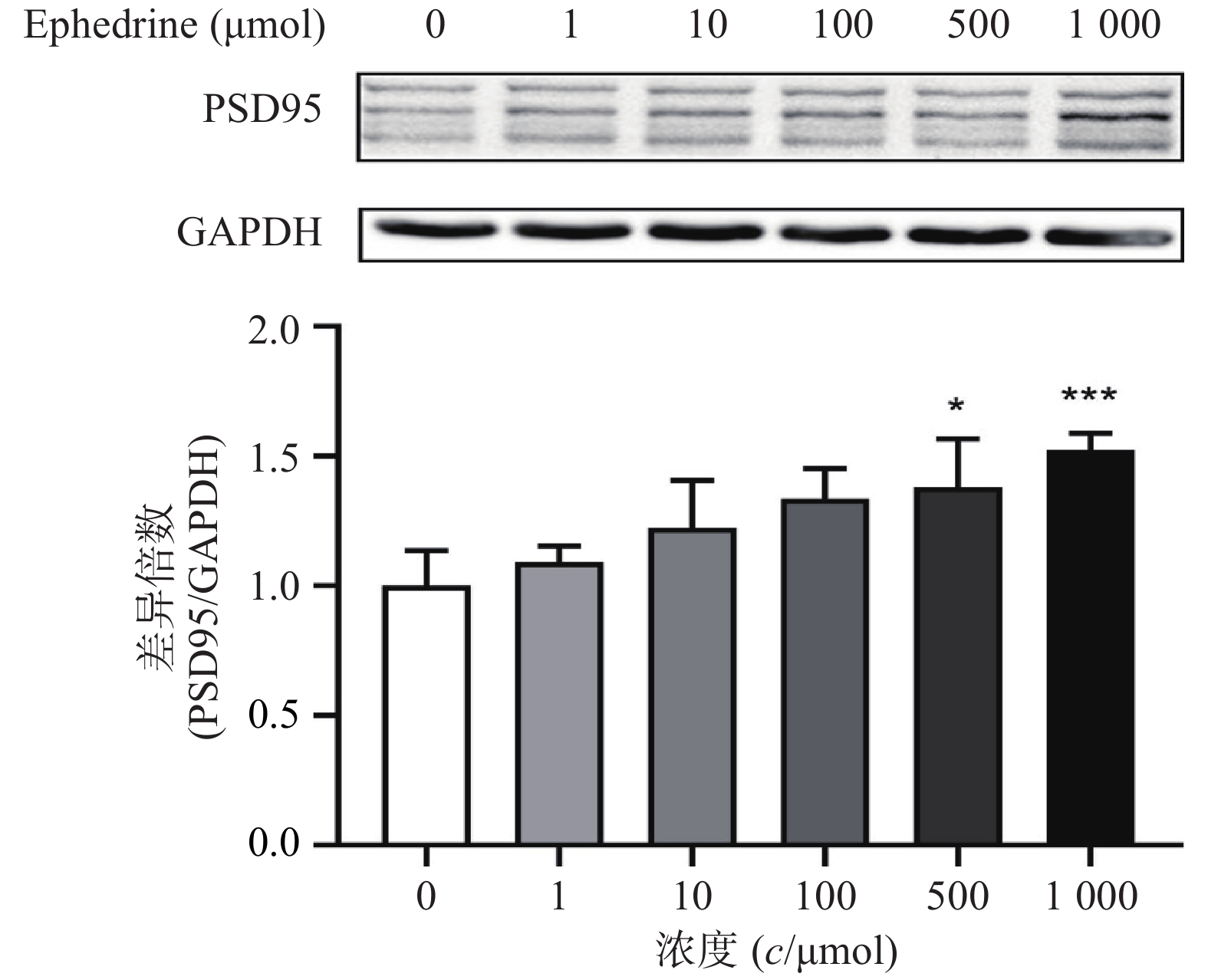
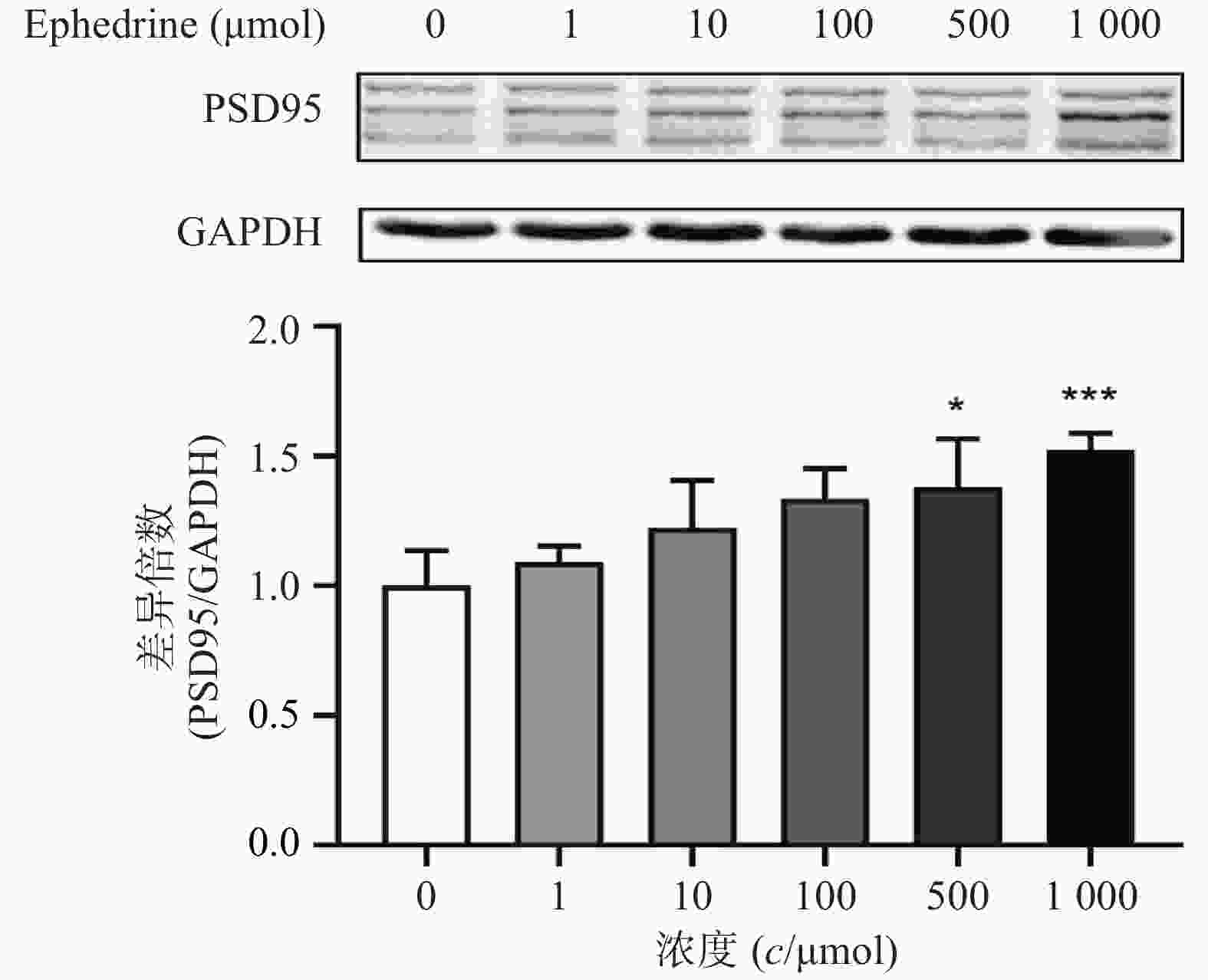
图4结果显示,随着麻黄碱剂量的增加,PC12细胞中PSD95的表达增加。麻黄碱浓度为500 μmol时,PSD95的蛋白表达水平约为空白对照组的1.38倍,有统计学差异(P<0.05);而当麻黄碱浓度达到1000 μmol时,PSD95表达量约上升为对照组的1.52倍(P<0.001)。说明该浓度范围内麻黄碱可以浓度依赖性的引起PC12细胞中PSD95表达升高。
-
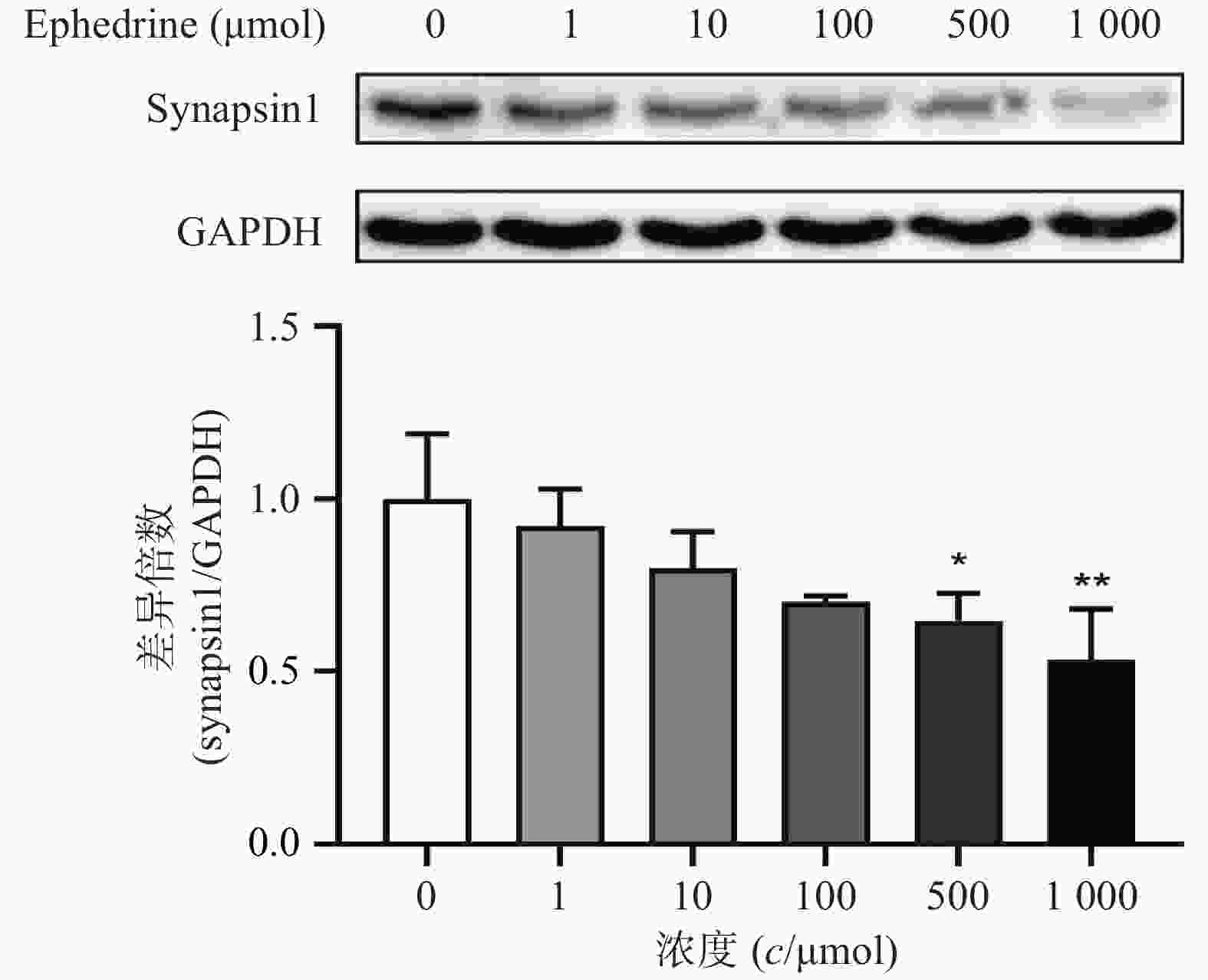
图5结果显示,随着麻黄碱剂量的增加,PC12细胞中synapsin1的表达量有下降的趋势。其中,麻黄碱浓度为500 μmol时,synapsin1的蛋白表达水平约为空白对照组的0.65,具有统计学差异(P<0.05);而当麻黄碱浓度达到1000 μmol时,synapsin1表达量下降至对照组的0.53(P<0.001)。说明麻黄碱在该浓度范围内可以引起PC12细胞中synapsin1表达降低。
-
麻黄历来被中医冠以“解表第一要药”,是治疗外感风寒表实证的重要中药,主要用于风寒感冒,胸闷喘咳,风水浮肿等,麻黄汤就是以麻黄为君药的治疗表寒实证的代表名方。然而前期研究发现,给予大鼠连续灌胃麻黄,可以造成大鼠不同脑区损伤,其中对额叶皮层影响较大,HE染色结果甚至观察到神经元凋亡早期的形态学改变 [8-9]。已经证实麻黄中对中枢神经系统有兴奋毒性作用的主要成分是麻黄碱。麻黄碱的神经毒性可能与升高兴奋性谷氨酸水平有关,过量的兴奋性谷氨酸能引起多巴胺神经末梢的破坏和额叶皮层、丘脑、边缘系统的神经变性。为了明确麻黄引起中枢神经系统毒性的机制,本研究中将麻黄碱单体作为研究对象,考察其在体外细胞模型中的毒性作用。
PC12细胞源于鼠嗜铬细胞瘤,在结构上和功能上与神经元有高度相似的地方,因其可重复性好,被广泛应用于中枢神经系统的研究。本研究首先考察了不同浓度麻黄碱对PC12细胞存活率的影响,确定了麻黄碱引起细胞毒性的浓度范围。在此基础上,分别考察不影响细胞存活率情况下(IC25值以下浓度)及显著影响细胞存活率情况下(IC25值以上浓度),麻黄碱对中枢神经系统中相关功能蛋白的影响。
BDNF是神经营养因子家族的肽生长因子的一员。在体实验发现,BDNF在大脑海马的CA1区可通过促进兴奋性突触的发育来增强突触强度。同时,BDNF可以在皮层神经元中增加介导中枢神经中快速兴奋性突触传递的AMPA受体的表达,提高动物兴奋性[10-13]。而外源性的BDNF则可以通过增强突触间的传递,增强海马神经元的兴奋性 [14]。以上研究表明,BDNF与神经细胞的兴奋性密切相关。PSD95定位于突触后膜,是高电子密度的半圆形区域形成的突触后致密区的主要组成部分之一。研究发现在海马神经元中过表达PSD95可以促进成熟谷氨酸能突触以及谷氨酸受体的活性 [6,15]。PSD95链接了兴奋性受体NMDAR(N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体)和下游信号分子,并且在神经元成熟以及突触的形成中发挥着重要作用[16]。尽管在多数神经退行性病变中,提高BDNF和PSD95的表达水平可以显著改善行为学,但是也有研究表明在生理状态下,神经元的过度激活会引起神经元的功能的减退甚至导致神经损伤。由于BDNF和PSD95与神经元兴奋性关系密切,在前期的行为学实验中,表明麻黄碱灌胃给药会引起大鼠自主活动的增加,并激活神经元,故我们在考察麻黄碱产生细胞毒性的机制时,检测了BDNF和PSD95的蛋白表达水平。结果显示,随着麻黄碱浓度的增加,BDNF和PSD95的表达水平浓度依赖性地升高,当浓度达到500 μmol时差异具统计学意义(P<0.05),说明麻黄碱可以引起体外神经细胞模型的兴奋状态。
与此同时,通过观察细胞形态变化,发现一定剂量的麻黄碱会引起PC12细胞突触数量下降和长度减短,说明麻黄碱会引起突触丢失。文献研究表明,synapsin1是突触的重要标志物,可以反应突触形态上的完整性和功能[7]。由此,我们在考察麻黄碱对PC12细胞形态影响的同时,采用Western blot检测了synapsin1的表达水平。梯度浓度麻黄碱处理PC12细胞后synapsin1的表达变化结果表明随着麻黄碱处理浓度的增加,synapsin1的表达水平降低,当浓度达到500 μmol时差异具统计学意义(P<0.05),说明麻黄碱有一定的细胞毒性的同时,也可以引起神经细胞的突触毒性,突触蛋白的丢失可能也是引起神经细胞毒性的原因之一。
综上所述,本实验结果表明麻黄碱可以对PC12细胞产生毒性。与正常细胞相比,麻黄碱处理组的细胞在形态学上发生了明显的变化,BDNF和PSD95等与兴奋性相关的蛋白表达出现了明显升高,而与突触功能有关的蛋白synapsin1表达出现了明显下降,说明麻黄碱产生中枢神经系统毒副作用的机制与BDNF、PSD95及synapsin1的表达变化有关。
Effects of ephedrine on the expression levels of BDNF, PSD95 and synapsin1 in PC12 cells
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202104014
- Received Date: 2021-04-02
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-10-05
- Publish Date: 2021-11-25
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Xian, NIU Bo, ZHENG Fanghao. Effects of ephedrine on the expression levels of BDNF, PSD95 and synapsin1 in PC12 cells[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2021, 39(6): 529-533. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202104014 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: