-
嘧啶类化疗药物在肿瘤治疗中的地位越来越重要,其代表药物5-氟尿嘧啶及其口服前药卡培他滨更受到了广泛关注,体内二氢尿嘧啶脱氢酶(DPD)是此类药物代谢的限速酶之一[1],前瞻性评价DPD的总体活性有利于提高药物疗效及减少患者的毒副反应,对临床具有重要意义。内源性物质尿嘧啶(U)是体内DPD的天然底物,在此酶的催化下生成二氢尿嘧啶(UH2),并最终通过尿液排出体外。测定血浆中U和UH2的含量,并通过(UH2)/(U)比值计算,可从代谢物的角度评价DPD的活性[2]。临床上常用评价DPD酶活性的方法是测定患者的基因表型,DPD的编码基因DPYD序列中包含了多达7 600个多态位点,使得DPD酶的活性在人群中是高度可变的[3]。不同的突变位点及不同位点的组合给临床检测带来了极大的困难。到目前为止,也只有DPYD*2A的多态性被用于临床实践,用来筛选出5-氟尿嘧啶代谢严重不良的患者,避免严重的毒副反应[4]。单一应用基因的多态性来评价DPD酶的活性在临床上存在一定的困难,基因的多态性并不能直接同下游的酶的活性联系起来,两者并没有完全对等的关系。基因需通过转录、翻译和蛋白的修饰之后才能发挥作用。基因多态联合下游代谢物的含量测定更能准确的评价DPD酶的活性[5]。目前常应用液相色谱-串联质谱联用法对人血浆或干燥唾液中U和UH2浓度进行检测[6-11],但所报道的方法均有一些复杂或难以重现。本研究成功的建立了一种灵敏、高效、准确、重现性好,且能同时测定人血浆中U和UH2浓度的UHPLC-MS/MS方法,为体内DPD总体活性提供更客观有效的评价途径。
HTML
-
1290-6460A超高效液相色谱-串联质谱仪,包含G4220A二元泵、G4226A自动进样器、G1316C柱温箱、MassHunter数据处理工作站(美国Agilent);调速涡旋混合器(美国Labnet);SK7200H超声仪(上海科导超声仪器有限公司);BSA124S-CW分析天平(德国赛多利斯);5810R型低温高速离心机、移液器(德国Eppendorf公司)。
-
尿嘧啶、二氢尿嘧啶和氯尿嘧啶(内标)对照品(纯度>99%,大连美仑生物有限公司);乙酸铵(美国赛默飞世尔科技);甲醇、乙腈、乙酸乙酯、异丙醇(色谱纯,德国默克公司);屈臣氏蒸馏水(广州屈臣氏食品饮料有限公司);牛血清白蛋白(BSA)(上海博光生物科技有限公司);生理盐水(长征医院药学部自制)。
-
色谱柱为Agilent poroshell 120 SB-Aq-柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,2.7 μm),流动相为5 mmol/L乙酸铵水溶液(A)和乙腈(B),流速为0.3 ml/min,梯度洗脱:0~0.3 min,100% A;0.3~1.0 min,100%~10% A;1.0~2.5 min,10% A;柱温为30 ℃,洗脱时间2.5 min,进样量5 μl。
-
采用ESI离子源,多重反应监测(MRM)进行一/二级质谱分析,用于定量分析的检测离子为:U[M+H]+ m/z 113.0→40.1,检测模式为正离子模式;UH2[M+H]+ m/z 115.0→55.1,检测模式为正离子模式;氯尿嘧啶(IS)[M-H]- m/z 145.0→42.1,检测模式为负离子模式。雾化温度为300 ℃,雾化气压力为40 psi,干燥气流速为10 L/min,鞘气温度300 ℃,鞘气流速12 L/min,解离电压为4 000 V。
-
选取8名血浆样品指标正常的成年人,于当日清晨8时空腹状态下静脉采血3 ml, EDTA-3K管抗凝,离心后分离上层血浆, 于−80 ℃冰箱冻存。
-
取100 μl样本,加10 μg/ml氯尿嘧啶(IS)10 μl,加乙酸乙酯3 ml,涡旋5 min,1710×g离心10 min,取上层有机相2.7 ml,45 ℃氮气挥干仪挥干,用10%甲醇溶液100 μl复溶,涡旋1 min,取上清液进样分析。
-
用含有3 %牛血清白蛋白作为空白基质代替血浆配置标准曲线样品。取100 μg/ml的尿嘧啶和二氢尿嘧啶各100 μl,加800 μl水,制成10 μg/ml标准混合液,置于−20 ℃备用。取10 μg/ml标准混合液适量,用3 %牛血清白蛋白稀释制成10、20、50、100、200、500、1000、1500 ng/ml系列浓度样品, 然后按照上述“1.6”项下样品的处理方法配制。
1.1. 仪器与耗材
1.2. 药品与试剂
1.3. 色谱分离条件
1.4. 质谱分离条件
1.5. 样本采集
1.6. 样本预处理
1.7. 标准溶液配制
-
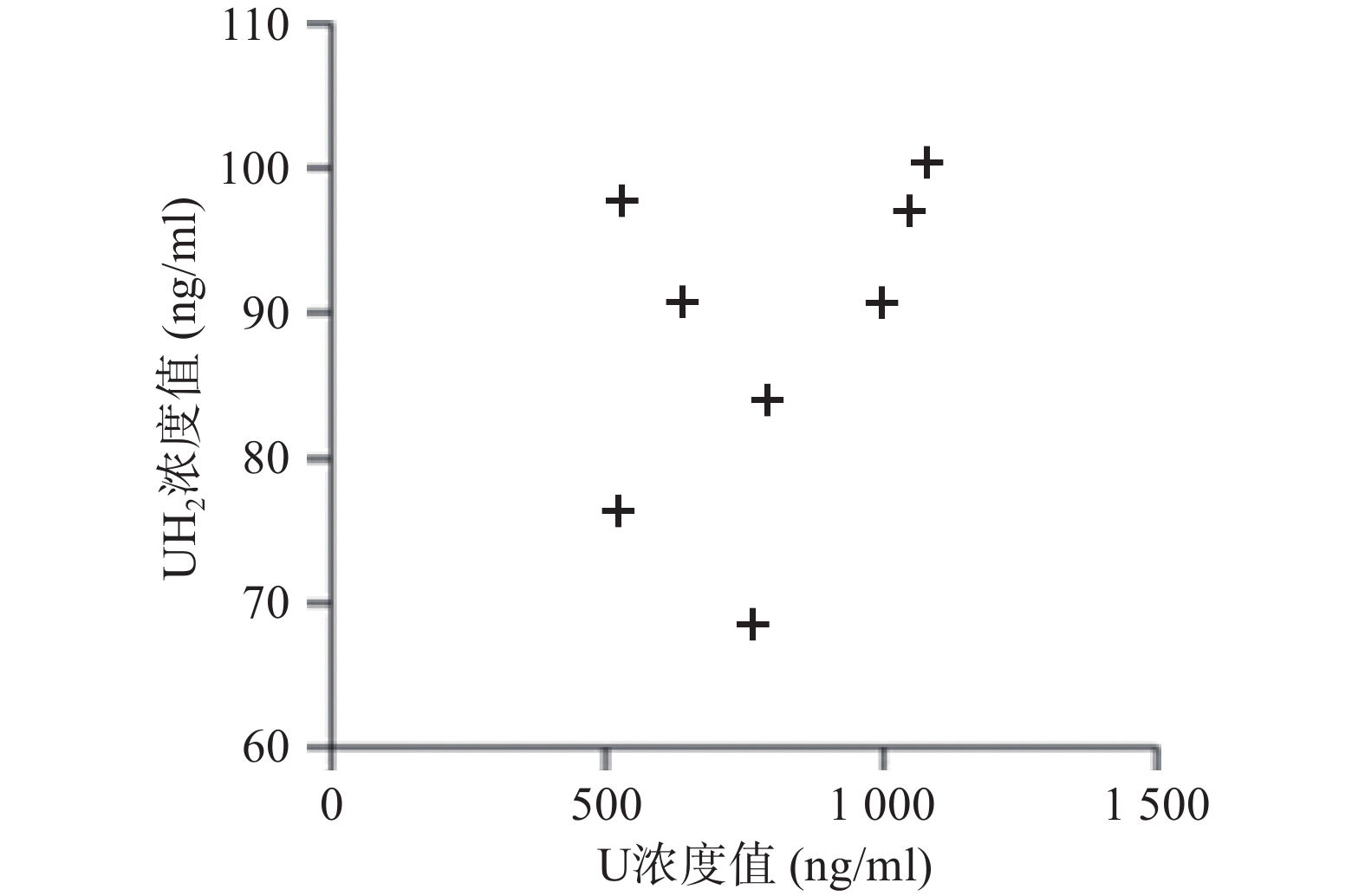
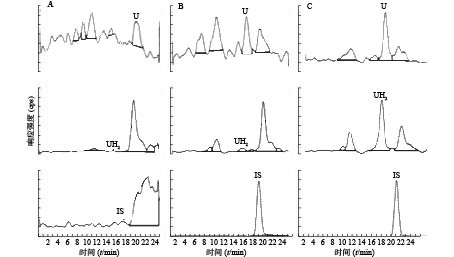
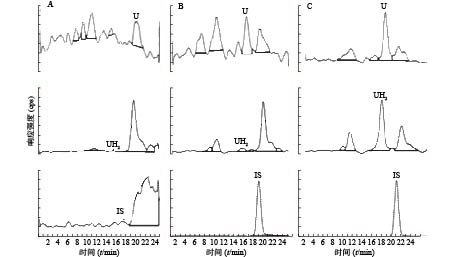
U和UH2的出峰时间以及峰型良好,代替血浆经过前处理后,对待测组分的测定没有干扰,内标对分析物的测定也没有干扰,且能很好分离,结果见图1。
-
U和UH2的线性范围是10.0~1 500.0 ng/ml,以空白BAS中U和UH2的浓度为横坐标(X),U和UH2与内标化合物氯尿嘧啶的峰面积比为纵坐标(Y),进行最小二乘法加权(权重系数为1/χ2),U和UH2的线性回归方程分别是Y=0.27X+0.0022、Y=0.58X+0.0380,r均>0.990,表明线性关系良好。
-
取定量下限、低、中、高标准添加血浆样本按照前处理方法进行处理,每个浓度样品平行制备5份进行分析,连续3 d重复操作,根据当天的标准曲线计算当天实测样本浓度,计算样本在低、中和高浓度下的日内、日间精密度和准确度,结果显示,精密度和准确度的偏差均在15%左右。准确度相对偏差在20%范围内时,最低定量下限精密度偏差不大于20%,结果见表1。
分析物 标示浓度 (ng/ml) 日内 日间 测定浓度 (ng/ml) 精密度(CV%) 准确性(RE%) 测定浓度 (ng/ml) 精密度(CV%) 准确性(RE%) 尿嘧啶 10 10.2±0.38 3.74 2.58 10.12±0.78 7.70 1.18 20 20.63±1.21 5.87 3.15 19.97±1.35 6.74 −0.16 500 529.73±4.64 0.88 5.95 484.32±35.72 7.37 −3.12 1000 1093.33±25.10 2.30 9.33 1098.25±25.16 2.29 9.82 二氢尿嘧啶 10 10.32±0.71 6.86 3.18 10.28±0.65 6.37 2.77 20 19.98±2.19 10.95 −0.12 19.86±1.85 9.31 −0.72 500 517.51±10.69 2.07 3.50 515.66±10.36 2.01 3.13 1000 1079.83±17.91 1.66 7.98 1080.11±24.50 2.27 8.01 -
取低、高2个浓度的样本进行基质效应和提取回收率考察,结果显示,U、UH2及内标氯尿嘧啶的基质效应和提取回收率良好,结果均较稳定,结果见表2。
分析物 标识浓度(ng/ml) 基质效应 提取回收率 平均基质效应 CV(%) 平均回收率 CV(%) 尿嘧啶 1000 101.00 6.15 94.98 9.01 20 99.99 3.63 100.01 7.64 二氢尿嘧啶 1000 85.72 2.07 106.47 1.58 20 93.58 4.53 99.54 9.77 -
考察低、高2个浓度的血浆样品经历3次冷冻与解冻循环的稳定性、血浆样品在室温(25 ºC)放置6 h后经样品处理后稳定性和血浆样品经样品处理后室温放置24 h的稳定性,结果显示,3次冻融、6 h室温(25 ºC)条件下和24 h放置自动进样器中的稳定性均符合要求,结果见表3。
分析物 冻融3次 室温放置6 h 置自动进样器24 h 低 高 低 高 低 高 尿嘧啶 100.71 98.34 93.49 106.60 108.20 107.99 二氢尿嘧啶 92.67 92.64 93.61 107.26 106.97 107.15 -
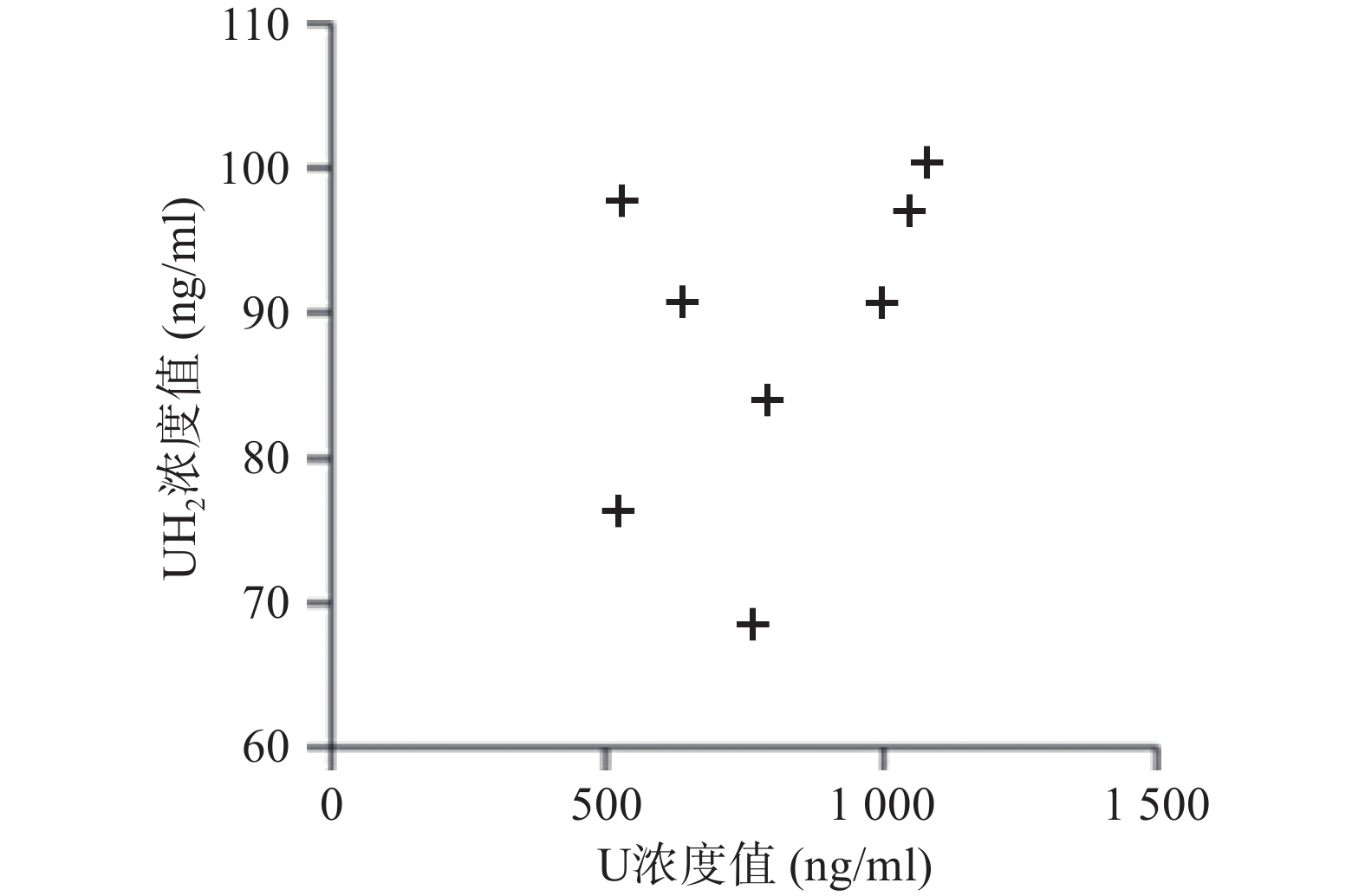
应用本研究所建立的方法,对8名健康成人的血浆样本测定分析,在样本实测过程中, 同时插入已知浓度的随行质控样本(QC样本), 随时监控样本测定的准确度。U和 UH2 浓度测定结果见图2。
2.1. 专属性考察
2.2. 标准曲线和线性范围
2.3. 精密度和准确度
2.4. 基质效应和提取回收率
2.5. 样品稳定性
2.6. 样本检测
-
U和UH2是人体内常见的两种物质,且同核酸的代谢密切相关,由于U和UH2均为人体内源性物质,故不能采用人源的基质进行方法学的开发及验证,通过查阅资料,选择了不含U和UH2的3%牛血清蛋白作为基质进行方法学的开发[12]。也有文献报道采用去除U和UH2的人源血浆基质进行方法学实验[9],但基质的来源较珍贵,不适合方法的普及,所以选用3%牛血清蛋白作为替代基质。
-
U因其特殊的化学性质,在大部分的色谱柱上均没有保留。U和UH2的LogP值分别为−0.707和−0.840,有较强的亲水性,决定了其不保留的性质。在定量方法的开发过程中,先后采用了Agilent Zorbax SB-C18色谱柱,Agilent Zorbax Eclipse-C18色谱柱,Waters Atlantis T3色谱柱,Waters Xselect色谱柱,Waters Xbridge等色谱柱来进行条件摸索,但上述色谱柱对U和UH2均没有保留。最后,采用Agilent Zorbax SB-Aq对U和UH2进行定量分析,该色谱柱对强极性的化合物有较好的保留效果,同时,兼容100%的起始流动相也对保留产生了良好的结果。
-
本研究还分别考察了几种常见的处理方法,包括甲醇和乙腈的蛋白沉淀、Waters Oasis HLB萃取板的固相萃取以及乙酸乙酯,甲基叔丁基醚,二氯甲烷/三氯甲烷,环己烷进行的液液萃取,结果发现乙酸乙酯对U和UH2的萃取效果较好,同时,还分别考察了5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%的异丙醇、乙酸乙酯溶液对U和UH2的萃取效果,结果发现,单纯的乙酸乙酯对待测化合物具有较好的提取效率。提取回收率均高于90%,且RSD<10%。另外对3%牛血清蛋白的基质效应进行了考察,结果发现平均基质效应在85%~101%之间,RSD<7%,说明该前处理方法对于基质的清除较为彻底,测定结果稳定,没有明显的基质干扰。
本研究虽重在方法开发,收集的样本数量较少,但从测定的U和UH2浓度分布来看DPD对内源性U的代谢存在个体差异,建议临床应用5-氟尿嘧啶及其卡培他滨筛查DPD总体活性[12-13],后续可进一步扩大样本数量进行深入研究。
3.1. 空白基质的选择
3.2. 色谱柱的选择
3.3. 样本预处理的优化
-
本实验建立了一种快速,稳定,高灵敏度的UHPLC-MS/MS方法,可用于测定人体内源性物质U和UH2的含量,从代谢物的角度评价DPD酶的活性,从而协助临床医生制定化疗药物5-氟尿嘧啶及其口服前药卡培他滨合理的用量,以较低的毒副反应获得最大的临床疗效。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: