-
松科(Pinaceae)植物马尾松(Pinusmassoniana Lamb.)主要产于江苏、安徽、河南、陕西及长江中下游各省区,资源丰富[1]。松叶“味苦,温;暖,无毒”,具有祛风燥湿、杀虫、止痒之功用。水煎、浸酒以外用或内服[2]用于治风湿痿痹、跌打损伤、湿疮、疥癣、慢性气管炎等症以及预防感冒、流脑。文献报道马尾松叶中的主要化学成分为挥发油、黄酮、多糖、木脂素和树脂等,现代药理研究表明马尾松叶提取物具有抗氧化、抗衰老、抑菌等多方面活性[3-15]。
近年来由于抗生素的滥用、器官移植、免疫抑制剂以及HIV患者的增多,深部真菌感染发病率逐年上升,其中白念珠菌是最主要的致病菌。氮唑类药物氟康唑是临床上首选的抗白念珠菌(Candida albicans)感染药物。但是长期和重复给药导致白念珠菌对氟康唑耐药越来越强。目前联合用药是恢复耐药真菌对治疗药物的敏感度,提高耐药菌对氟康唑的敏感性,治疗深部耐药菌感染的一种有效的治疗途径。从天然活性成分中寻找与现有的抗真菌药物联合发挥协同作用的小分子化合物是近年来的研究方向之一[16-20]。本文选用接近“传统水煎或浸酒法”的传统中药提取方法,用乙醇加热提取后,石油醚再萃取的方法得到马尾松叶低极性部位,通过测定马尾松叶低极性部位协同氟康唑抗耐药白念珠菌的MIC80值,同时,采用气相色谱-质谱的方法对低极性部位的化学成分进行分析鉴定,初步探究其联合氟康唑的体外抗真菌活性。
HTML
-
Thermo Trace GC Ultra气相色谱、Thermo DSQ Ⅱ质谱、Xcalibur工作站(美国赛默飞世尔公司);马尾松叶(浙江东阳市,经海军军医大学黄宝康教授鉴定为马尾松Pinusmassoniana Lamb.);所有试剂均为分析纯;水为重蒸水;载气为高纯氦气。
氟康唑注射液(上海信谊金朱药业有限公司);黄芩素(上海历鼎生物技术有限公司);二甲基亚砜(DMSO,中国医药集团上海化学试剂公司);白念珠菌103(Candida albicans103,海军军医大学长海医院真菌室提供)。
-
取干燥马尾松叶,粉碎,称取二份,每份50.0 g,分别用150 ml石油醚和80%乙醇加热回流提取1h,滤过;滤渣再分别用150 ml石油醚和80%乙醇加热回流提取1 h,滤过。分别合并两次滤液,滤液用旋转蒸发仪减压浓缩,回收溶剂,得石油醚提取物(简称醚提取物)2.5 g和80%乙醇提取物(简称醇提取物)8.0 g。取干燥后的醇提取物5.0 g,加入水100 ml混溶,获得混悬液。混悬液用50 ml石油醚萃取3次,合并浓缩石油醚萃取液,获得石油醚浸膏(简称醚浸膏)即马尾松叶低极性部位0.8 g。取125 mg醚浸膏,置于100 ml量瓶中,加入80%甲醇,超声、加热使其几近完全溶解,放置、冷却;再加入80%甲醇定容,摇匀、放置;吸取1 ml定容后的浸膏液,微孔滤膜过滤后待测。
-
色谱柱TR - 35MS石英毛细管(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm),程序升温,起始温度40 ℃,保持2 min后以10 ℃/min的速度升至300 ℃并保持5 min;汽化温度250 ℃,进样量1 μl;分流比10∶1。载气为高纯氦气,流速1.0 ml/min。离子源:EI源;离子源温度为250 ℃;电子能量:70 eV;扫描范围:50~650 m/z。
1.1. 试剂与设备
1.2. 马尾松叶低极性部位的制备
1.3. 色谱-质谱条件
-
菌株选用临床分离耐药菌株白念珠菌103(氟康唑的MIC80>128.0 μg/ml)。采用美国临床和实验室标准协会(CLSI)提出的RPMI1640 培养基微量稀释法,取无菌96孔板,于每排1号孔加RPMI1640液体培养基100 μl作空白对照;3~12号孔各加新鲜配制的菌液100 μl,菌液浓度范围为(1~5)×103cfu/ml;2号孔分别加菌液160 μl和受试药物溶液40 μl;12号孔不含药物,只加菌液100 μl作阳性生长对照。2~11号孔进行倍比稀释,使各孔的最终药物(醚提取物、醇提取物和醚浸膏)浓度分别为250.0、125.0、62.5、31.25、15.63、7.81、3.91、1.95、0.98和0.49 μg/ml,对照品黄芩素浓度分别为128.0、64.0、32.0、16.0、8.0、4.0、2.0、1.0、0.5和0.25 μg/ml,各孔中DMSO含量均低于1%,氟康唑溶液的终浓度为8.0 μg/ml。96孔板于30℃恒温培养箱培养24 h后取出,读取受试药物与氟康唑(8.0 μg/ml)联用时的MIC80值。微量稀释法测试结果见表1。
化合物 MIC80 联合抑菌浓度
分数指数
(FICI)联合作用 单用(μg/ml) 与氟康唑联用(μg/ml)* 醚提取物 >250.0 >250.0 1.031 无关 醇提取物 >250.0 7.81 0.047 协同 醚浸膏 >250.0 31.25 0.094 协同 黄芩素 16.0 4.0 0.281 协同 氟康唑 >128.0 − − − *与8 μg/ml 氟康唑联合使用 协同药效的判定采用联合抑菌浓度分数指数(FICI),即联用抑菌时每种药物所需最低抑菌浓度(MIC)与单用这种药物抑菌时所需MIC的比值的和。当FICI≤0.5时,两种药物的相互作用效果被定义为具有协同作用;当FICI>0.5时,认为两种药物无相互作用。
-
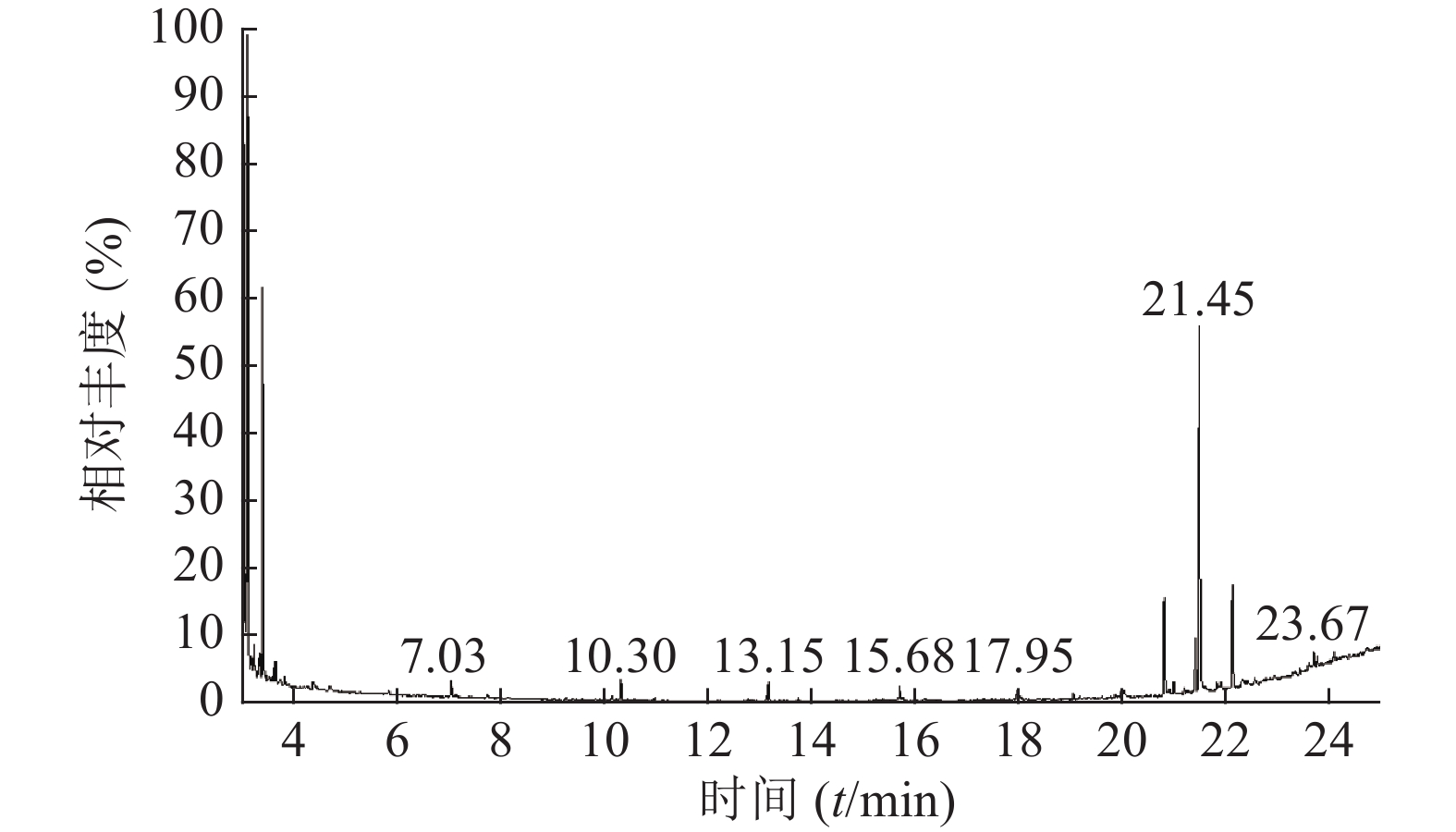
按“1.3”项下实验条件对马尾松叶低极性部位进行分析,25 min得到马尾松叶低极性化学成分的总离子流图(图1)。共检测出30个峰,通过检索NIST08光谱数据库,按60%以上匹配率(SI和RSI均大于600,最大值1 000),并结合质谱裂解规律确定其化学成分。运用峰面积归一法通过Xcalibur化学工作站数据处理系统,测得各个化学成分在石油醚部位中的质量百分数。
2.1. 抑菌实验方法
2.2. 色谱-质谱分析方法
-
由表1可见,各受试药物单用时,对照品黄芩素的MIC80为16.0 μg/ml,提示了其具有一定的抗菌活性,其他的化合物的MIC80均大于250 μg/ml。各受试药物与氟康唑(8.0 μg/ml)联用后,对照品黄芩素、醇提取物及醚浸膏的MIC80降至4.0~31.25 μg/ml,相应的FICI值均小于0.5,显示黄芩素、醇提取物、醚浸膏分别与氟康唑联用对耐药白念珠菌均具有协同活性,但醇提取物和醚浸膏的协同活性不及对照品黄芩素,醚浸膏协同活性小于醇提取物。醚提取物单用及与氟康唑联用的MIC80均大于250 μg/ml,FICI大于0.5,显示其单用及与氟康唑联用均没有协同氟康唑抗耐药白念珠菌活性。
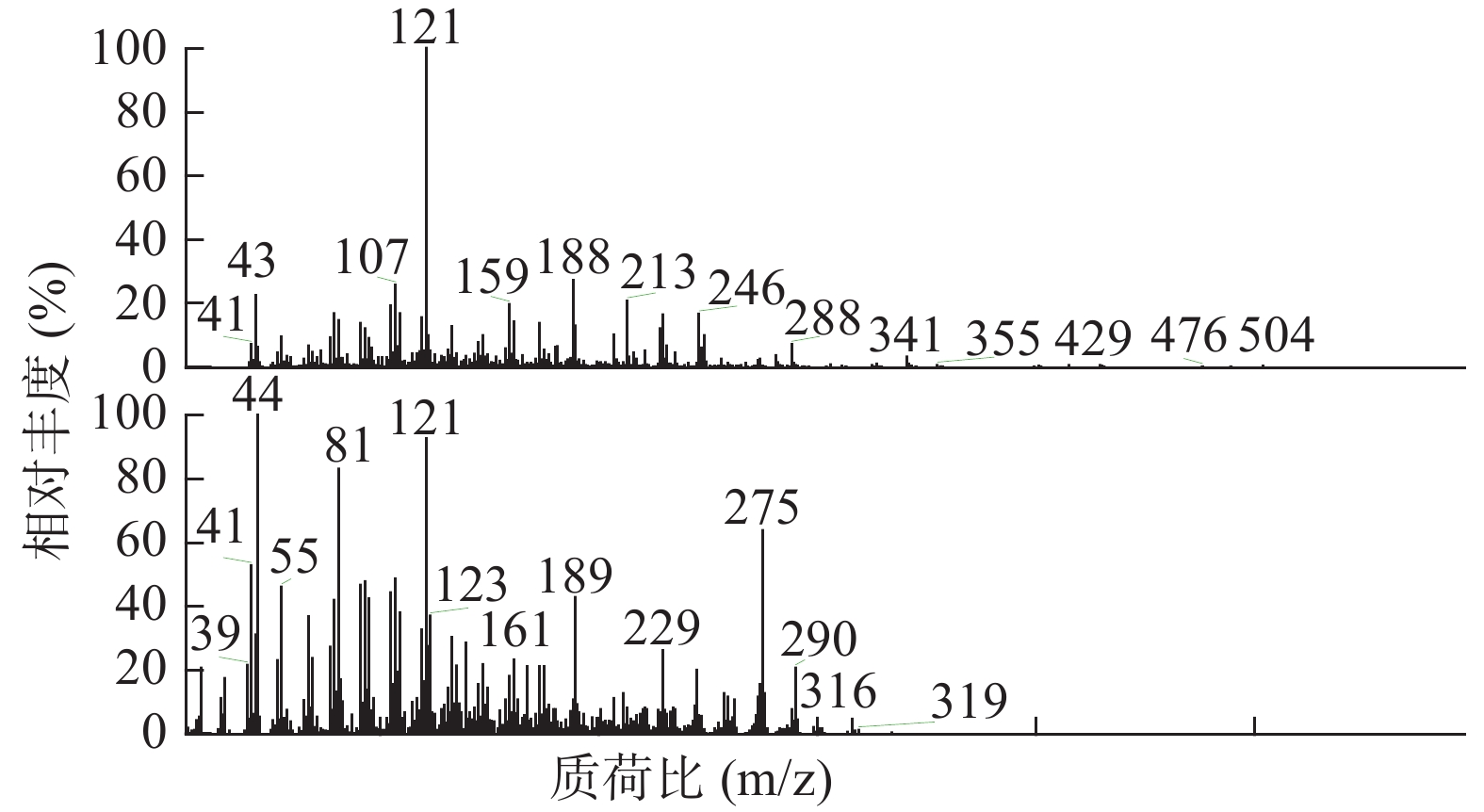
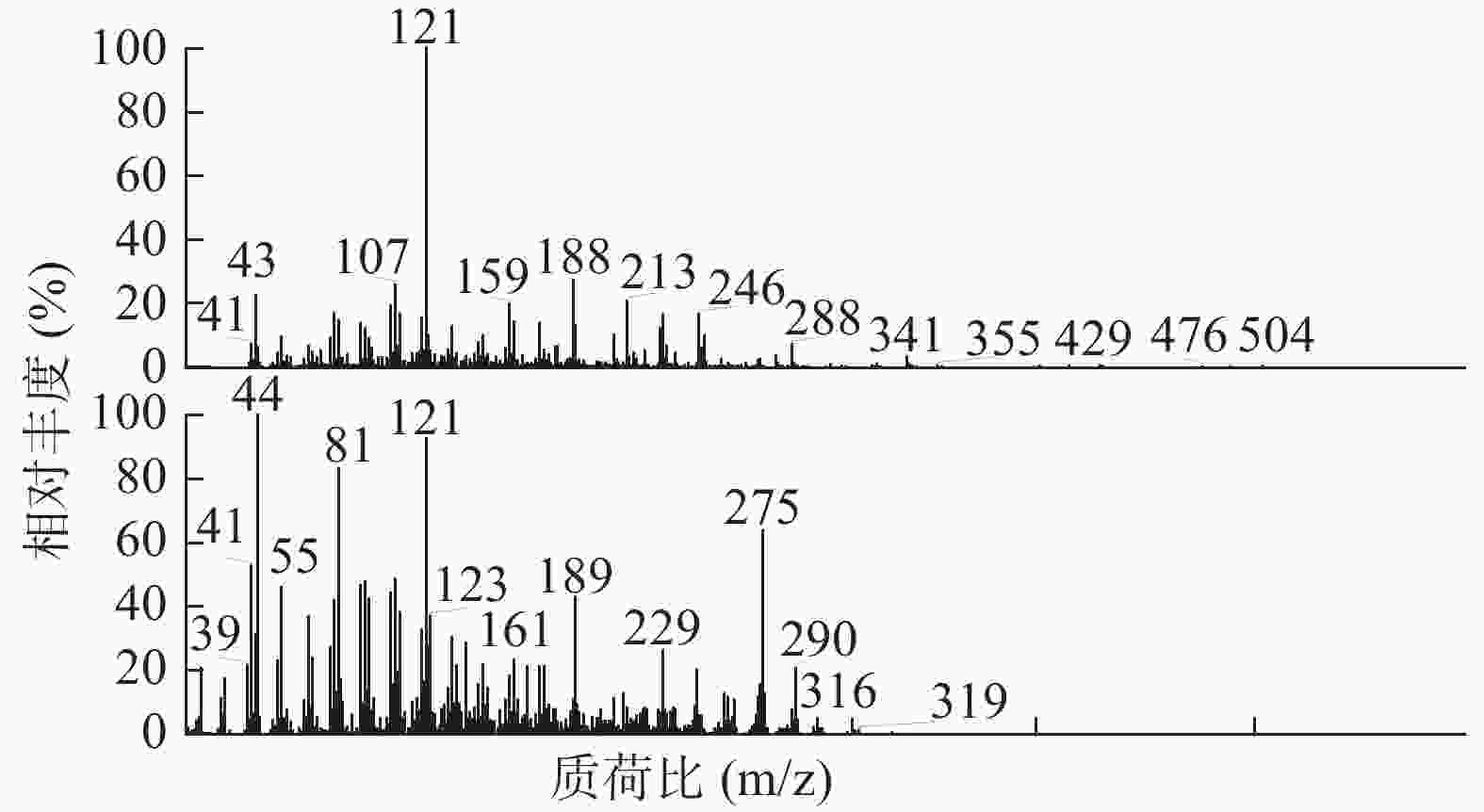
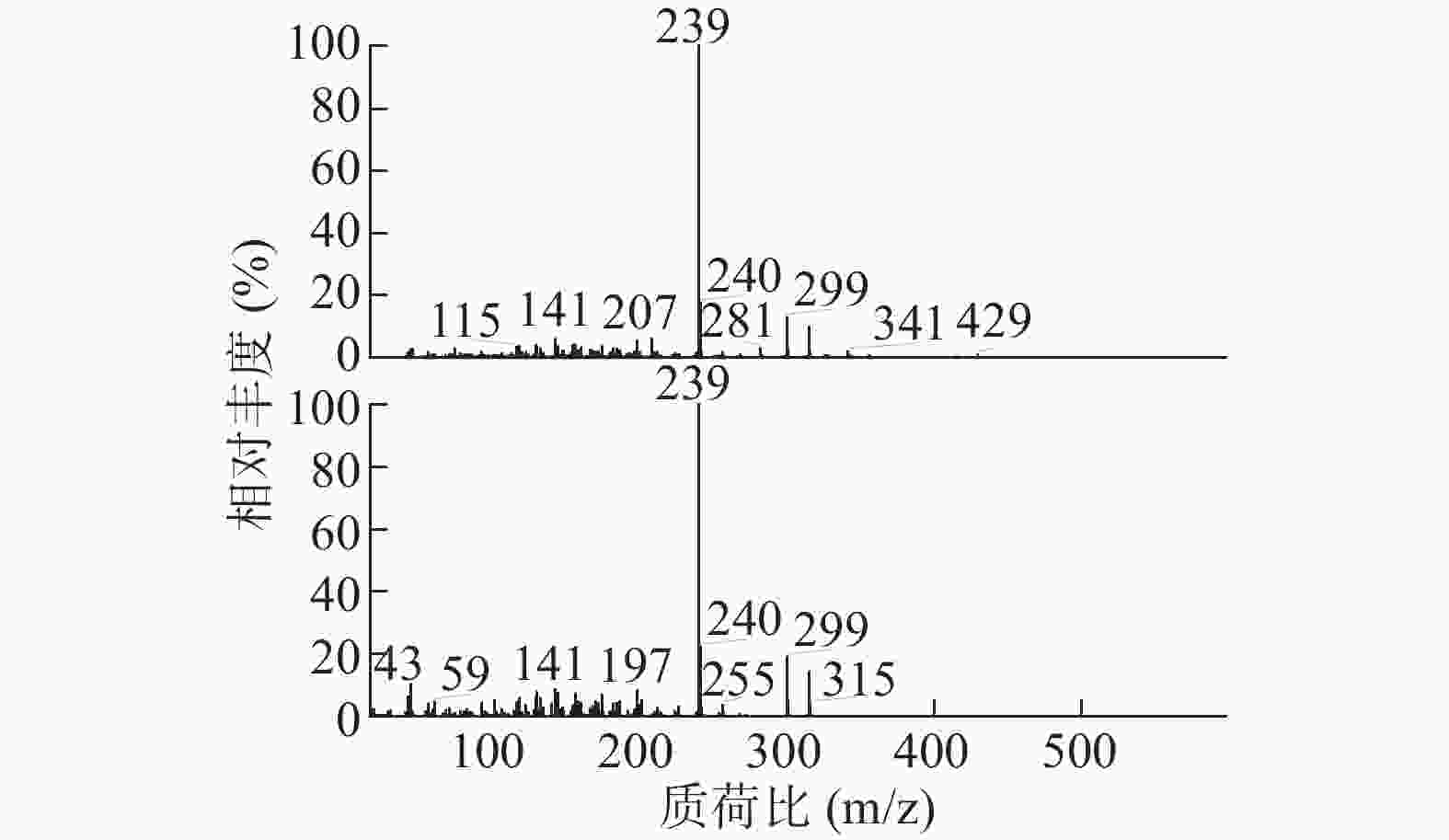
如表2所示,本次GC-MS检测出30种成分,鉴定出17个化合物。统计出本次所测马尾松叶的低极性化学成分中含有烷烃4个(6.1%),甾烷类5个(4%),脂肪酸1个(0.75%),二萜5个(53.99%),其他峰均提示为聚硅氧烷(35.16%),其中含量较高的化学成分是:玛瑙酸(8.38%,见图2)、脱氢枞酸甲酯(8.41%,见图3)。
序号 保留时间(min) 相似度SI值 相似度RSI值 化合物 含量(%) 1 10.30 821 850 正十五烷 1.52 2 13.15 797 840 2,6,11,15-四甲基-十六烷 2.23 3 15.68 781 822 2,6,10-三甲基-十四烷 1.37 4 17.95 709 727 3-乙基-5-(2-乙基丁基)-十八烷 0.98 5 19.03 661 770 泪柏醚 0.68 6 19.96 641 684 1-单烯丙基甘油三甲基硅醚 0.75 7 20.00 639 670 3,3-亚乙基二氧基-5β-胆甾烷 1.00 8 20.78 688 700 玛瑙酸/贝壳杉萘甲酸 8.38 9 20.88 621 690 N-[24-氧代-3α-(三甲基硅氧基)-5β-胆安-24-基]甘氨酸甲酯 0.51 10 20.96 636 739 24, 25-二羟基维生素D3 / 24R, 25-二羟胆钙化醇 1.11 11 21.16 609 633 17-乙酰氧基-4,4,10,13-四甲基-7-氧代-2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氢-1H-环戊烷(a)菲-3-基,乙酸 0.61 12 21.38 777 915 隐青霉酸甲酯 / 山莨菪碱酸甲酯 /海松酸甲酯 4.62 13 21.45 626 636 3-羟基-2,5,5,8a-四甲基-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-八氢萘-1-羧酸,2-三甲基硅乙基酯 31.90 14 21.79 645 662 3,11,18-三乙酰氧基-3,19:14,15-二环氧孕烷-20-酮 0.77 15 21.87 625 765 1,1,3,3,5,5,7,7,9,9,11,11,13,13,15,15-十六甲基八硅氧烷 1.50 16 22.09 841 889 脱氢枞酸甲酯 8.41 17 22.29 676 788 1,1,3,3,5,5,7,7,9,9,11,11,13,13-十四甲基七硅氧烷 1.30
-
近年来研究发现马尾松叶提取物具有抗真菌活性:马尾松叶石油醚、氯仿等溶剂的提取物以及不同比例的乙醇水提取物可以抑制曲霉、青霉、啤酒酵母的生长;马尾松叶乙醇提取物对枯萎病、灰霉菌有显著的抑菌活性;马尾松叶水提物对白色念珠菌有较弱抑菌性[21-25]。但马尾松叶提取物对氟康唑耐药白念珠菌的协同抗菌活性未见报道。
本研究发现,马尾松叶的醇提取物和醚浸膏单独使用时均不及黄芩素,没有抗耐药白念珠菌活性,但联用氟康唑(8 μg/ml)后,醇提取物和醚浸膏均表现出协同活性,醇提取物的活性更好,而醚提取物无论是单独使用还是联用氟康唑都没有抗耐药白念珠菌活性。醚浸膏与醚提取物相比,提取方法的改变,导致了提取物抑菌效果的有无。醚浸膏的活性应该源于乙醇加热提取获得的更丰富、含量更高的化学成分,尽管醚浸膏的主要成分也是低极性成分,但与醚提取物相比无论在含量和组成上均应不同。醚提取物含有更丰富的挥发油等低极性成分,但是可能缺少了一些重要的活性抗真菌成分,导致其没有协同抗耐药真菌作用。我们进一步对活性部位醚浸膏进行了GC-MS化学成分分析,结果表明,其化学成分与文献报道的采用水蒸气和超临界CO2提取法获得的马尾松叶挥发油成分相比差异大。活性部位醚浸膏中化合物结构类型和数量比文献报道的直接提取的挥发油少,且没有以蒎烯、莰烯为主的单萜和以石竹烯等为主的倍半萜,仅有烷烃类少量化合物重合[26-31]。活性部位醚浸膏采用了乙醇加热提取后,再经石油醚萃取得到,加热提取可能导致了蒎烯、莰烯、石竹烯等低沸点萜类化合物的丢失,但分子量更大的二萜类化学成分含量升高(53.99%)。二萜类化学成分中脱氢枞酸甲酯、海松酸甲酯是主要化学成分,两者也是松香酸的主要成分。有文献报道松香酸具有抗赤霉菌、灰霉菌等多种抗真菌活性[32-35]。因此,醚浸膏中的二萜类化合物可能是其协同氟康唑抗耐药白念珠菌作用的重要活性成分,值得进一步研究。此外,Zuzana研究发现云杉提取物中的β-谷甾醇抑制微生物生长,同时低浓度的脱氢枞酸甲酯破坏细胞壁,两者相互协同可能是云杉提取物对青霉菌、链格孢菌、米根霉的抑菌活性的关键[36]。本研究获得的醚浸膏中也含有丰富的树脂酸(13.03%)和甾烷(4%)。树脂酸和甾烷的协同可能也是醚浸膏具有协同氟康唑抗耐药白念珠菌活性的原因,这一点也值得进一步研究。
综上所述,本文首次报道了马尾松叶乙醇提取物以及马尾松叶低极性部位具有协同氟康唑抗耐药白念珠菌作用,并首次对马尾松叶低极性部位进行了GC-MS分析,鉴别的化合物除了烷烃、脂肪酸、脱氢枞酸甲酯外其它11种成分都是首次从该植物中发现,丰富了马尾松叶的化学成分。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: