-
金线莲Anoectochilus roburghii (Wall.) Lindl,又名金线兰、金蚕、乌人参、金线入骨消等,是一种多年生兰科草本植物[1],主产地为福建。文献报道多糖类、黄酮类、生物碱类、氨基酸类等是金线莲主要化学成分[2]。其中金线莲多糖是其主要药理活性物质,具有降血糖、抗氧化、抗肝损伤、增强免疫功能、抗肿瘤等药用功效[3]。本研究为提高金线莲多糖提取率,采用超声提取的方法,在单因素实验的基础上以响应面法优化其提取工艺。蛋白质的存在往往影响到多糖的活性,蛋白的脱除是多糖提取纯化的一个关键步骤[4],且天然植物中多糖与蛋白质两种高分子成分分子量相近,严重制约了进一步的分析[5],而Sevage试剂法、三氯乙酸(TCA)法、盐法(氯化钙和氯化钠法)、盐酸法等是多糖脱蛋白的常用方法[4-6],为此,笔者对以上方法在金线莲多糖提取中的影响进行了考察,为进一步深入研究金线莲多糖奠定一定的基础。
HTML
-
UV-3200紫外分光光度计(上海美谱达仪器有限公司);AR224CN电子天平(美国奥豪斯仪器常州有限公司);HWS-12型电热恒温水浴锅、电热鼓风干燥箱(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司);SC-04低速离心机(安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司);KQ-500DE型超声波清洗器(昆山市超声仪器有限公司)。
-
福建永泰产金线莲样品经福建中医药大学药学院黄泽豪副教授鉴定为兰科开唇兰属的金线莲Anoectochilus roburghii (Wall.) Lindl。D-水葡萄糖(中国食品药品检定研究院,批号:110833-201506);乙醇(批号:20181208)、苯酚(批号:P815401)、氢氧化钠(批号:20160509)购自上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司;硫酸(批号:1706191)、盐酸(批号:1903301,)、氯化钠(批号:1610141)、氯仿(批号:1803121)购自广东西陇科学股份有限公司;氯化钙(广东光华化学有限公司,批号:20091031);正丁醇(江苏强盛功能化学股份有限公司,批号:20130418);超纯水(实验室制备)。
1.1. 仪器
1.2. 材料
-
取D-葡萄糖50 mg溶于1000 ml的量瓶中,加水定容,得对照品溶液。
-
取金线莲鲜品清洗干净,于60 ℃恒温干燥箱中烘干,打粉,过60目筛,得金线莲干品。取金线莲粉末5 g,以料液比为1:10加水,48 ℃超声提取30 min,超声功率为300 W,超声提取2次;对上述提取液3600 r /min离心15 min,弃去沉淀,即得金线莲原始液。取上述原始液5 ml加4倍体积无水乙醇放置过夜,4000 r/min下离心10 min,沉淀加水溶解,于1000 ml的量瓶中定容,得供试品溶液。
-
按本课题先前研究的“优化的苯酚硫酸法”[7],计算金线莲多糖提取得率。
-
按“2.2”项下的方法,对超声提取工艺中各单因素进行考察:①以超声温度30、40、50、60、70、80 ℃分别进行提取;②以超声功率200、250、300、350、400 W分别进行提取;③用超声分别提取10、20、30、40、50 min;④以1∶5、1∶10、1∶15、1∶20、1∶30的料液比加水;⑤用超声分别提取1、2、3次。
-
在单因素考察的基础上,利用软件Design-Expert.V8.0.6.1中Box-Behnken试验原理,选择对多糖提取率影响较大3个因素料液比(A)、超声提取时间(B)、超声温度(C)为自变量,以多糖提取率(R)为响应值,设计3因素3水平实验。因素与水平设计如表1。
因素 水平 −1 0 1 料液比(A) 5 10 15 超声时间(B) 20 30 40 超声提取温度(C) 40 50 60 -
取5 ml金线莲原始液,用2 mol/L盐酸调节至pH 3,并保持过夜。将该混合物在4000 r/min下离心10 min,弃去沉淀,上清液加入4倍体积无水乙醇放置过夜,4000 r/min下离心10 min,所得沉淀物加水溶解,于1000 ml的量瓶中定容,得脱蛋白供试品溶液。
-
取5 ml金线莲原始液,以2% NaOH溶液将其调至pH 8~9,加热至85 ℃。将CaCl2固体调至5%(50 g/L)的浓度,煮沸30 min,冷却至室温并过滤,用稀盐酸将滤液调至pH 7,加入4倍体积无水乙醇放置过夜,4000 r/min下离心10 min,得多糖沉淀。加水溶解重复上述操作3次,所得沉淀物加水溶解,于1000 ml的量瓶中定容,得脱蛋白供试品溶液。
-
取5 ml金线莲原始液,在沸腾(90 ℃)条件下,用2%NaOH溶液将多糖溶液调节到pH 9~10。加入NaCl固体,浓度调至5%(50 g/L),然后混合煮沸30 min。冷却至室温并过滤,上清液用稀盐酸调至pH 7。添加4倍体积无水乙醇放置过夜沉淀多糖,在4000 r/min下离心10 min,弃上清液得多糖沉淀。加水溶解重复上述操作3次,所得沉淀物加水溶解,于1000 ml的量瓶中定容,得脱蛋白供试品溶液。
-
取5 ml金线莲原始液,加入10% TCA溶液将其调节到pH 3,静置过夜。样品4000 r/min离心10 min,沉淀物丢弃,上清液加4倍体积无水乙醇放置过夜,在4000 r/min下离心10 min,弃去上清液得多糖沉淀。加水溶解重复上述操作3次,所得沉淀物加水溶解,于1000 ml的量瓶中定容,得脱蛋白供试品溶液。
-
取5 ml金线莲原始液,以金线莲水提溶液:正丁醇:氯仿按1:1:4的比例进行除蛋白,振荡器振荡20 min 后,4000 r/min 转速离心 5 min,弃去下层有机相。该过程重复3次,上层水相添加4倍体积无水乙醇放置过夜,在4000 r/min下离心10 min,弃去上清液得多糖沉淀物,所得沉淀物加水溶解,于1000 ml的量瓶中定容,得脱蛋白供试品溶液。
-
以“紫外分光光度法”对蛋白含量进行测定[5],
蛋白质浓度C(mg/ml) = 1.45A280−0.74A260
多糖损失率=[(供试品多糖含量-脱蛋白供试品多糖含量)/供试品多糖含量]×100%
蛋白脱除率=[(供试品蛋白含量-脱蛋白供试品蛋白含量)/供试品蛋白含量]×100%
2.1. 对照品溶液的制备
2.2. 供试品溶液的制备
2.3. 金线莲多糖含量
2.4. 单因素实验
2.5. 响应面法优化超声提取工艺
2.6. 脱蛋白方法的考察
2.6.1. 盐酸法脱蛋白[4,6]
2.6.2. NaOH-CaCl2法脱蛋白[5]
2.6.3. NaOH-NaCl法脱蛋白[5]
2.6.4. 三氯乙酸(TCA)法脱蛋白[5]
2.6.5. Sevage法脱蛋白[6]
2.7. 多糖损失率与蛋白脱除率
-
参考相关文献,按“2.2” 项下使用不同提取方法制得对应的供试品,比较多糖得率,结果如表2。
实验结果表明,超声提取和酶提取均能获得较高的多糖提取率,由于酶价格昂贵,超声提取操作简便,且能获得高提取率,故选择超声提取进行下一步研究。
-
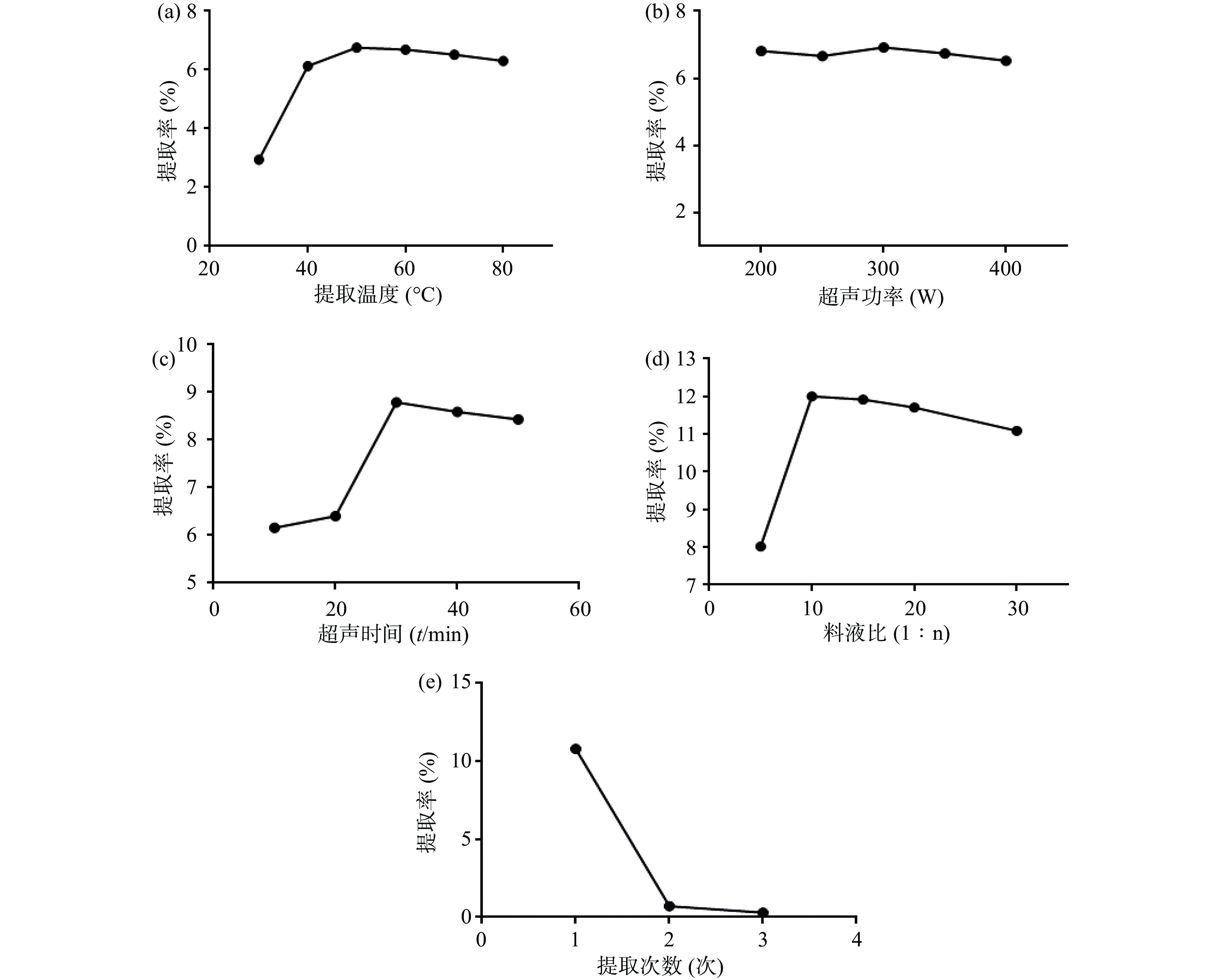
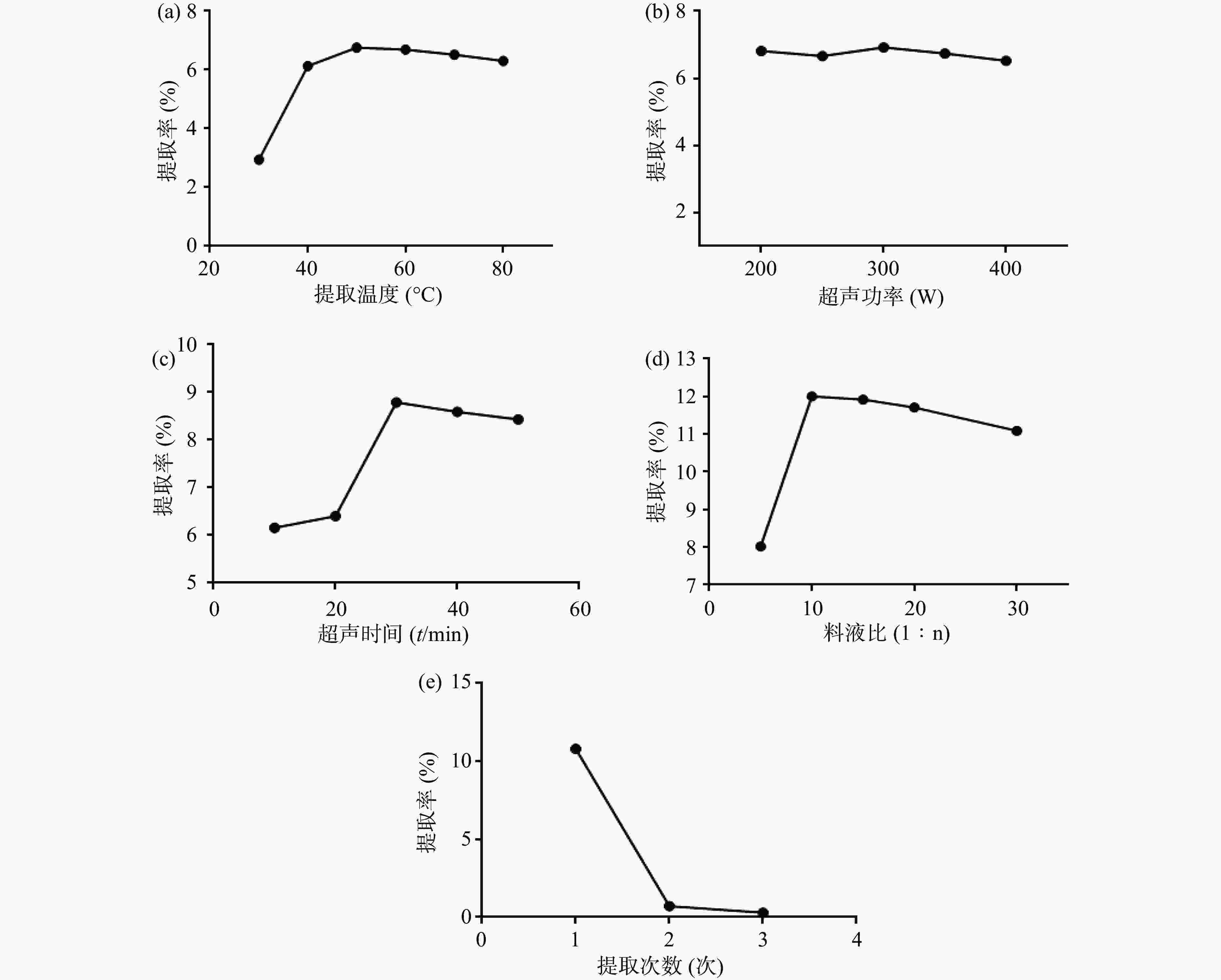
如图1所示:①随着提取温度的增加,提取得率逐渐增加,在50 ℃提取得率达到最大值,后随着温度的增加提取率逐渐下降并趋于稳定,故初步确定提取温度40~60℃作为进一步响应面考察设计的水平;②在超声功率为300 W时多糖提取率最高,实验结果显示,随着超声功率的增加,多糖提取率先上升后下降,但影响相对较小,故选定功率为300 W进行下一步分析;③以超声提取30 min,提取率最高,故初步确定超声时间20~40 min作为进一步响应面考察设计的水平;④料液比为1∶10时,多糖提取率最高,随着料液比的增加,提取率稍有下降且趋于平稳,故初步确定料液比1∶5~1∶15作为进一步响应面考察设计的水平;⑤随着提取次数的增加,提取率逐渐降低,提取3次后,多糖已基本提取完全,考虑实际操作及原料等,选定提取2次进行下一步分析。
-
在单因素考察的基础上,利用软件Design-Expert. V 8.0.6.1中Box-Behnken试验原理,设计3因素3水平实验。响应值设计方案及结果见表3,方差分析见表4。对数据分析后得到回归方程为:
实验号 A B C 多糖提取率(%) 1 −1.000 0.000 −1.000 12.22 2 1.000 0.000 −1.000 10.16 3 0.000 1.000 −1.000 13.13 4 0.000 0.000 0.000 13.03 5 1.000 0.000 1.000 12.98 6 0.000 −1.000 −1.000 10.86 7 −1.000 −1.000 0.000 11.19 8 0.000 0.000 0.000 13.21 9 0.000 1.000 1.000 12.28 10 0.000 −1.000 1.000 12.25 11 −1.000 1.000 0.000 11.88 12 1.000 −1.000 0.000 11.08 13 0.000 0.000 0.000 13.12 14 0.000 0.000 0.000 12.85 15 −1.000 0.000 1.000 10.83 16 1.000 1.000 0.000 12.11 17 0.000 0.000 0.000 13.21 来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 模型 15.41 9 1.71 51.68 < 0.0001 A 5.513×10−3 1 5.513×10−3 0.17 0.6955 B 2.02 1 2.02 60.98 0.0001 C 0.49 1 0.49 14.64 0.0065 AB 0.029 1 0.029 0.87 0.3814 AC 4.43 1 4.43 133.76 < 0.0001 BC 1.25 1 1.25 37.87 0.0005 A2 4.65 1 4.65 140.33 < 0.0001 B2 0.92 1 0.92 27.87 0.0011 C2 0.99 1 0.99 29.99 0.0009 残差 0.23 7 0.033 失拟项 0.14 3 0.047 2.07 0.2463 纯误性 0.091 4 0.023 总离性 15.64 16 多糖提取率(R)=13.08+0.026A+0.50B+0.25C+0.085AB+1.05AC−0.56BC−1.05A2−0.47B2−0.49C2。
由表3知,回归模型有很好的显著性(P< 0.0001),说明二项式方程拟合良好,模型二项式方程失拟项不显著(P=0.2463),说明未知因素对实验干扰较小,拟合的相关系数r=0.9926,模型可信度良好,故可运用此模型实现超声提取金线莲多糖最佳工艺的分析探究。
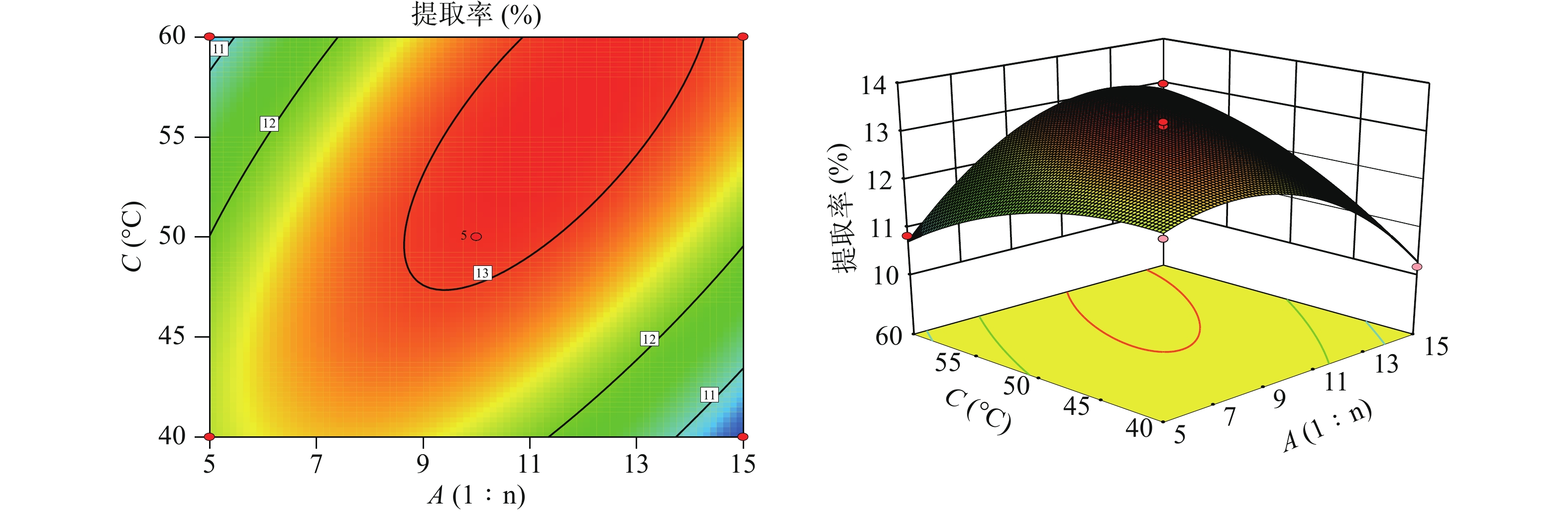
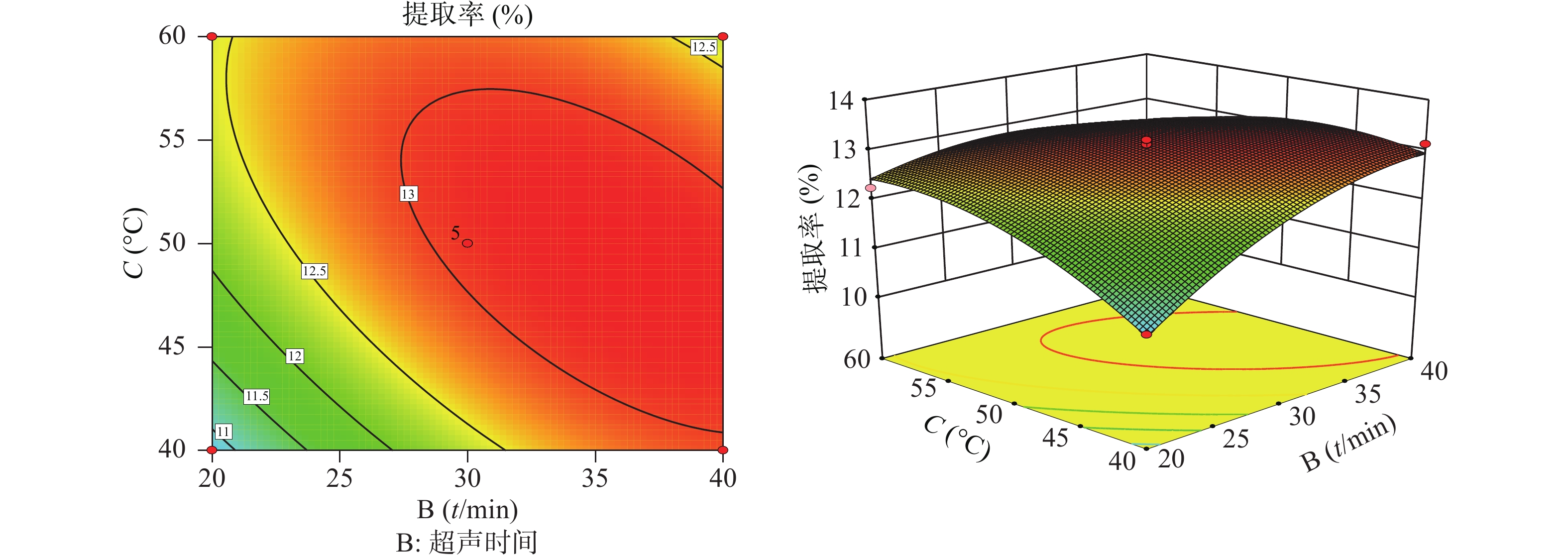
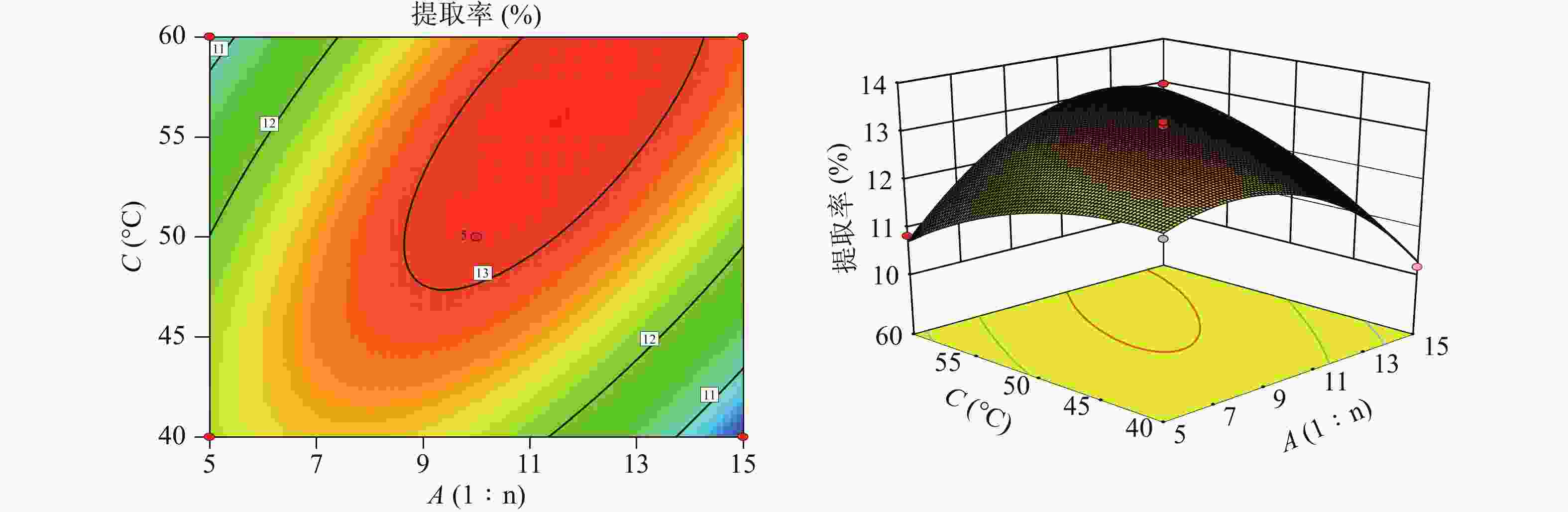
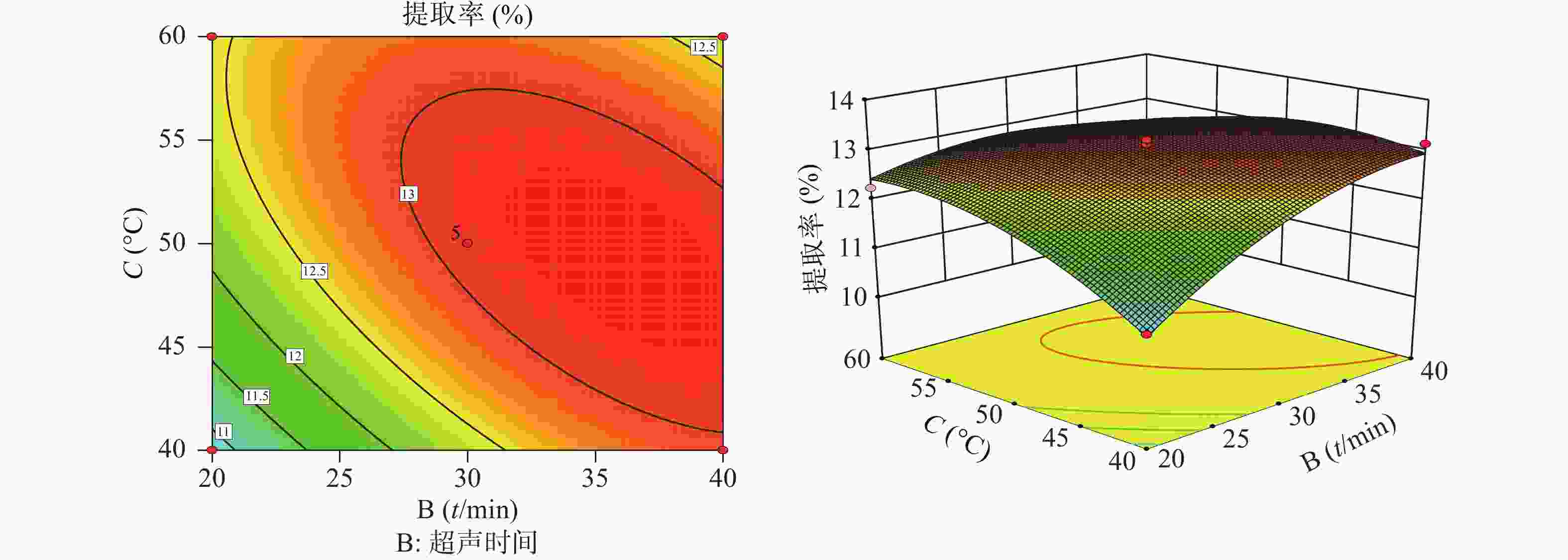
根据拟合方程绘制响应面图谱,响应面分析的等高线图和响应面图(图2、图3),AC、BC具有相互影响,各图为料液比(A)、超声时间(B)、超声提取温度(C)中任意一个变量取零水平,其余变量对金线莲多糖提取率的交互作用影响。由图2、图3可以看出,提取时间对提取率影响最为显著,三者的主效应关系为:提取时间(B)>提取温度(A)>料液比(C),其中料液比与提取温度的响应曲面最为陡峭,证明料液比与提取温度的交互作用最为强。
通过Design-Expert. V 8.0.6.1软件对二项式回归方程进行最优值的计算,确定理论上的多糖提取最佳工艺:料液比为1∶9.88,超声提取温度为48.76 ℃,超声提取时间为36.08 min,超声提取次数为2次,超声功率为300 W,其多糖提取的理论得率为13.22%,考虑到实际操作的可行性,最佳工艺定为料液比1∶10,超声提取温度48 ℃,超声提取时间36 min,超声提取次数为2次,超声功率为300 W。为验证实验结果,进行3组平行实验,多糖提取得率分别为13.14%、13.05%、13.20%,其RSD为0.57%,提取得率的均值13.13%与理论值13.22%偏差0.09%,表明优化后的提取工艺可行,适用于金线莲中多糖的提取。
-
按“2.6”项下的方法进行脱蛋白操作,得出多糖损失率及蛋白脱除率结果如表5。实验结果表明,NaOH-CaCl2法脱蛋白可以获得较高蛋白脱除率,同时也能获得最低的多糖损失率。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: