-
肾衰宁颗粒由太子参、黄连、制半夏、陈皮、茯苓、大黄、丹参、牛膝、红花、甘草等十味中药制成;具有补气健脾,活血化痰,祛浊的功效[1]。有文献表明,肾衰宁在治疗慢性肾脏疾病中疗效较为显著[2];在尿毒症腹膜透析患者的治疗过程中能够降低血清硫酸吲哚酯浓度[3];对于慢性肾脏病的Ⅳ期患者,在西医基础治疗的同时服用肾衰宁颗粒,可以明显改善肾功能,同时提升患者的治愈率,具有较高的临床使用价值[4]。由于中药成分复杂[5],使得如何控制中药的质量成为十分重要的问题。指纹图谱是在了解中药物质整体作用的基础上,通过光谱和色谱技术获得中药化学成分的光谱或色谱图,以鉴别中药的真伪,评价质量的一致性和产品的稳定性,其具有信息量大、特征性强、完整性和模糊性等特点[6]。指纹图谱中的质量控制技术既能保证中药的功效,又在实现中药现代化过程中起关键性作用[7]。因此,本实验以10个批次的肾衰宁颗粒为研究对象,拟建立肾衰宁颗粒的指纹图谱,对肾衰宁颗粒进行质量评价。
肾衰宁颗粒是由十味中药组成的复方制剂,其化学成分十分复杂,且许多复方治疗疾病的药物基础并不明显,因此检测成分必须是发挥药效的有效成分[8],本实验针对大黄中的大黄酚(chrysophanol)[9-10]、丹参中的丹酚酸B(salvianolic acid B)[11]、陈皮中的橙皮苷(hesperidin)[9, 12]3种指标性成分,进行HPLC法含量测定。在多成分的质量控制检测成本高而对照品紧缺的情况下,能较大程度地节约检验成本,又可较全面地控制该制剂的质量,保证临床用药的有效性和安全性,同时为肾衰宁颗粒的质量控制提供参考。
HTML
-
Agilent 1260高效液相色谱仪(美国Agilent公司),包含G1311C四元泵,G1329B自动进样器,G1316A柱温箱,G4212B-DAD二极管阵列检测器,Chemstation色谱工作站;光电分析天平(德国Sartorius公司,CPA 225D型),最大载荷220 g,分度值0.01 mg;冷冻真空浓缩仪(丹麦Labogene公司,ScanVac ScanSpeed 40型);超声波清洗器(上海科导超声仪器有限公司,SK7200H型);涡旋混匀器(海门市其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司,Vortex QL-901型)。
-
肾衰宁颗粒(德元堂制药集团,批号:51103111、51103009 346、51103010 471、51103011 593、51103105、51103018 486、41103033 563、51103110、61103102、61103101)。蜕皮激素(ecdysterone,批号:P11N6F5706)、甘草苷(liquiritin,批号:2O1027BA14)、甘草酸(glycyrrhizic acid,批号:230A6B1)、大黄酚(chrysophanol,批号:T31O6F5345)、丹酚酸B(salvianolic acid B,批号:Y14M7H14804)、橙皮苷(hesperidin,批号:K02M3C1)对照品,均由上海源叶有限公司提供。大黄素(modin,批号:110756-200110)、盐酸小檗碱(berberine hydrochloride,批号:09030522)对照品,由中国食品药品检定研究院提供。甲醇、乙腈、甲酸,均为德国Merck公司生产,色谱纯。二氯甲烷,色谱纯。水为纯净水,娃哈哈公司生产。
1.1. 仪器
1.2. 试剂
-
色谱柱:Waters SunFire™ C18(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm)。流动相A:乙腈;流动相B:0.1%甲酸溶液,梯度洗脱。流速:1 ml/min。柱温:25 ℃。进样量:10 μl。检测波长:254 nm。梯度洗脱条件见表1。
时间(t/min) 乙腈(%) 0.1%甲酸溶液(%) 0 5 95 1 23 77 18 25 75 19 30 70 31 75 25 60 85 15 -
精密依次称取丹酚酸B、橙皮苷、大黄素标准品10.25、10.35、10.05 mg,分别置于10 ml容量瓶中,以纯甲醇定容至刻度,摇匀,得储备液并将其分装后储存于−20 ℃的冰箱中。精密称取10.10 mg大黄酚,置于10 ml容量瓶中,加入少量二氯甲烷溶解,超声处理3 min,然后用纯甲醇稀释至刻度,摇匀,得到对照品的储备液,置于−20 ℃冰箱保存。
-
取肾衰宁颗粒适量,研磨成细粉,混合均匀,精密称取0.10 g,加适量70%甲醇溶液使其溶解,超声45 min,再用70%甲醇溶液定容至2 ml,冷却,过0.45 μm微孔滤膜后,取续滤液进样分析。
-
取肾衰宁颗粒(批号:41103033 563),按照“2.3”项制备供试品溶液,在“2.1”项色谱条件下连续进样5次,通过大黄素(7号色谱峰)作为参照峰,确定相对保留时间和相对峰面积。相对保留时间的RSD在1.0%以内,相对峰面积的RSD在2.0%以内,表明进样仪器的精密度良好。
-
取肾衰宁颗粒(批号:41103033 563),按照“2.3”项平行制备5份供试品溶液,测定在“2.1”项色谱条件下的相对保留时间和相对峰面积。相对保留时间RSD在1.0%以内,相对保留面积RSD在2.0%以内。表明该实验方法的重复性良好。
-
取肾衰宁颗粒(批号:41103033 563),并根据“2.3”项下平行制备5份供试品溶液,在“2.1”项色谱条件下,分别记录0、4、8、24、36 h的相对保留时间和相对峰面积。相对保留时间RSD在1.0%以内,相对保留面积RSD在2.0%以内。表明供试样品溶液在36 h内稳定性好。
-
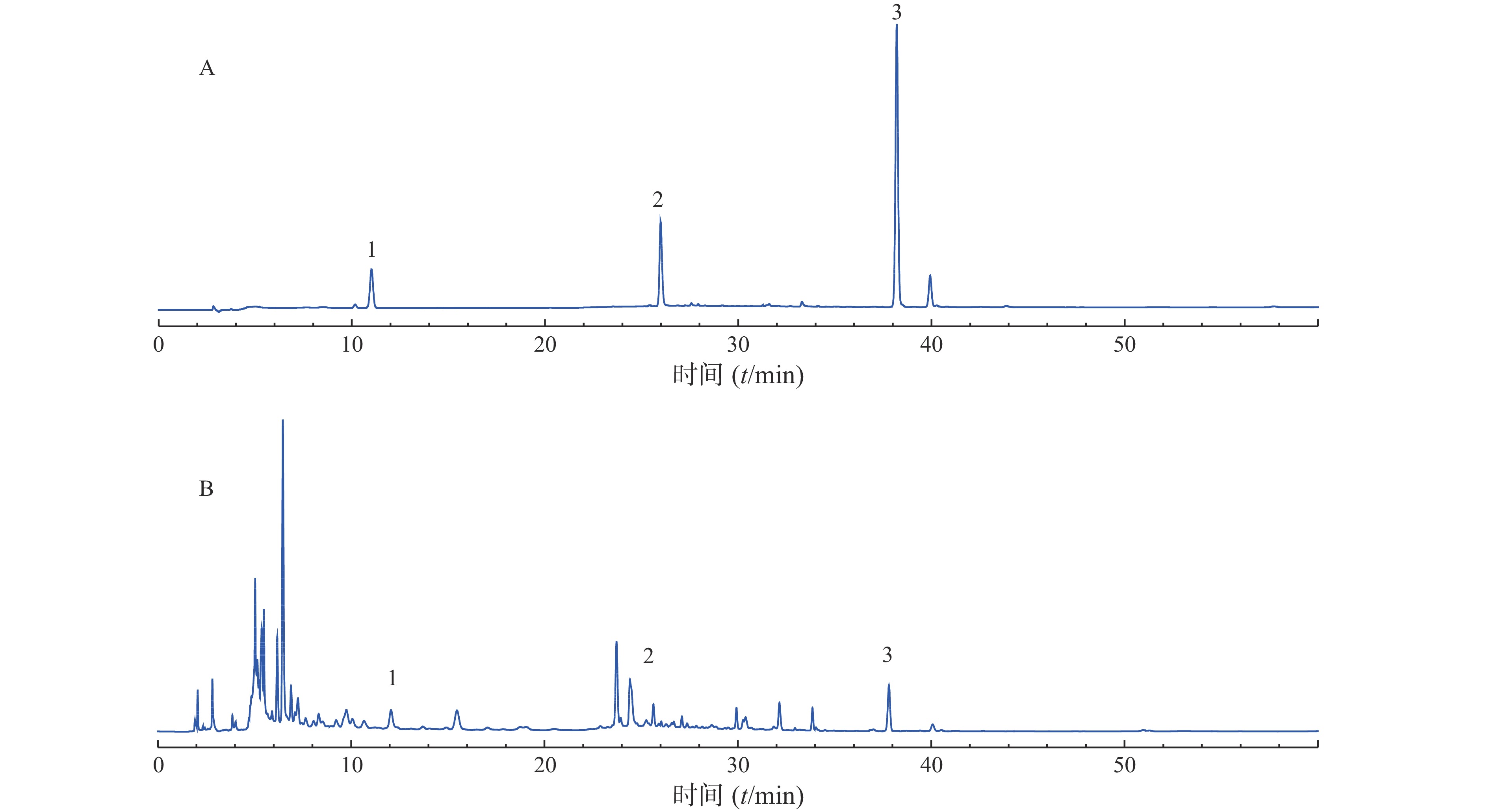
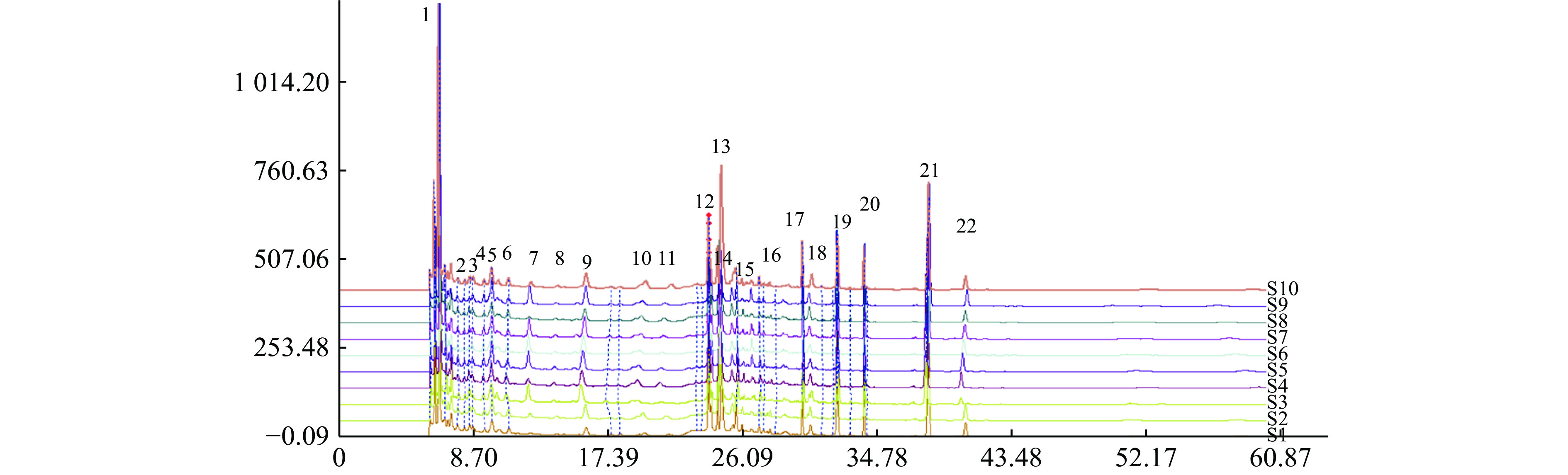
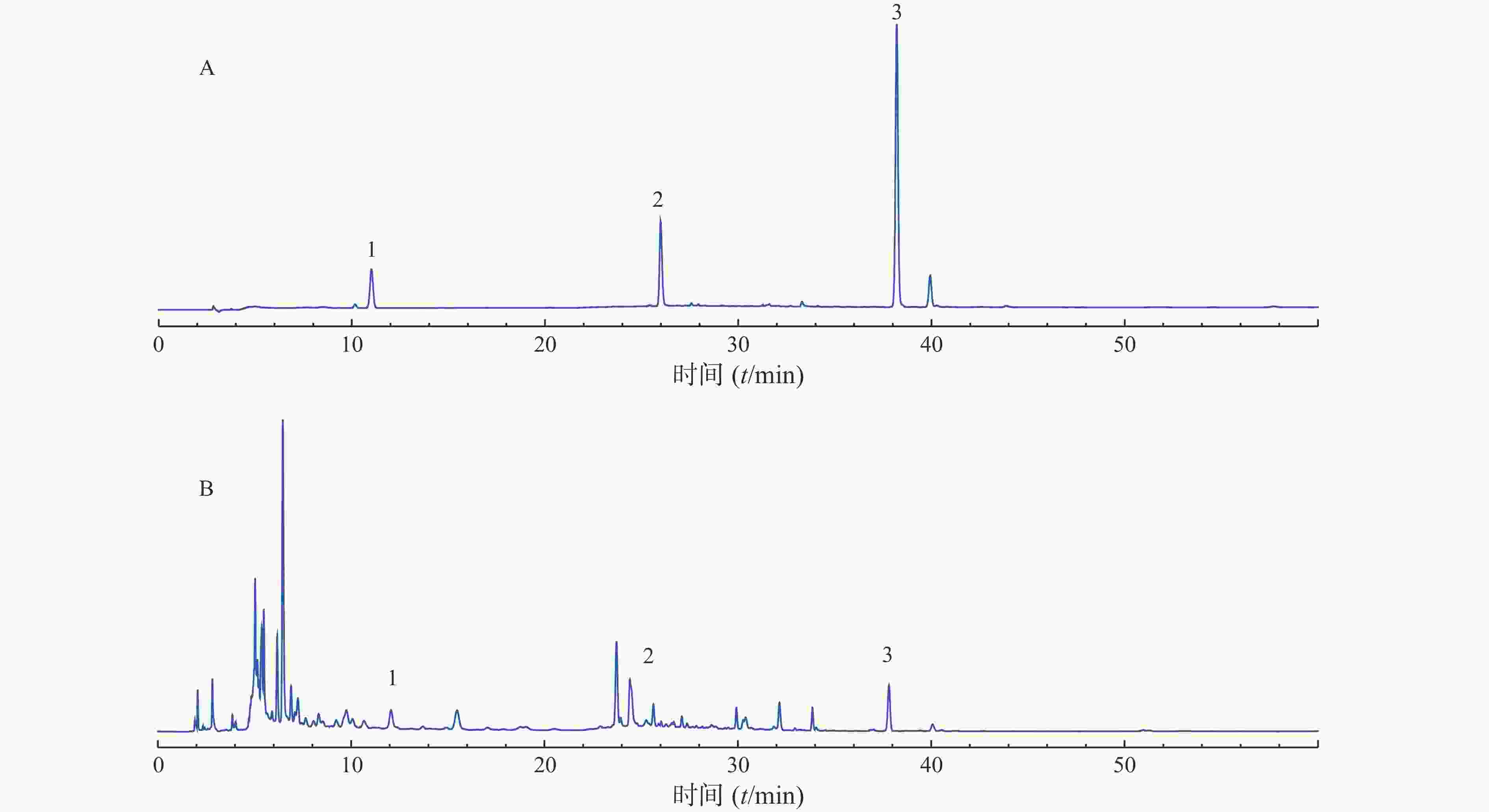
分别称取10个批次的肾衰宁粉末,按照“2.3”项制备供试品溶液,每个批次平行制备3份供试品溶液,记录图谱,见图1。利用中国药典委员会“中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统2008A版”的软件,将10批次肾衰宁颗粒的图谱导入,将批号为61103102的样品溶液用作针对相似性计算校正的参考图。结果显示,1~9批制剂间指纹图谱与对照图谱之间相似度均不小于0.90,见表2,表明相似度良好。对保留时间0~60 min内的色谱峰进行分析,均有22个稳定的特征峰,确定其为肾衰宁的共有指纹峰,经过标准品比对,其中,6号峰为橙皮苷,14号峰为丹酚酸B,21号峰为大黄酚。
样品号 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 对照指纹图谱 S1 1.000 0.980 0.910 0.941 0.934 0.948 0.916 0.941 0.950 0.874 0.965 S2 0.980 1.000 0.934 0.934 0.932 0.945 0.951 0.946 0.978 0.867 0.973 S3 0.910 0.934 1.000 0.952 0.947 0.937 0.972 0.940 0.945 0.914 0.973 S4 0.941 0.934 0.952 1.000 0.990 0.984 0.951 0.971 0.923 0.940 0.986 S5 0.934 0.932 0.947 0.990 1.000 0.978 0.938 0.976 0.910 0.910 0.979 S6 0.948 0.945 0.937 0.984 0.978 1.000 0.954 0.987 0.931 0.923 0.986 S7 0.916 0.951 0.972 0.951 0.938 0.954 1.000 0.949 0.966 0.913 0.979 S8 0.941 0.946 0.940 0.971 0.976 0.987 0.949 1.000 0.928 0.890 0.980 S9 0.950 0.978 0.945 0.923 0.910 0.931 0.966 0.928 1.000 0.892 0.969 S10 0.874 0.867 0.914 0.940 0.910 0.923 0.913 0.890 0.892 1.000 0.937 对照指纹图谱 0.965 0.973 0.973 0.986 0.979 0.986 0.979 0.980 0.969 0.937 1.000 -
按照“2.2”项下制备标准品溶液,得到混合对照品色谱图见图2。将标准品储备液用纯甲醇稀释,丹酚酸B浓度梯度为:10、20、40、80和100 μg/ml;橙皮苷浓度梯度为:40、80、160、320和400 μg/ml;大黄酚浓度梯度为:8、16、40、100和350 μg/ml。在“2.1”项色谱条件下,分别记录3种成分的峰面积,以峰面积(Y)对浓度(X)进行线性回归,结果见表3。
对照品 回归方程 r 线性范围(μg/ml) 橙皮苷 Y=2.391 8X–2.798 3 0.999 7 40~400 丹酚酸B Y=10.689X–5.578 3 0.999 8 10~100 大黄酚 Y=58.983X+121.99 0.999 9 7~350 -
取同一对照品溶液,根据“2.1”项下色谱条件进行测定,重复进样5次,并记录峰面积。橙皮苷、丹酚酸B、大黄酚峰面积的RSD分别为0.17%、0.20%、0.15%,表明仪器精密度良好。
-
精密吸取橙皮苷、丹酚酸B、大黄酚对照品溶液适量,使用甲醇逐步稀释,至色谱图中上述3种成分的峰高分别为噪音的3倍和10倍,测得橙皮苷的检测限和定量限分别为0.18和1 μg/ml;丹酚酸B的检测限和定量限分别为0.3和1.2 μg/ml;大黄酚的检测限和定量限分别为1和5 μg/ml。
-
取同一供试品溶液(批号:41103033 563),并根据“2.1”项色谱条件在0、2、4、8、24、36 h测定。橙皮苷、丹酚酸B、大黄酚的峰面积的RSD分别为2.01%、2.22%、2.05%,结果表明:供试品在36 h内稳定。
-
取同一供试品溶液(批号:41103033 563),平行制备6份,并根据“2.1”项色谱条件进行测定,橙皮苷、丹酚酸B、大黄酚的峰面积的RSD分别为0.67%、2.00%、2.02%,表明系统重复性良好。
-
精密量取肾衰宁溶液1 ml,分别加入100%含量橙皮苷对照品(理论值为192.02 μg),100%含量丹酚酸B对照品(理论值为62.66 μg),100%含量大黄酚对照品(理论值35.22 μg),按照“2.2”项平行制备6份,并根据“2.1”的色谱条件进行测量,按照下述公式计算加样回收率,平均加样回收分别为119.20%、84.69%、84.58%。结果见表4。
成分 取样量(V/ml) 样品含量(m/μg) 加入量(m/μg) 测得量(m/μg) 回收率(%) 平均回收率(%) 橙皮苷 1.00 383.02 95.88 773.46 101.80 100.27 1.00 380.39 95.88 764.91 100.26 1.00 380.31 95.88 763.64 99.95 1.00 384.46 95.88 771.17 100.83 1.00 385.81 95.88 772.95 100.94 1.00 389.20 95.88 764.32 97.81 丹酚酸B 1.00 120.79 31.80 250.42 101.91 98.82 1.00 122.50 31.80 251.14 101.12 1.00 125.56 31.80 248.78 96.87 1.00 127.57 31.80 254.87 100.07 1.00 127.74 31.80 251.44 97.25 1.00 127.75 31.80 249.44 95.66 大黄酚 1.00 72.67 17.79 138.19 92.06 97.36 1.00 69.62 17.79 135.41 92.44 1.00 68.46 17.79 140.83 101.69 1.00 71.03 17.79 141.25 98.66 1.00 68.98 17.79 141.57 102.00 1.00 71.92 17.79 141.17 97.30 回收率=(实测量-样品含量)/加入量×100%。
-
取10批肾衰宁颗粒,按“2.2”项制备试液,按“2.1”项色谱条件测定,结果见表5。
药品批号 橙皮苷(μg/ml) 丹酚酸B(μg/ml) 大黄酚(μg/ml) 61103102 66.99 42.29 44.65 51103110 83.41 39.34 42.89 51103111 94.75 41.36 44.51 51103009 346 80.57 43.21 43.44 51103011 593 83.51 42.04 42.58 51103018 486 79.94 41.94 42.96 51103010 471 90.03 41.88 44.03 41103033 563 83.48 43.01 43.94 61103101 85,92 42.93 43.85 51103105 88.04 41.76 42.94
2.1. 色谱条件
2.2. 对照品溶液的制备
2.3. 供试品溶液的制备
2.4. 肾衰宁颗粒HPLC指纹图谱的建立
2.4.1. 精密度试验
2.4.2. 重复性试验
2.4.3. 稳定性试验
2.5. 指纹图谱结果与分析
2.6. 肾衰宁颗粒中3种有效成分的含量测定
2.6.1. 线性结果考察
2.6.2. 精密度试验
2.6.3. 检测限和定量限
2.6.4. 稳定性试验
2.6.5. 重复性试验
2.6.6. 加样回收率试验
2.6.7. 样品含量测定
-
在190~400 nm处全波长扫描,盐酸小檗碱、大黄素、大黄酚、丹酚酸B、蜕皮激素、甘草酸、甘草苷、橙皮苷分别在345、254、254、286、250、237、237、283 nm处有最大吸收,通过对比分析,在波长254 nm处,上述8种成分具有良好的响应,样品中相邻色谱峰的基线分离可以满足含量检测的要求。因此,选择波长254 nm作为检测波长。
-
将肾衰宁粉末直接用水溶解后进样,发现样品出峰很少,所测成分在色谱条件下没有吸收。后用50%、70%、80%的甲醇溶解样品,发现用70%甲醇溶解出峰数最多,且所测成分在此条件下均有吸收,故选择70%甲醇进行样品的前处理。
-
有文献报道,肾衰宁含量测定使用甲醇-0.1%磷酸[13]、乙腈-水-1%甲酸[14]、乙腈-05%磷酸[15]进行90 min的大梯度洗脱,发现色谱峰分不开,且特征峰较少。经过反复实验,确定乙腈-0.1%甲酸水溶液用作梯度洗脱的流动相,分离出样品中测得的特征峰,特征峰很多,峰形良好。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: