-
马齿苋(Portulaca oleracea L.)是一种药食两用植物,味酸、性寒,具有清热解毒、凉血消肿之功效。现代药理研究证实其有抗衰老、降血糖、降血脂、抗动脉粥样硬化,以及保肝护肝等方面的药理活性[1-2]。目前对马齿苋保肝护肝的有效成分还不甚了解。本研究进一步明确马齿苋提取物对四氯化碳致小鼠急性肝损伤具有保护作用,并通过超高效液相色谱-四极杆-飞行时间质谱(UPLC-Q-TOF/MS)技术分析马齿苋提取物的主要成分,采用电喷雾电离源正离子模式和负离子模式对色谱流出物进行检测,通过高分辨质谱分析结合相关文献鉴定出苹果酸、柠檬酸、亮氨酸、异亮氨酸、腺苷、琥珀酸、染料木素、酪氨酸、苯丙氨酸等15种主要成分。
-
80只ICR雄性小鼠,体重18~20 g。来源:海军军医大学实验动物中心购买于上海斯莱克实验动物有限公司[生产许可SCXK(沪)2017-005,使用许可SYXK(沪)2017-0004]。
-
马齿苋干药材(上海雷允上中药饮片厂,产品批号:2012110235);CCl4溶液、乙醇、NaOH(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司);橄榄油(益海嘉里食品营销有限公司);甲醇、乙腈(色谱纯,美国默克公司);甲酸(色谱纯,美国Sigma-Aldrich公司);实验用水(屈臣氏蒸馏水);Agilent 1290 Infinity型超高效液相色谱仪、Agilent 6538 UHD、Accurate-Mass Q-TOF/MS(美国安捷伦公司)。
-
马齿苋药材加15倍80%乙醇,煎煮1 h。提取液滤过,滤液减压浓缩至无醇味,加水调节浓度为2 g/ml。以10% NaOH溶液调节pH至中性,记为A液。5000 r/min,离心10 min,上清液记为B液,沉淀记为C液。A、B液分别减压浓缩至半干状态,与C液分别转移至60 ℃真空干燥,粉碎过120目筛,即得马齿苋全草、上清、沉淀提取物。用去离子水分别配制不同浓度的马齿苋提取物混悬液,超声过夜,4 ℃储存,备用。
-
ICR雄性小鼠80只,根据体重随机分为8组,分别为对照组、CCl4急性化学性肝损伤模型组(模型组)、全草提取物低剂量(12.5 mg)组(全草低剂量组)、全草提取物高剂量(50 mg)组(全草高剂量组)、上清提取物低剂量(12.5 mg)组(上清低剂量组)、上清提取物高剂量(50 mg)组(上清高剂量组)、沉淀提取物低剂量(12.5 mg)组(沉淀低剂量组)和沉淀提取物高剂量(50 mg)组(沉淀高剂量组)。适应性喂养一周后,对照组和模型组小鼠分别经口灌胃0.5 ml去离子水,3种提取物的低剂量组和高剂量组小鼠分别以0.5 ml对应浓度的马齿苋提取物混悬液连续灌胃7 d,并监测体重。7 d后,模型组、马齿苋提取物干预组小鼠按照3 ml/(kg·BW)分别腹腔注射10% CCl4橄榄油溶液,对照组小鼠注射等量橄榄油。实验期禁食不禁水,16 h后,腹腔注射10%水合氯醛麻醉,摘眼球取血,将血液2 000 r/min离心15 min得血清,于长海医院检验科检测谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、谷草转氨酶(AST),ELISA试剂盒检测血清IL-6。
-
首先,检索马齿苋及其相关种属药材化学成分相关的文献,根据文献报道,收集马齿苋中可能的化学成分信息;其次,通过Agilent提供的“Formula-Database-Generator”软件建立马齿苋中已知化学成分的数据库。
-
取马齿苋适量,加入5 ml 80%甲醇超声15 min,13000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液供超高效液相色谱仪检测用。
-
色谱柱:Waters XSELECTTM HSS T3(100 mm×2.1 mm,2.5 μm);流动相:0.1%甲酸(A)和0.1%甲酸乙腈(B)流动相体系。梯度洗脱程序如下:0~2 min,5%B;2~13 min,5%→95%B;13~15 min,95%B;分析时间15 min;流速为0.4 ml/min,进样量为3 μl。
-
离子源:电喷雾离子化(ESI)正、负离子模式;雾化气压力:50 psi;干燥气流速:11 L/min;干燥气温度:350 ºC;毛细管电压:4000V(+)/3500V(−);去簇电压:120 V;Mass扫描范围:m/z 50~1000。
-
采用SPSS 20.0统计分析软件处理,结果以均值 ± 标准差(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )表示,多组间比较采用单向方差分析检验,组间两两比较,方差齐时采用LSD法,方差不齐时采用Dunnett's T3法,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。 -
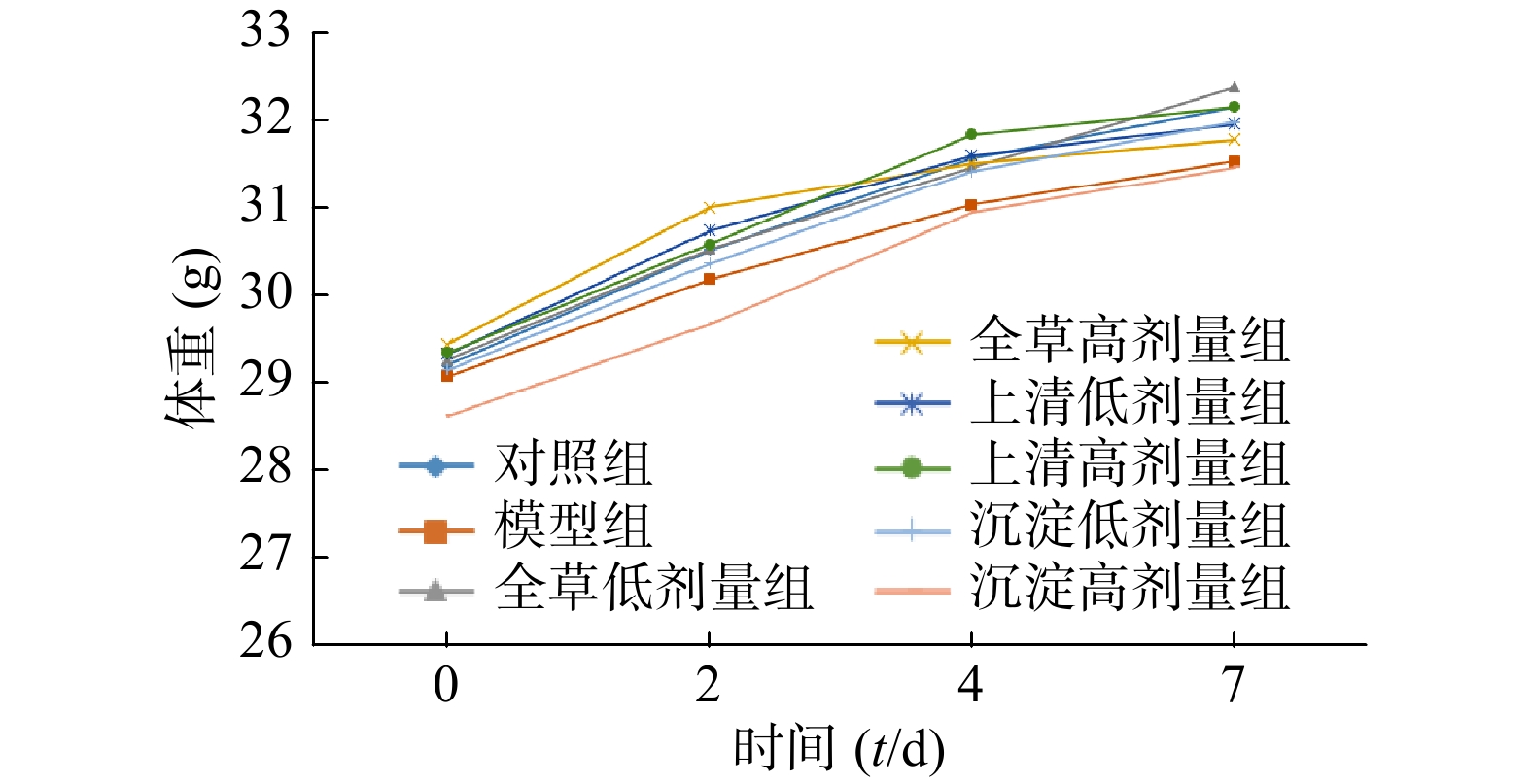
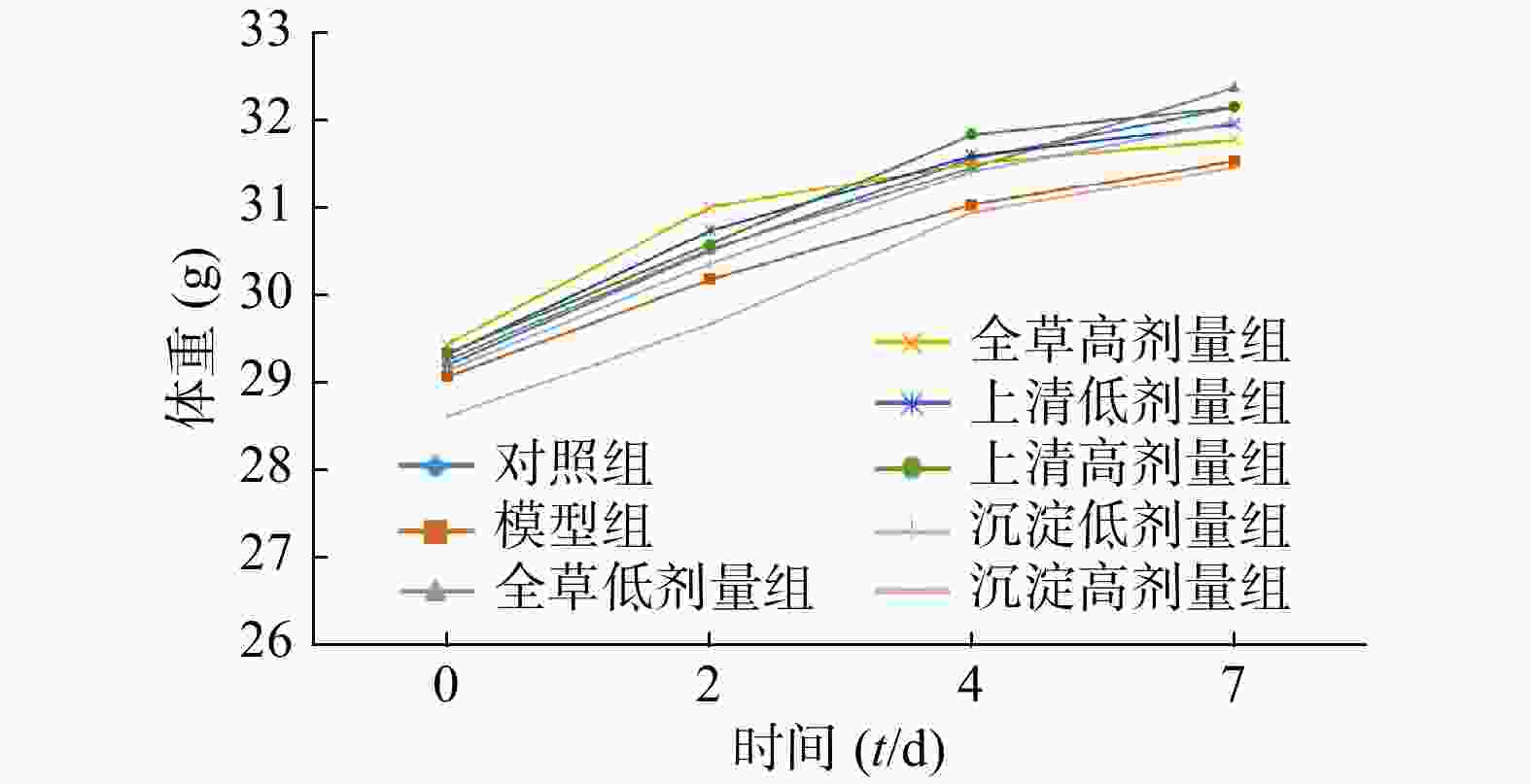
各组小鼠体重均呈上升趋势,各组体重差异无统计学意义(见图1),初步说明马齿苋提取物对小鼠生长没有明显的毒副作用。
-
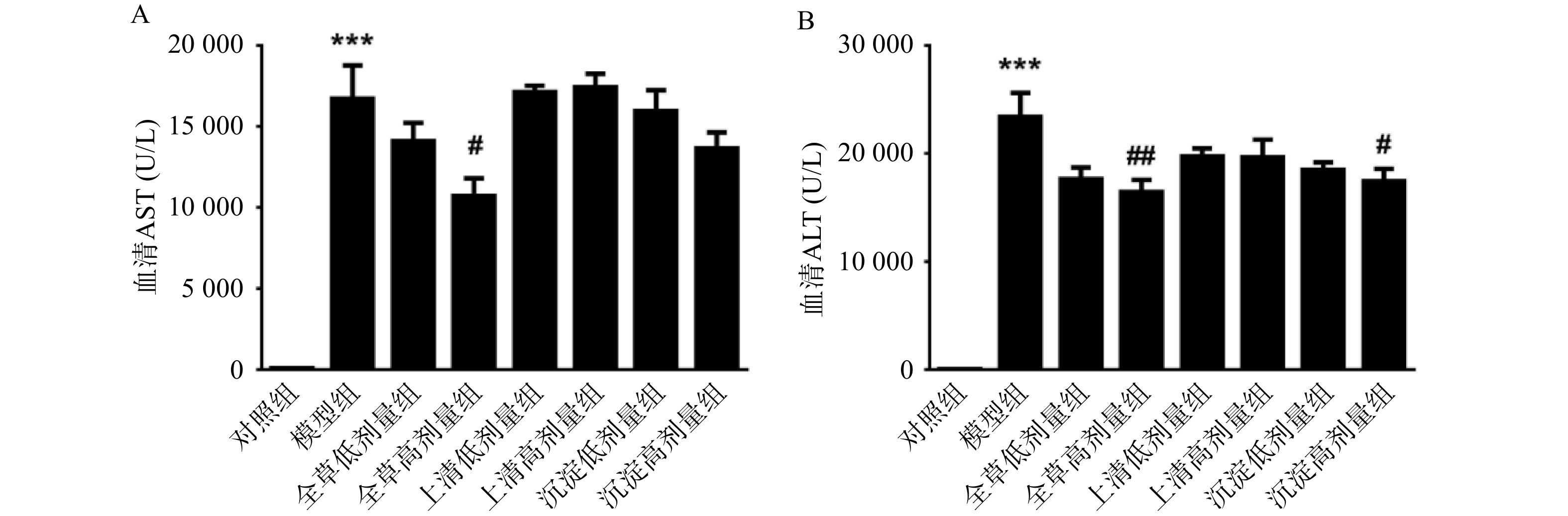
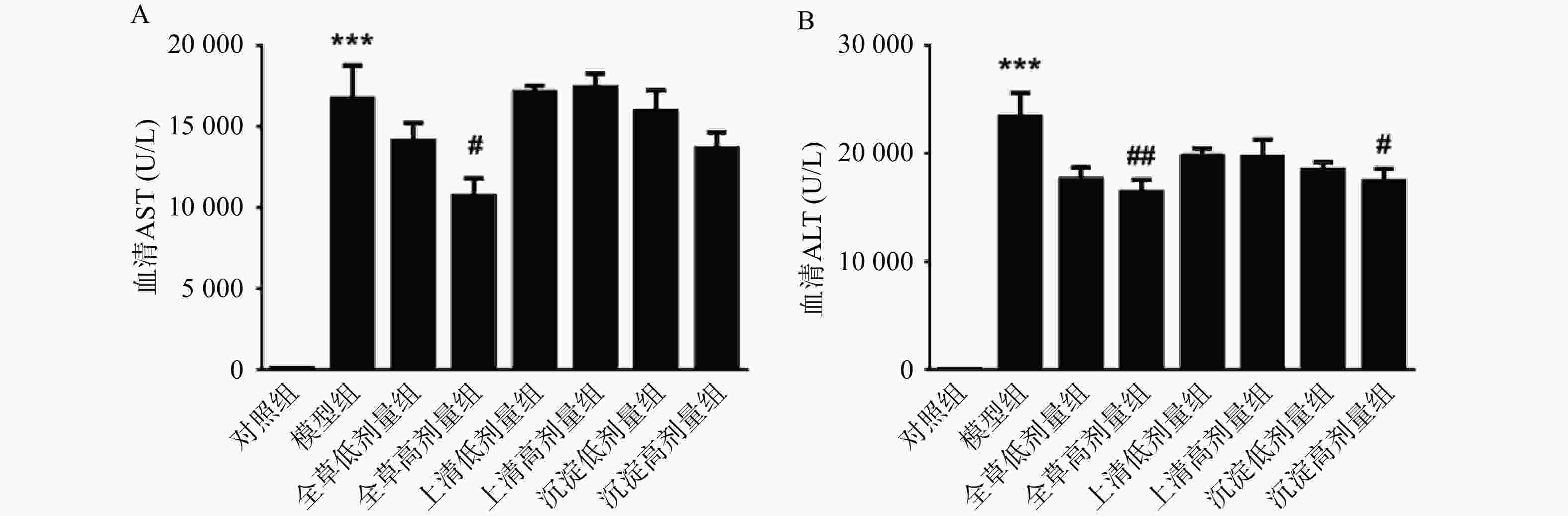
由图2可见,与对照组相比,CCl4急性化学性肝损伤模型组血清ALT、AST水平显著升高(P<0.001),说明造模成功。与模型组相比,全草高剂量组小鼠血清AST、ALT水平显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01);沉淀高剂量组小鼠血清ALT显著降低(P<0.05),AST水平有降低趋势但不具有统计学意义。
-
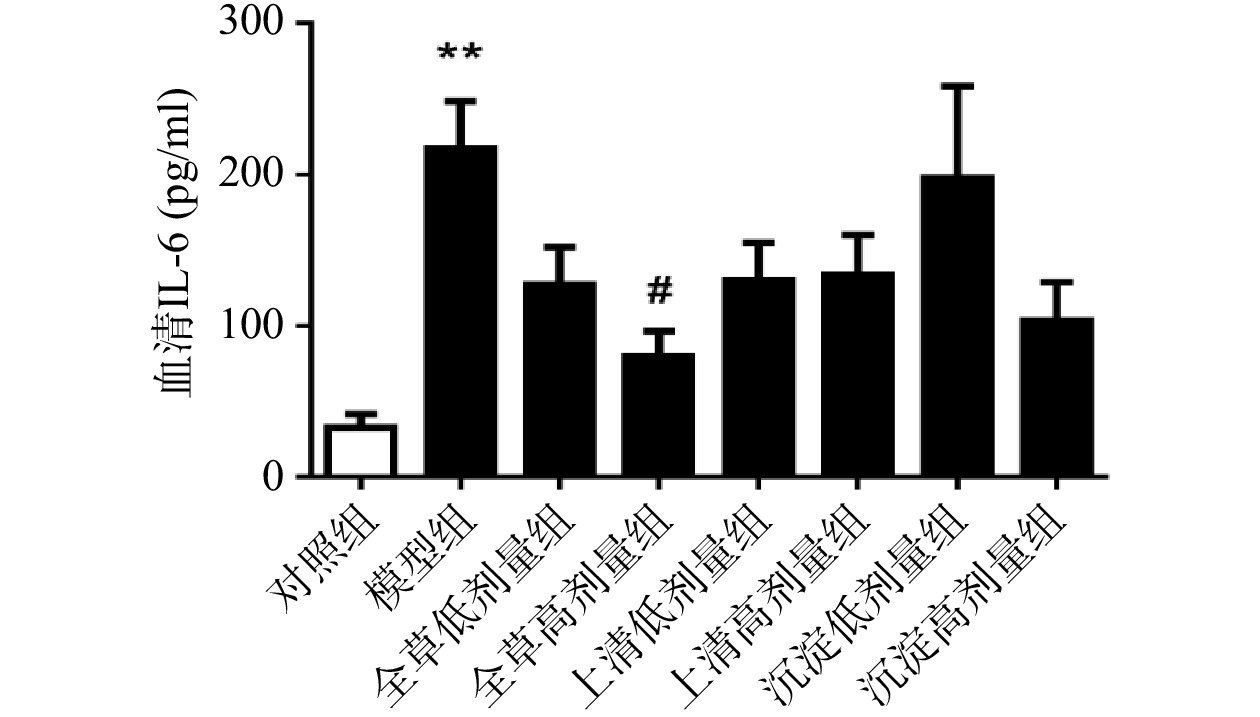
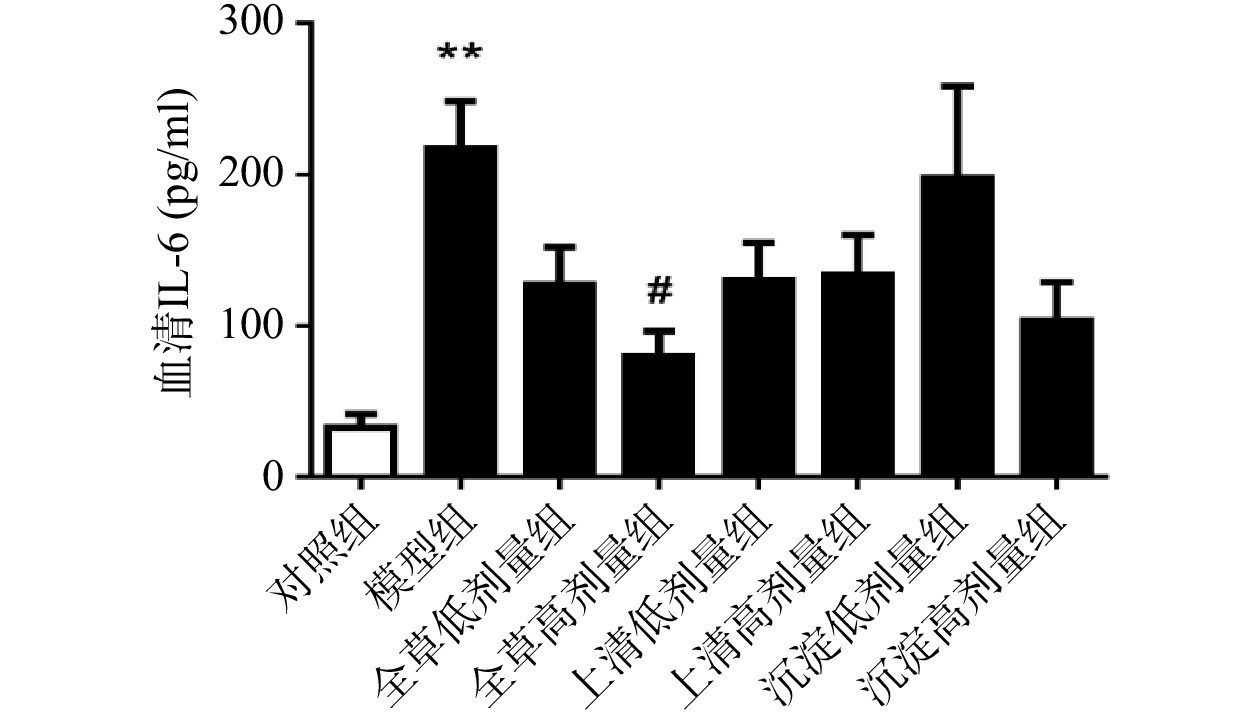
由图3可见,与对照组相比,CCl4急性化学性肝损伤模型组血清IL-6水平显著升高(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,全草高剂量组小鼠血清IL-6水平显著降低(P<0.05),沉淀高剂量组小鼠血清IL-6水平有降低趋势但不具有统计学意义。
-
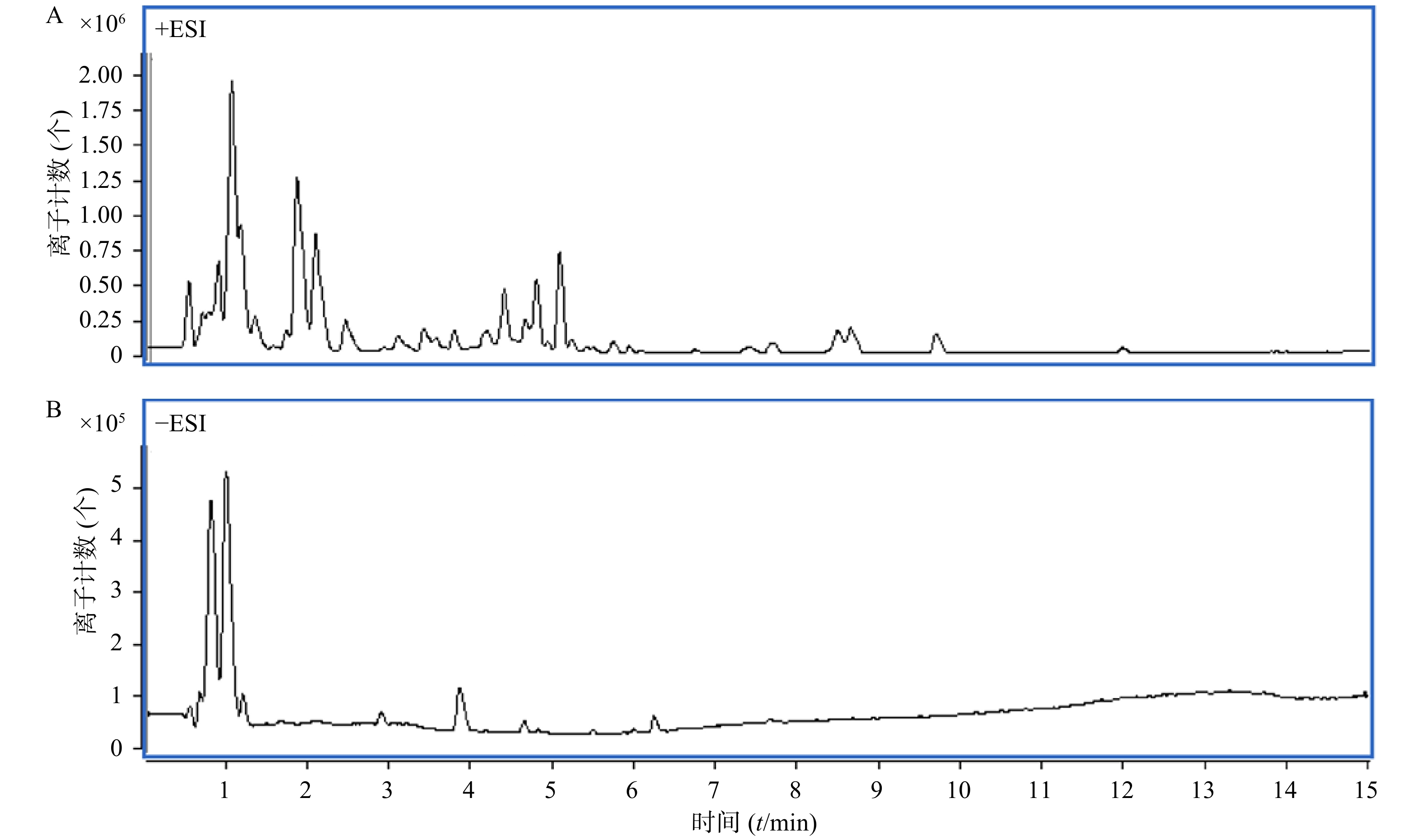
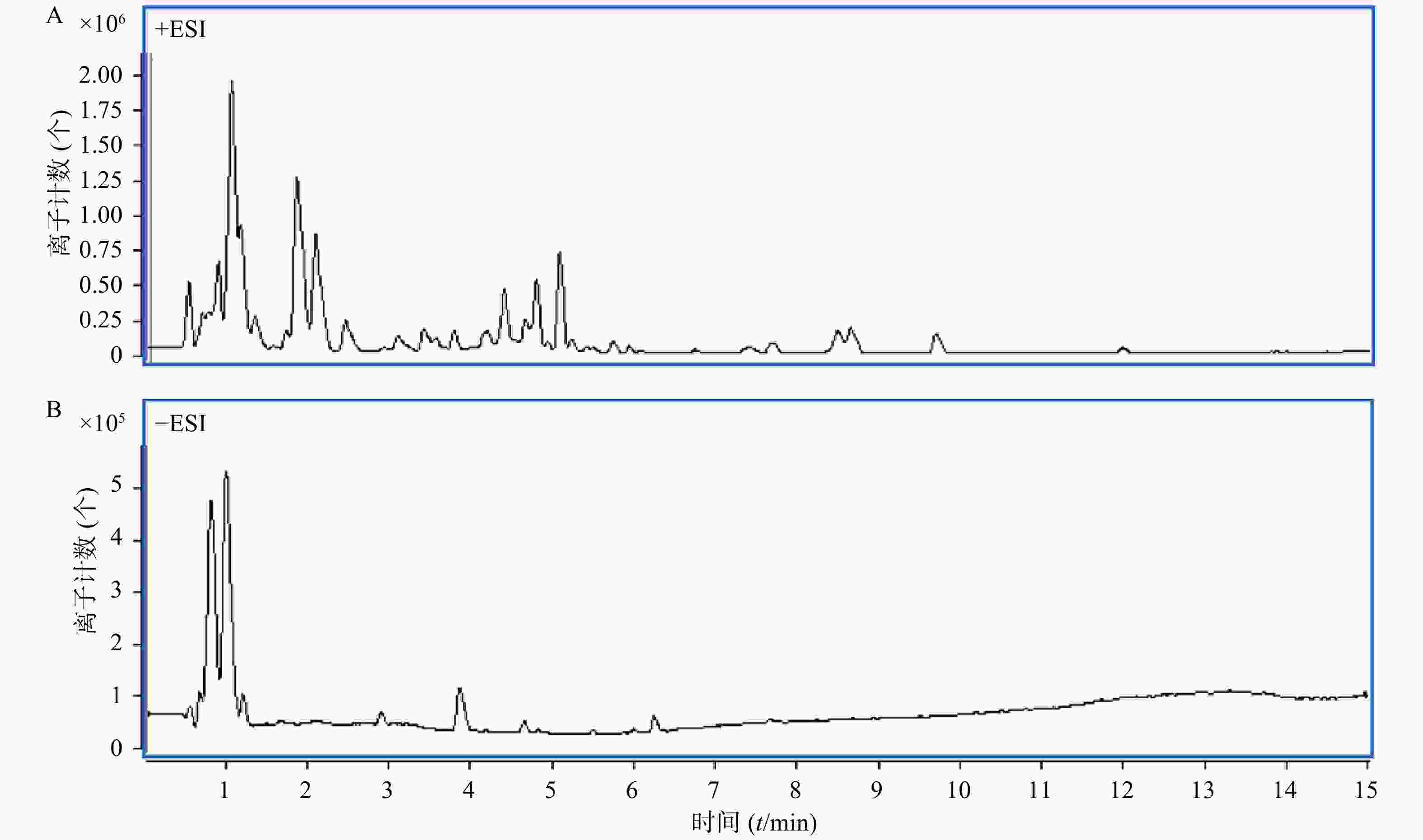
取马齿苋样品溶液,按照“1.4.3”项下进样分析,全扫描总离子流图如图4所示。
-
将“Formula-Database-Generator”软件建立的马齿苋已知化学成分的数据库导入“Masshunter Qualitative Analysis”软件系统,依据数据库对马齿苋提取物总离子流质谱图进行鉴定和确证,将检索到的化学成分信息按照保留时间、质荷比、加合离子情况等进行分类整理。并将化合物按其质荷比在原质谱数据中进行反向提取,对提取到的质谱信息进行质量准确度的验证并根据同位素峰比例等信息进行元素组成分析。推测出15种化合物为马齿苋80%乙醇提取物的主要成分,按照保留时间顺序依次为:苹果酸、柠檬酸、亮氨酸、异亮氨酸、腺苷、琥珀酸、染料木素、酪氨酸、苯丙氨酸、佛手苷内酯、金莲花碱、6,7-二羟基香豆素、芳樟醇、金色酰胺醇/橙黄胡椒酰胺、金色酰胺醇酯/咸南藤酰胺乙酸酯(见表1),另外还有多糖、黄酮等化学成分。
时间
(tR/min)分子式 离子峰归属 质荷比 偏差 化合物 理论值 实测值 0.847 C4H6O5 [M-H]- 133.0142 133.0147 −0.49 苹果酸[3-4] 1.019 C6H8O7 [M-H]- 191.0197 191.0198 −0.62 柠檬酸[3] 1.097 C6H13NO2 [M+H]+ 132.1019 132.1014 3.91 亮氨酸[5] 1.203 C6H13NO2 [M+H]+ 132.1019 132.1015 2.72 异亮氨酸[4] 1.293 C10H13N5O4 [M+H]+ 268.104 268.1047 −2.55 腺苷[6] 1.305 C4H6O4 [M-H]- 117.0193 117.0197 −3.23 琥珀酸[3] 1.555 C15H10O5 [M+NH4]+ 288.0866 288.0867 −0.21 染料木素[7] 2.053 C9H11NO3 [M+NH4]+ 199.1077 199.1074 1.69 酪氨酸[5] 2.168 C9H11NO2 [M+H]+ 166.0863 166.0859 2.03 苯丙氨酸[5] 3.567 C12H8O4 [M+NH4]+ 234.0761 234.0765 −1.81 佛手苷内酯[8] 4.638 C12H13NO3 [M+H]+ 220.0968 220.0967 0.61 金莲花碱[9] 4.929 C9H6O4 [M-H]- 177.0193 177.0192 0.98 6,7-二羟基香豆素[5] 7.301 C10H18O [M+COOH]- 199.034 199.1342 −1.21 芳樟醇[10] 8.646 C25H26N2O3 [M+H]+ 403.2016 403.2029 −3.12 金色酰胺醇/橙黄胡椒酰胺[9] 9.685 C27H28N2O4 [M+H]+ 445.2122 445.2128 −1.34 金色酰胺醇酯/咸南藤酰胺乙酸酯[9] -
马齿苋是一年生肉质草本植物,是常用的药食两用植物,已被列入“中国卫生部药食两用名单”,具有清热解毒、凉血消肿等功效,特别是在保肝抗炎方面具有较好的功效[2]。
CCl4是经典的化学性肝损伤动物模型的肝毒物,可破坏肝细胞膜,从而使胞浆内可溶性酶如ALT、AST等渗入血液中,并最终导致各种类型的肝细胞病变,甚至坏死[11]。正常肝内转氨酶的含量约为血中的100倍,1%的肝特异性细胞坏死即可使血清酶活性增加1倍。因此,转氨酶是肝细胞受损的敏感标志[12]。因而,血清中的ALT、AST水平的高低可以敏感地反映肝脏细胞膜的受损程度。
本研究以CCl4诱导的急性肝损伤小鼠模型为研究对象,考察了马齿苋乙醇提取物的保肝抗炎作用,结果显示,高剂量马齿苋全草提取物可以显著降低CCl4导致的肝损伤和炎症。马齿苋沉淀提取物能够显著降低CCl4诱导的急性肝损伤小鼠血清ALT水平,对血清AST和IL-6水平有降低趋势但不具有统计学意义。马齿苋沉淀提取物对降低CCl4导致的肝损伤和炎症有一定效果,但效果不及全草提取物,说明马齿苋上清提取物可能也含有效成分,与沉淀提取物共同发挥保肝作用。因此,从本研究可以看出,马齿苋沉淀及上清中均存在保肝抗炎的有效成分,且沉淀提取物可能起主要作用,但马齿苋发挥保肝抗炎作用是沉淀与上清提取物中有效成分共同发挥的。中药是世界四大传统医药体系中理论最完整、医疗实践最丰富、疗效最确切的传统医药体系[13]。因为中药的复杂性,中药的药效机制研究一直是个难点。有学者归因于中药功效相关的多成分、多靶点、多环节之间组成的一个相互协同与制约的复杂网络[14]。笔者认为,与马齿苋全草提取物相比,沉淀提取物的抗炎保肝作用较差的原因可能是马齿苋的抗炎保肝作用是通过多成分、多靶点、多环节的相互协同作用实现的,且需维持一定的药物浓度才能显著性的发挥抗炎保肝作用。
为了进一步分析马齿苋抗炎保肝作用的有效成分,本研究通过UPLC-Q-TOF/MS技术对该全草提取物进行分析和鉴定,初步发现约有15种主要化学成分。已研究发现,苹果酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸为小分子有机酸,具有抗肿瘤、抑菌、抗血栓、抗病毒等作用[15];亮氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、苯丙氨酸等氨基酸为营养增补剂;6,7-二羟基香豆素等化合物是自然界重要的天然有机化合物,具有抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等多种功效[16]。因而,马齿苋提取物能够发挥抗炎护肝作用可能是由以上主要化学成分共同作用的结果,具体的作用机制有待深入研究。
Protective effect of Portulaca oleracea L. extract on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice and its chemical composition analysis
doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202101001
- Received Date: 2021-01-03
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-11-05
- Publish Date: 2021-11-25
-
Key words:
- purslane /
- extract /
- acute chemical liver injury of CCl4 /
- protection
Abstract:
| Citation: | SHI Wencai, ZHAO Yanyun, ZHENG Xuan. Protective effect of Portulaca oleracea L. extract on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice and its chemical composition analysis[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2021, 39(6): 504-508. doi: 10.12206/j.issn.1006-0111.202101001 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: