-
小胶质细胞是一种神经胶质细胞,是存在于中枢神经系统中的炎症免疫相关细胞,相当于中枢神经器官(脑和脊髓)中的巨噬细胞[1]。小胶质细胞的生理作用是清除中枢神经系统中受损的神经组织、通过血脑屏障入侵中枢的感染源及异物等。在病理状态下,已有多项研究表明,小胶质细胞在多种中枢神经系统疾病的发生发展中发挥重要的作用,包括缺血性脑梗、多发性硬化、神经退行性疾病等[2-3]。因此,抑制小胶质细胞的促炎反应对多种疾病的治疗具有重要意义。
α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体(α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, α7nAChR)是一种n型乙酰胆碱能受体亚型,从属于配体门控的离子通道受体家族[4]。从传统意义上来说,α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体位于神经肌肉接头后膜,接受传出神经末梢突触释放的化学递质(Ach)的作用,使得电信号继续传播。然而,近年来越来越多的研究表明,激动 α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体可以参与胆碱能抗炎通路的激活,进而在多种病理状态下发挥抗炎作用[5]。目前研究已表明,α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体介导的胆碱能抗炎通路在多种疾病的发生发展中发挥抑制作用[6]。
与其他巨噬细胞一样,小胶质细胞也分为经典活化的M1型巨噬细胞和选择性活化的M2型巨噬细胞[7]。一般来讲,M1型巨噬细胞主要分泌促炎因子,如IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、IL-12、IL-18等;而M2型巨噬细胞主要分泌抗炎因子,如IL-4、IL-10、IL-13等[8]。因此,在炎症免疫相关疾病中,降低M1/M2细胞的比例成为重要的治疗手段。
自噬是生物体的一种重要的代谢机制,利用溶酶体降解自身受损细胞器和大分子物质的进化上高度保守的过程[9]。自噬通常分为大自噬、小自噬和分子伴侣介导的自噬,由于大自噬的研究相对较多,在疾病中的作用也较为突出,因此,本研究主要讨论大自噬的作用(后续将描述为“自噬”)。在自噬过程中,自噬小体形成,包裹细胞组分或入侵的病原体,与溶酶体融合形成自噬溶酶体,最后自噬溶酶体将包裹的底物降解并释放入胞浆供细胞重新利用[10]。已有报道,自噬具有抗炎的作用[11]。
由此,本课题组探究在小胶质细胞中,α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体是否具有抗炎的作用,并且探究这一过程是否有调节M1型与M2型巨噬细胞的比例与诱导自噬过程的参与。
HTML
-
75%乙醇、异丙醇、甲醇、吐温-80、20×PBS、BSA、Tris碱、多聚甲醛、引物、LPS、DMEM高糖培养基、抗LC3抗体、抗Beclin-1抗体、抗p62/SQSTM1抗体、荧光二抗、DAPI染料、氯仿、细胞/组织蛋白裂解液、蛋白酶抑制剂(三联装)、甘氨酸、30%聚丙烯酰胺溶液、过硫酸铵、TEMED、1.5 mol/L Tris(pH 8.8)、1.5 mol/L Tris(pH 6.8)。JA2003电子天平(上海天平仪器厂);电热恒温水浴槽DK-8D(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司);STS-8A转移脱色摇床(上海琪特分析仪器有限公司);离心管(Corning公司);移液枪(Eppendorf公司);7500RT-PCR仪器(Applied Biosystems公司);超纯水仪(Millipore公司);荧光显微镜IX71(日本Olympus公司);锥形瓶;激光共聚焦显微镜(日本Olympus公司);酶标仪(瑞士Tacan公司);细胞操作超净台(苏州净化设备有限公司);Odyssey扫膜仪(LI-COR公司)。
-
BV2小胶质细胞系(美国ATCC细胞库)。细胞常规培养加入10% FBS的DMEM高糖培养基中,培养在37°C、5% CO2的培养箱中。在实验中,我们提前10 min加入PNU282987孵育,后加入LPS(1 000 ng/ml)刺激BV2细胞12 h。
-
提取细胞总RNA,逆转录成cDNA,使用cDNA进行实时定量PCR检测,引物由上海生工生物合成,序列见表1。
引物名称 引物序列 IL-1β (上游) 5′-CTCGTGCTGTCGGACCCCAT-3′ IL-1β (下游) 5′- AGTGTTCGTCTCGTGTTCGGAC-3′ IL-6 (上游) 5′-TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC-3′ IL-6 (下游) 5′-TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC-3′ TNF-α (上游) 5′-AAGCCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTA-3′ TNF-α (下游) 5′-GGCACCACTAGTTGGTTGTCTTTG-3′ GAPDH (上游) 5′-GTATGACTCCACTCACGGCAAA-3′ GAPDH (下游) 5′-GGTCTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG-3′ 按规范程序设置PCR仪,所得CT值按照2–∆∆CT公式计算。
-
提取细胞/组织蛋白,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,经加样、跑胶、转膜等步骤后,PVDF膜孵育牛奶封闭3 h,后分别孵育一抗(4 ℃过夜)、二抗(35 min,避光),用PBST液进行漂洗后,置于Odyssey扫膜仪中获取Western blot图像。
-
取出经过处理后的BV2细胞,弃掉培养基,加入PBS液润洗,用4%多聚甲醛室温孵育固定10 min,用PBS液洗涤5 min×3次,后用0.1% Triton X-100室温孵育5 min,用PBS洗涤5 min×3次;用山羊血清封闭室温10 min,后孵育一抗(室温1 h)、二抗(37 ℃,30 min,避光),加入DAPI染核3 min,后用PBS洗涤5 min×3次,加入抗荧光淬灭剂后于激光共聚焦显微镜拍照。
-
实验数据以(
$\bar{x}\pm s$ )表示,数据处理过程中,多组间比较用单因素方差分析(analysis of variance,ANOVA)并Bonferroni检验,P<0.05时认为差异具有统计学意义。
1.1. 药品、试剂与仪器
1.2. 主要方法
1.2.1. BV2细胞的培养与处理
1.2.2. 实时定量PCR
1.2.3. Western blot
1.2.4. 细胞免疫荧光
1.2.5. 统计学分析
-
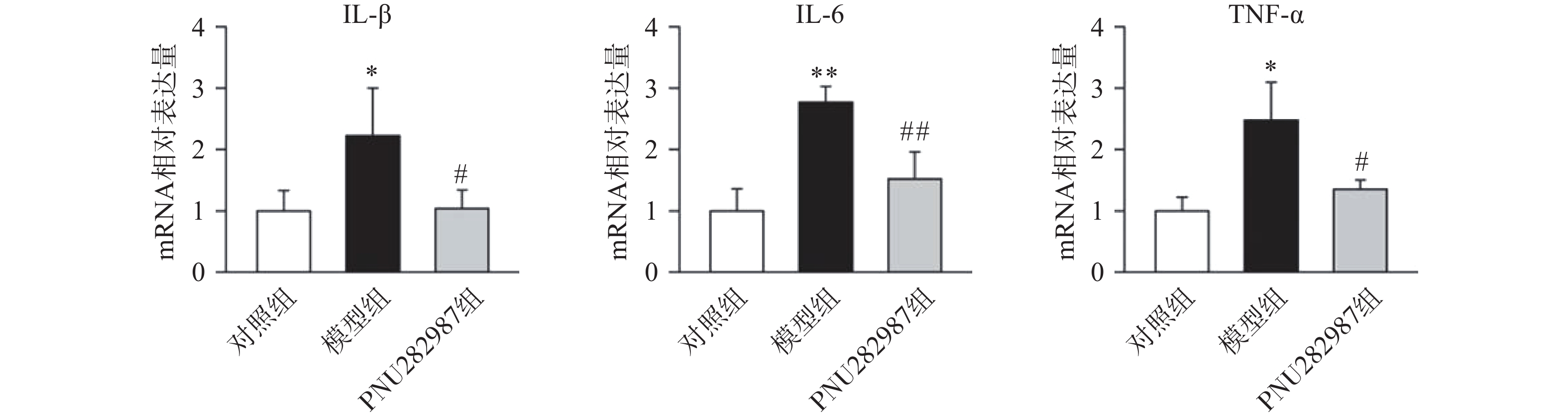
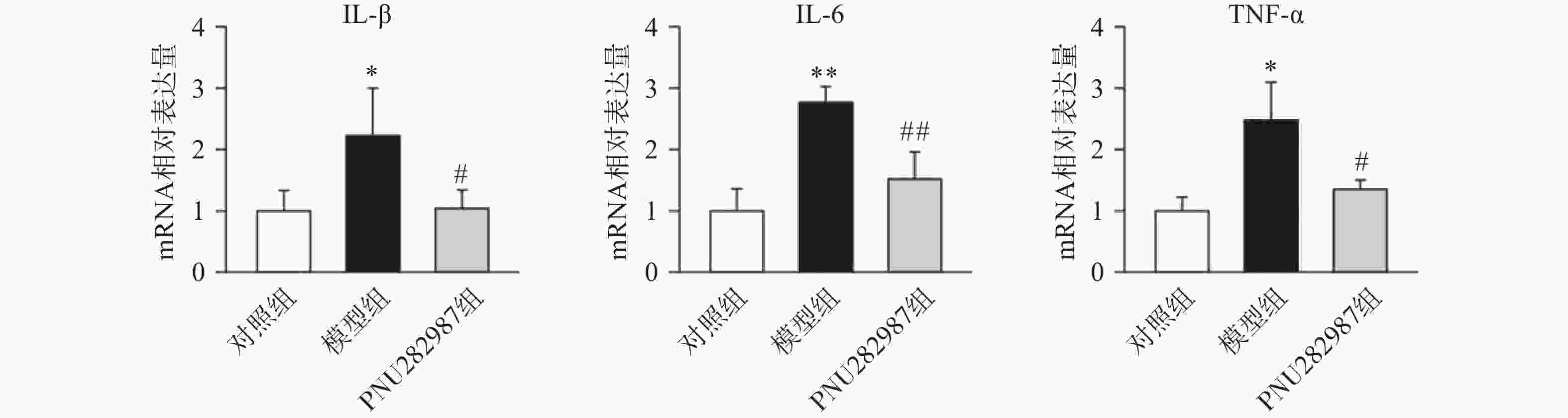
首先,我们探究在小胶质细胞中,α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体对炎症反应水平的影响。提前10 min加入PNU282987(10 μmol/L)孵育,后加入LPS(1 000 ng/ml)刺激BV2细胞,刺激12 h后,通过实时定量PCR技术检测BV2细胞的促炎因子IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平(图1)。
从图1中可以看出,在LPS的刺激下,小胶质细胞中促炎因子IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的mRNA水平显著增加,而应用PNU282987激动α7nAChR极大地降低了促炎因子IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的mRNA水平。由此可以看出,炎症环境中激动α7nAChR在小胶质细胞中的抗炎作用。
-
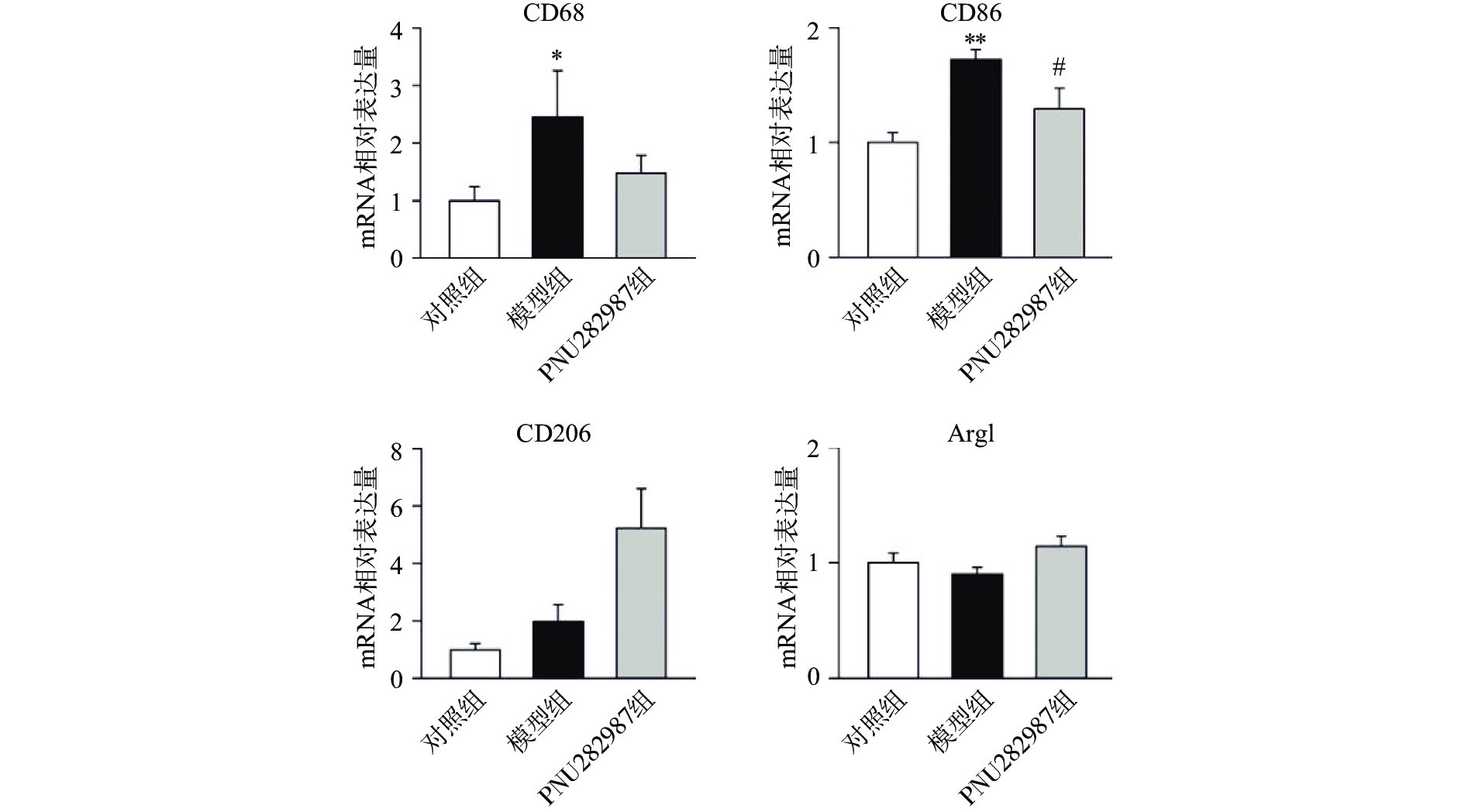
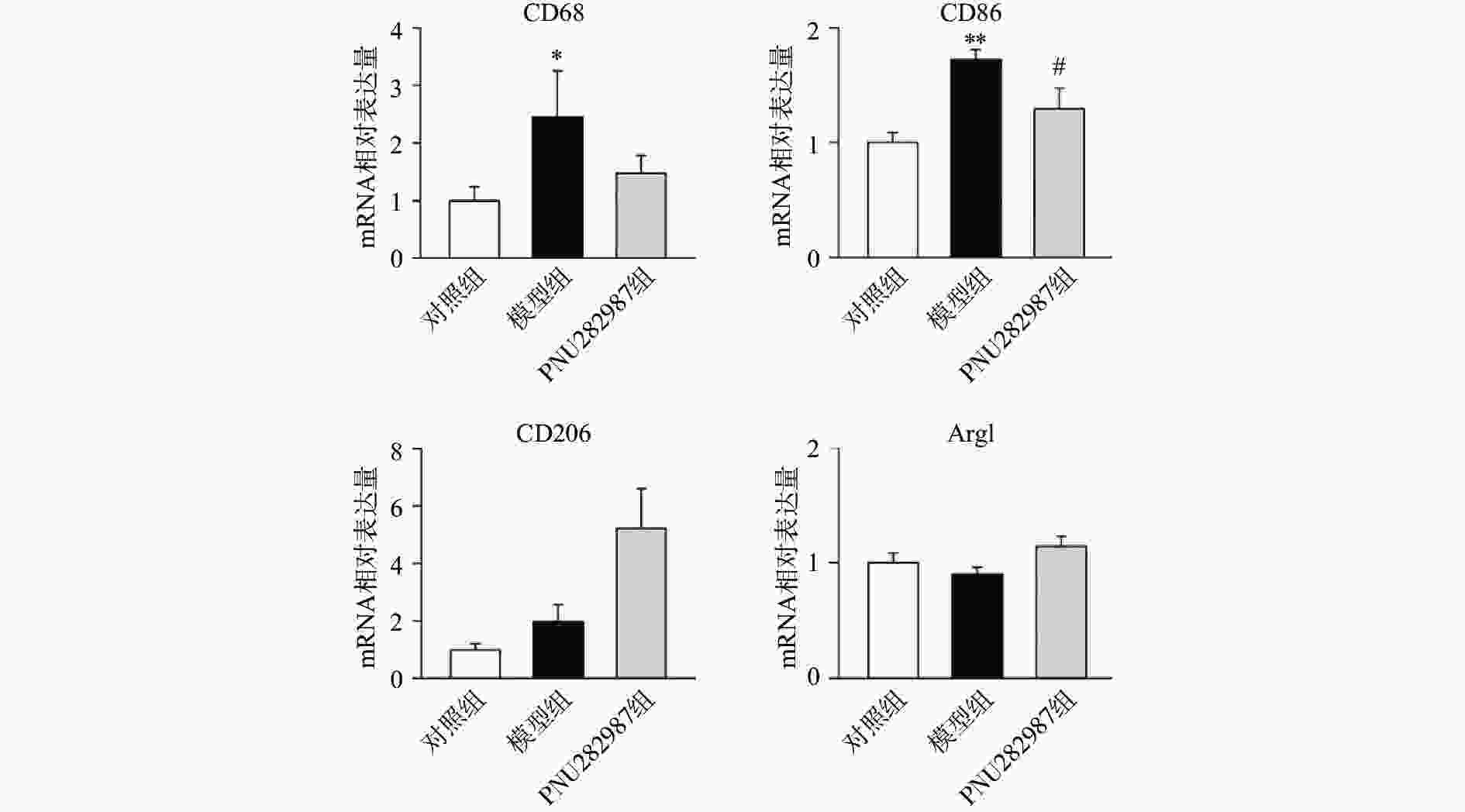
炎症环境中激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体在小胶质细胞中的抗炎机制。提前10 min加入PNU282987(10 μmol/L)孵育,后加入LPS(1 000 ng/ml)刺激BV2细胞,刺激12 h后,通过实时定量PCR技术检测BV2细胞的M1型巨噬细胞标记物CD68、CD86与M2型巨噬细胞标记物CD206、Arg1的mRNA水平(图2)。
从图2可以看出,在LPS的刺激下,小胶质细胞中M1型巨噬细胞标记物CD68、CD86的mRNA水平显著增加,而应用PNU282987激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体极大地降低了巨噬细胞标记物CD68、CD86的mRNA水平并增加了M2型巨噬细胞标记物CD206、Arg1的mRNA水平。
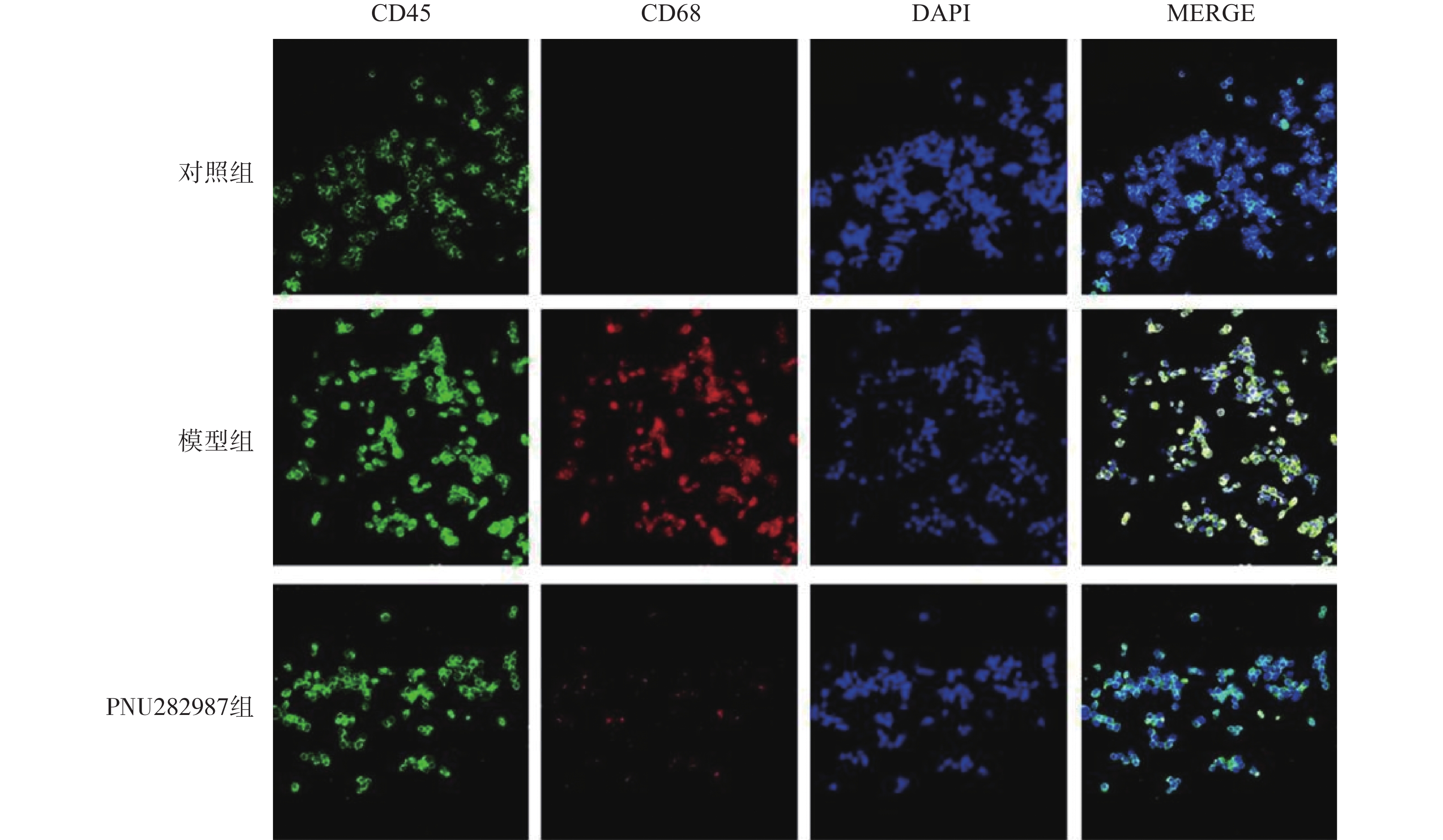
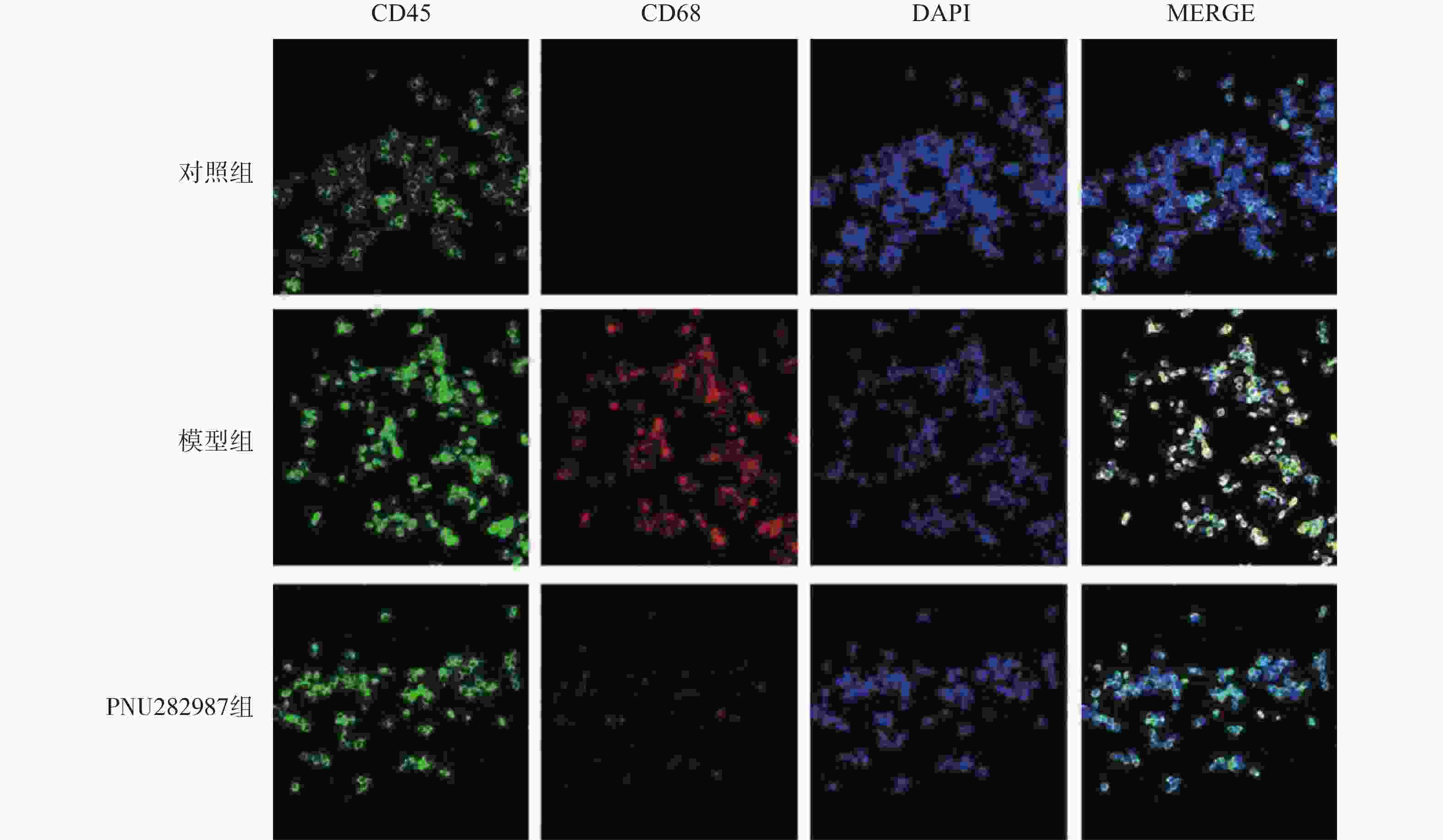
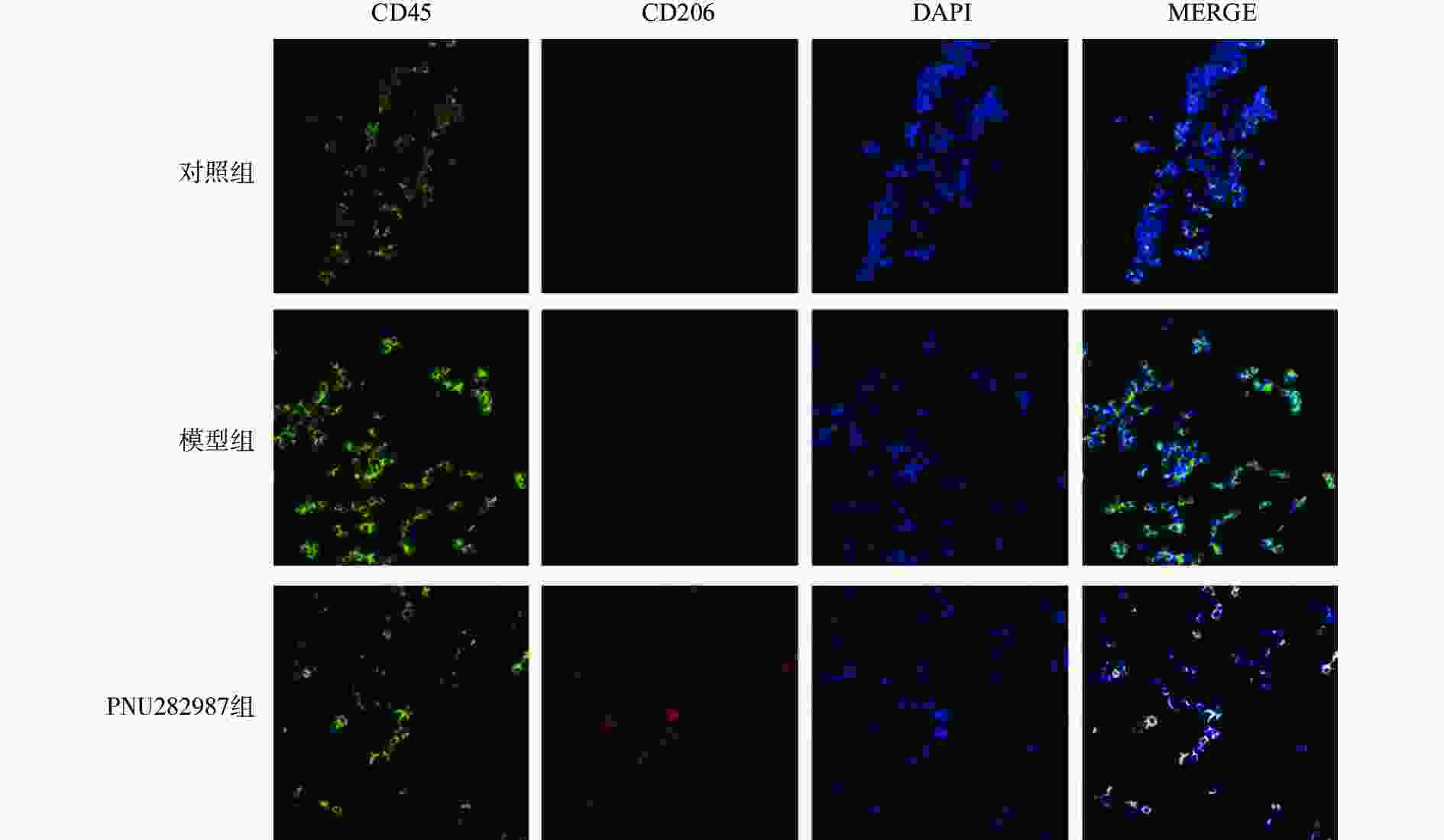
对BV2细胞进行同样的处理,而后通过细胞免疫荧光技术检测M1型巨噬细胞比例(CD45+、CD68+细胞,图3)与M2型巨噬细胞比例(CD45+、CD206+细胞,图4)。
从图3和图4可以看出,在LPS的刺激下,小胶质细胞中M1型巨噬细胞比例显著增加,而应用PNU282987激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体极大地降低了M1型巨噬细胞的比例并增加了M2型巨噬细胞的比例。
综合图2~4的结果可以发现,炎症环境中激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体可以调节小胶质细胞M1型与M2型比例,增加M2型巨噬细胞的比例并降低M1型巨噬细胞的比例。
-
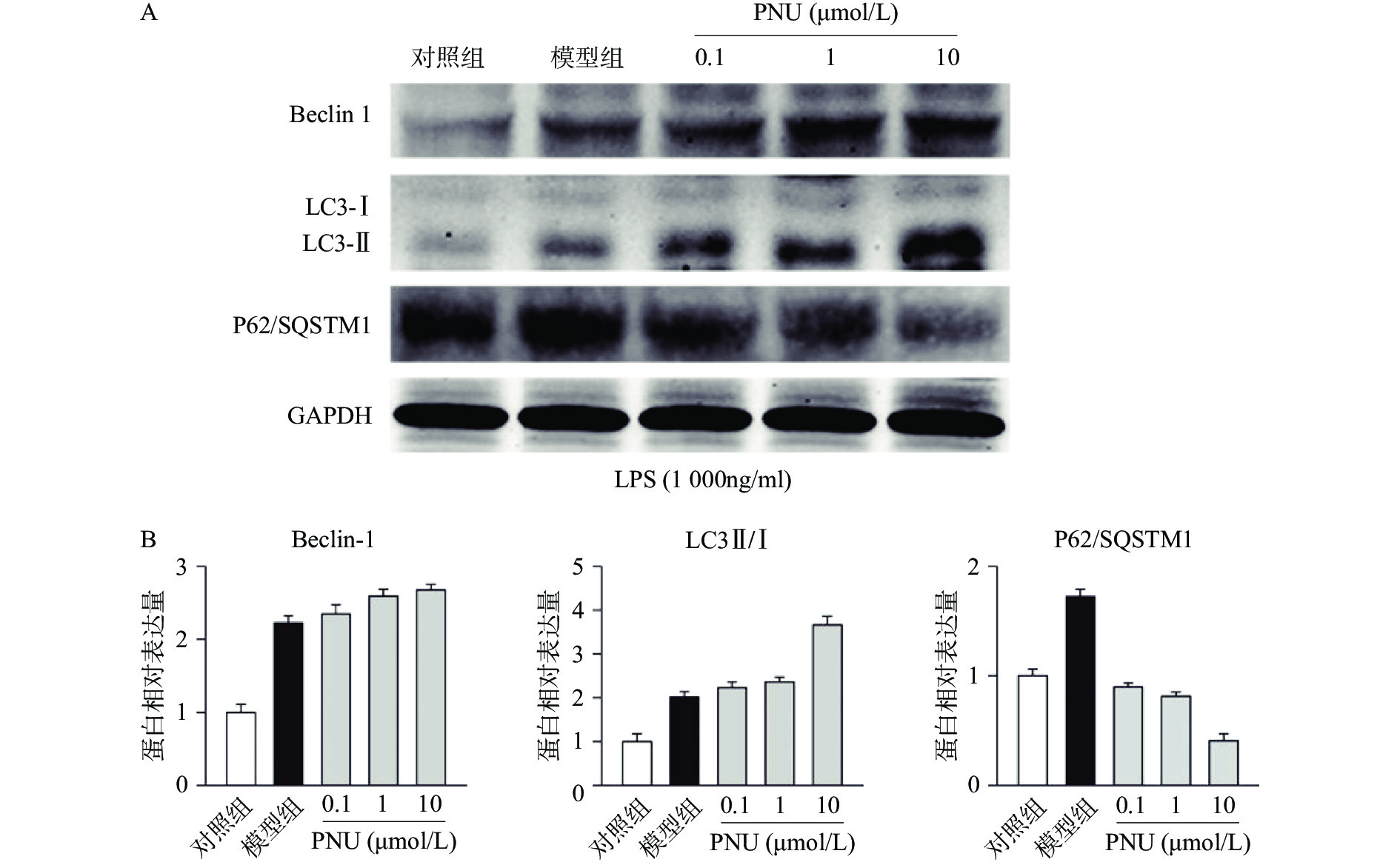
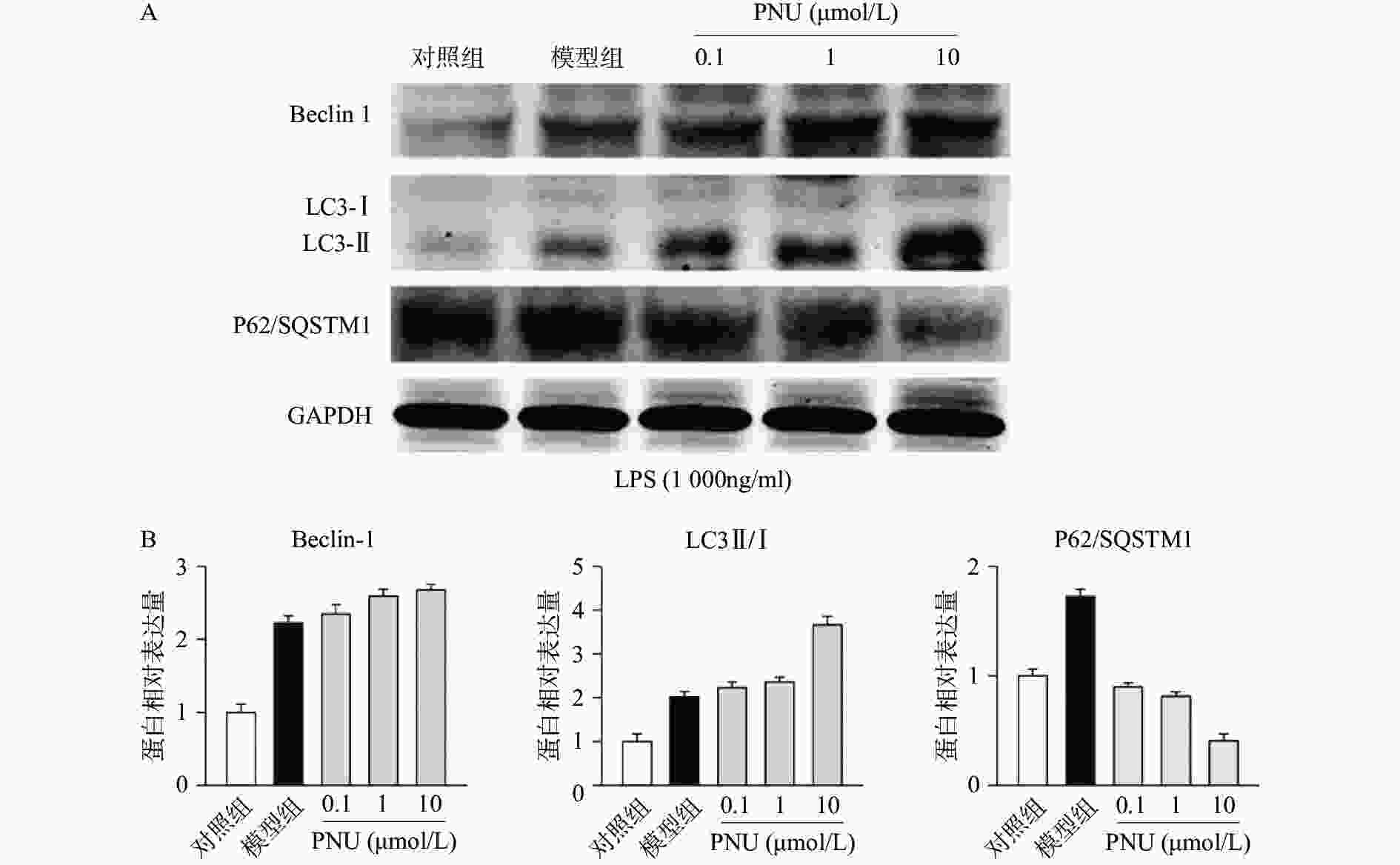
最后,我们探究炎症环境中激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体的抗炎作用是否有自噬过程的参与。选用不同剂量的PNU282987,提前10 min加入PNU282987(0.1、1、10 μmol/L)孵育,后加入LPS(1 000 ng/ml)刺激BV2细胞,刺激12 h后,通过Western blot技术检测BV2细胞中的自噬相关蛋白Beclin 1、LC3-II/I比例、p62/SQSTM1表达水平(图5)。
从图5中可以看出,在LPS的刺激下,小胶质细胞中自噬水平显著增加,而应用PNU282987激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体进一步增加了自噬水平。由此可以看出,炎症环境中激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体可以上调BV2细胞的自噬水平。
2.1. 炎症环境中激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体具有抗炎作用
2.2. 炎症环境中激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体调节小胶质细胞M1型与M2型比例
2.3. 炎症环境中激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体上调小胶质细胞自噬水平
-
α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体介导的胆碱能抗炎通路在多种炎症免疫相关疾病中发挥重要的调节作用。课题组的前期研究发现,在小鼠多发性硬化模型中,激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体可以发挥重要的抑制小胶质细胞炎症的作用[12]。本研究在细胞水平应用小胶质细胞系BV2细胞,再次证明了α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体的抗小胶质细胞炎症的作用。
对于在小胶质细胞中α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体抗炎作用的机制,本研究首次表明,其抗炎作用的实现有调节小胶质细胞M1型和M2型巨噬细胞比例的参与,即激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体可以上调具有抗炎作用的M2型巨噬细胞并且下调M1型巨噬细胞的比例。这一结论为利用α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体激动剂作用治疗相关疾病的药物提供了重要的理论依据。此外,我们也探讨了自噬这一重要的抗炎机制是否参与了这一过程。通过细胞实验得到了肯定的答案,与以往研究相一致,我们证明了上调小胶质细胞的自噬水平发挥抗炎作用。
由此我们得出,激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体可以发挥抑制小胶质细胞炎症反应的作用,其作用的实现依赖于调节小胶质细胞M1型和M2型巨噬细胞比例和上调自噬水平。下一步,我们将通过单核巨噬细胞特异性敲除α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体的小鼠进行研究,进一步验证激动α7 n型乙酰胆碱能受体是否可以通过调节巨噬细胞比例和自噬水平,进而抑制小胶质细胞炎症发挥作用,使实验结果更具说服力。我们相信,这一研究将为开发利用新的胆碱能抗炎药物提供新的思路。








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: