-
沙门菌是常见的导致食源性细菌疾病的肠杆菌科细菌,主要通过污染食物、饮水引起感染,临床表现为腹痛、腹泻,常见于胃肠炎、肠热病等[1-2],但也可能发生发病率和死亡率较高的侵袭性疾病,演变为菌血症或影响肺部、中枢神经系统、肾脏、皮下组织、骨骼和关节的局部感染。这类侵袭性疾病主要发生于儿童、老年人、免疫抑制以及营养不良等人群[3-4]。本文报道了一例没有基础疾病、沙门菌致髋关节假体感染并且反复出现皮肤瘙痒的高龄患者。
HTML
-
患者,女,81岁,10 d前患者因受凉感冒,出现发热、无上呼吸道感染症状,随后出现左侧髋部疼痛。5 d前患者因手术切口肿痛,于外院就诊,怀疑全髋关节置换术后关节腔内感染,予以关节腔穿刺引流、抗感染等治疗,未见明显好转,于2020年10月18日来我院就诊。患者在2003年行右侧髋关节置换术,2006年行左侧髋关节置换术,2012年行右侧髋关节翻修术,2017年行左髋关节翻修术,2020年6月患者因左侧全髋关节翻修术后疼痛,在我院行左髋关节部分翻修术,后因左髋关节翻修术后切口脂肪液化,行3次左髋关节清创+负压装置引流术,引流液细菌培养结果为沙门菌D群。既往一般健康状况良好,青霉素过敏。
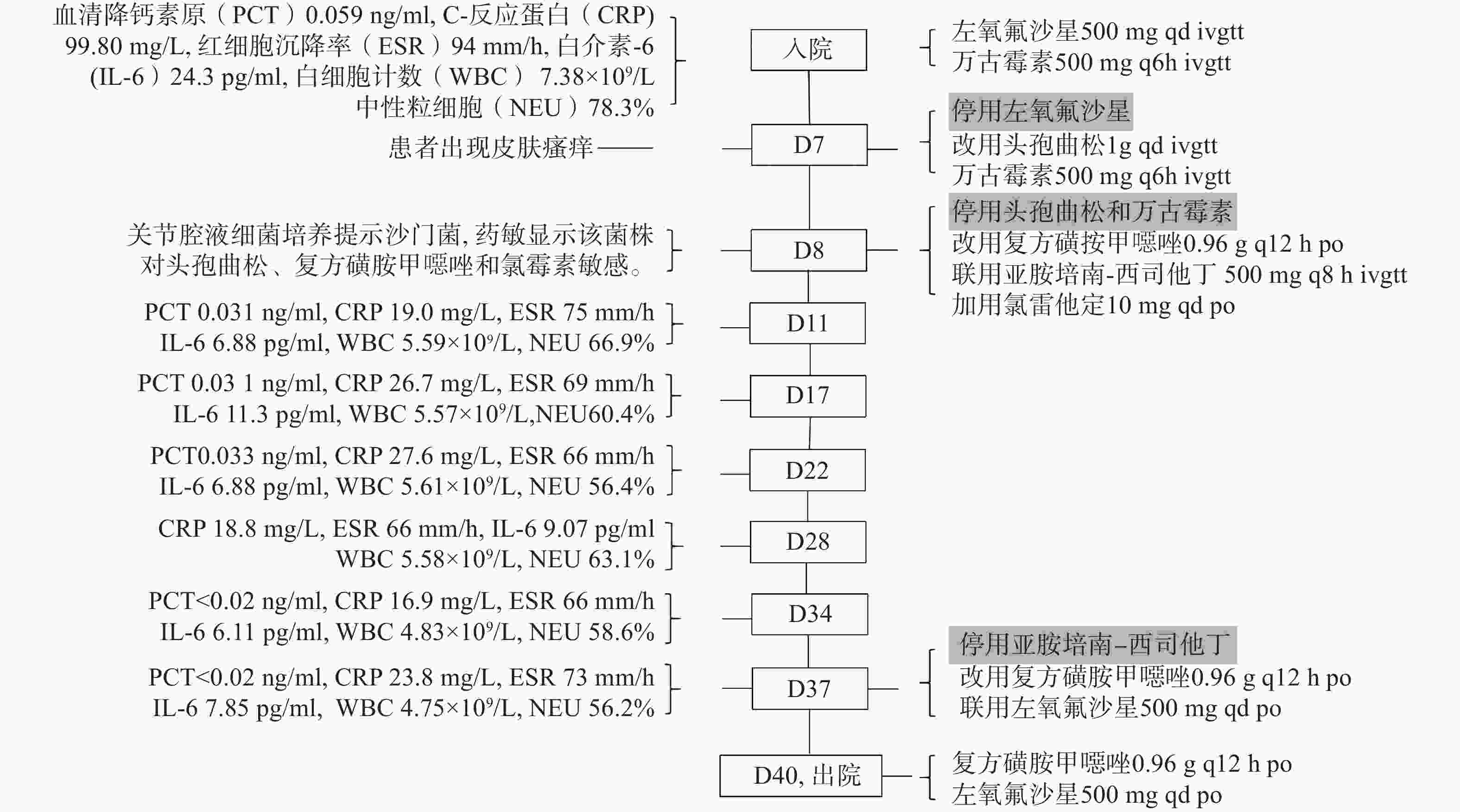
入院查体:体温37.3 ℃,心率80次/min,呼吸18次/min,血压120/80 mmHg。专科检查:跛行入病房,左髋部无明显肿胀,左髋部后外侧可见陈旧性手术疤,局部有一肿块,无发红,有压痛,余部位愈合良好。左髋关节活动范围:屈曲85°,后伸0°,内收15°,外展25°,内外旋转15°。辅助检查:盆骨正位DX:盆骨、腰椎退行性改变,双侧人工髋关节置换术后。入院诊断为左髋关节假体感染,诊疗过程见图1。
-
关节置换术后假体感染是关节置换术的严重并发症,据报道,关节假体植入后的感染发生率为1%~3%[5-6],全髋关节置换术后的感染率在0.5%至2%之间[7],而关节翻修术后假体感染发生的风险是初次置换的2.28倍(OR,2.28;CI,1.26~3.98)[8]。假体感染的发生涉及多个因素,包括患者自身状况、手术时机和手术室环境、以及植入物的选择等[9]。有研究[10]通过多因素Logistic回归分析,表明体重指数(BMI)较大、手术时间长、术后引流多、住院时间长、切口既往手术史、免疫抑制剂使用、术前低蛋白血症、无症状细菌尿以及有表浅感染均是假体感染的独立危险因素 (P<0.05)。本案例患者进行过多次翻修术,前期翻修术后又经多次引流,且住院时间长,这可能是导致该患者假体感染发生的因素。
金黄色葡萄球菌是假体关节感染(PJI)最常见的病原体,而沙门菌是引起PJI的罕见病原体[11]。沙门菌致髋关节假体感染的病例非常罕见,文献中仅有少数报道。国内外研究表明[12-14],沙门菌引起的PJI通常是一种血行性的局部感染,主要的发病机制是沙门菌通过胃肠道进入血液,然后散播至各组织器官包括骨和关节,由于免疫力低下,原本存在于人体内的沙门菌大量繁殖,当达到一定阈值时,会从细胞内释放入血,从而引发菌血症出现临床症状。因此,沙门菌引起的PJI常见于有基础疾病的人群,如系统性红斑狼疮、镰状细胞病、糖尿病、风湿性关节炎、胶原血管疾病等,使用免疫抑制剂和细胞毒性药物,高龄、酗酒、吸毒等也会增加沙门菌感染的发生率[7, 15-16]。其最常见的症状是急性发热并伴有关节疼痛和肿胀,ESR和CRP水平显著升高[17]。此外,也有文献报道,6例中有2例沙门菌PJI患者在确诊前患有胃肠炎或感染动物接触史引起的腹泻症状[18],因此,当有上述易感因素的患者出现发热、关节疼痛或胃肠道症状时,提示医生应怀疑沙门菌感染,并及时进行关节腔液或血液、粪便培养以及必要的影像学检查。
本案例患者既往无其他疾病,进行过多次双侧髋关节置换。追问病史与接触史,患者最近几个月无腹泻情况,也无动物接触史,但患者2020年6月左髋关节翻修术后,手术切口愈合不良。怀疑可能是由于手术切口没有彻底愈合,沙门菌经食物带入消化道而进入血液,散播至髋关节,同时因高龄、营养及情绪不佳等致使免疫力低下,从而使得沙门菌在体内大量繁殖,引起手术切口处化脓性感染。
-
PJI患者主要有三种治疗方式[19]:①保留假体并清除感染,进行抗菌药物治疗(清创,抗菌药物治疗并保留假体—DAIR)。②移除假体并清除感染,进行抗菌药物治疗:更换假体(一期或二期置换)或不再植入假体(关节融合或切除成形)。③保留假体,长期抗菌药物压制(SAT),不试图完全清除感染。本例患者在2020年6月翻修术后,关节腔液培养出沙门菌,患者无明显感染症状未予以治疗。而出院几天后患者手术切口化脓感染,关节腔液再次培养出沙门菌,予以3次清创及抗菌药物治疗,CRP、PCT等感染相关指标恢复至正常水平患者出院。本次入院,患者关节腔液仍培养出沙门菌,考虑患者高龄,移除假体风险高,医生采取保守治疗,保留患者假体,长期服用抗菌药物压制。沙门菌假体关节感染的抗菌药物选择包括氨苄西林、氯霉素、复方磺胺甲噁唑、第三代头孢菌素和喹诺酮类,这些药物不仅能够杀死繁殖期的细菌,而且能够杀死那些处于静止期并粘附在假体材料上的病原菌。氟喹诺酮类可作为治疗假体关节沙门菌感染的首选药物[13, 15]。鉴于沙门菌菌株的耐药率不断增加,治疗应以药敏试验为依据。临床药师查阅相关文献及指南,并结合药敏结果,向医生推荐复方磺胺甲噁唑(0.96 g,q12 h,po)和左氧氟沙星(500 mg,qd,po)口服序贯治疗,医生接受临床药师的建议。患者出院后临床药师进行了电话随访,提高了患者的用药依从性并对患者的用药安全性进行监护。本案例表明及时清创、早期部件更换和适当的抗菌药物治疗是至关重要的,同时临床药师的参与也是临床治疗中重要的一环。
-
沙门菌可引起伤寒和副伤寒,感染了伤寒杆菌的病人75%以上可发生典型的玫瑰疹,但本例患者并无明显可见压之退色的淡红色斑丘疹,排除沙门菌引起瘙痒的可能性,患者既往无过敏性疾病,也无食物过敏史;患者住院期间先后使用了左氧氟沙星、头孢曲松、复方磺胺甲噁唑及亚胺培南-西司他丁抗感染治疗,均出现了皮肤瘙痒。根据我国卫生部对药物不良反应因果关系的评估[20],患者在上述4种药物滴注期间或滴注后出现皮肤瘙痒,有明确的时间相关性;有文献报道此4种药物均会导致皮肤瘙痒;但由于药物是联合使用的,所以不能排除药物的累加作用。综上分析,患者出现的皮肤瘙痒与此4种药物的因果关系均为“可能”。
有研究报道[21-22],药物化学结构中的母核、侧链、特有结构均可成为识别位点,若药物之间有相同或相似的结构,则可能发生交叉过敏反应。而根据识别位点的不同,药物之间的交叉过敏反应也会有差异。对于高敏患者来说,其IgE可识别母核或整个分子结构,可能对多种抗菌药物过敏。对于本案例患者,有青霉素过敏史,头孢菌素类、碳青霉烯类与青霉素类均有β-内酰胺环,两类之间可能发生交叉过敏反应,该患者使用头孢曲松和亚胺培南后均出现皮肤瘙痒,这提示该患者可能发生了交叉过敏。同时该患者使用左氧氟沙星和磺胺甲噁唑后也出现皮肤瘙痒,推测该患者为高敏患者,其IgE可识别药物共有结构及特殊结构,因而对多种抗菌药均有过敏反应。








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: