-
疲劳的定义为机体生理过程不能维持其机能在一特定水平上,或不能维持预定的运动强度[1]。由于疲劳的分子机制并不清楚,目前并无真正官方认可的抗疲劳药物。一些天然产物,如人参、红景天、大蒜等,以及营养补充剂,如维生素、矿物质和肌酸等,报道有抵抗肌肉疲劳、提高运动成绩的效应,但是效果缓慢而不显著[2];苯丙胺、莫达非尼、咖啡因等药物虽能快速改善疲劳,但实质为中枢兴奋药,存在成瘾、耐受、改变生物节律等问题[3]。因此,抗疲劳药物的进一步研发,对改善生活质量、提升运动成绩、提高军事作业能力有重要意义。
组织糖原含量与疲劳的发生密切相关[4]。本课题组通过大规模化合物合成和筛选,获得了一个全新小分子化合物HMS-01,可以通过促进肝脏和肌肉组织糖原的储存,改善疲劳后组织损伤,显著增加肌肉耐力,发挥抗疲劳的作用。为了进一步了解HMS-01的药动学特点以及在组织中的分布,本课题组采用液相色谱-串联质谱(LC-MS/MS)技术[5-6],研究建立灵敏、特异的测定血浆等生物样品中HMS-01浓度的分析方法,并开展HMS-01在大鼠体内的药动学研究,为后续药物研发提供理论依据。
HTML
-
Agilent 1290 InfinityⅡ液相色谱仪(Agilent Technologies,美国)、4000 Q-Trap型串联质谱仪(AB Sciex,美国);低温高速离心机(Thermo,德国);XW 80A型涡旋混合器(医大仪器,上海);Mettler AE240十万分之一电子天平(梅特勒-托利多,瑞士);Millipore-Q超纯去离子水净化仪(Millipore,美国)。
-
HMS-01(西安秦申嘉合药物研究有限公司,批号HMS-1-1010-3);罗红霉素(Sigma,CAS:2058-46-0);乙腈(色谱纯,Fisher Chemical);甲酸(色谱纯,Fisher Chemical);其他试剂为市售分析纯。
1.1. 仪器
1.2. 试药
-
色谱柱为Gemini C18(50 mm×2.0 mm, 5 μm),流动相:含5 mmol甲酸铵及1 mmol甲酸的水溶液(A)-含1 mmol甲酸的乙腈(B),梯度洗脱,洗脱程序如下:0~2 min,90% A;2~6 min,5% A;6~8 min,90% A。流速:0.35 ml/min,柱温:25 ℃,进样量5μl,运行时间8 min。
-
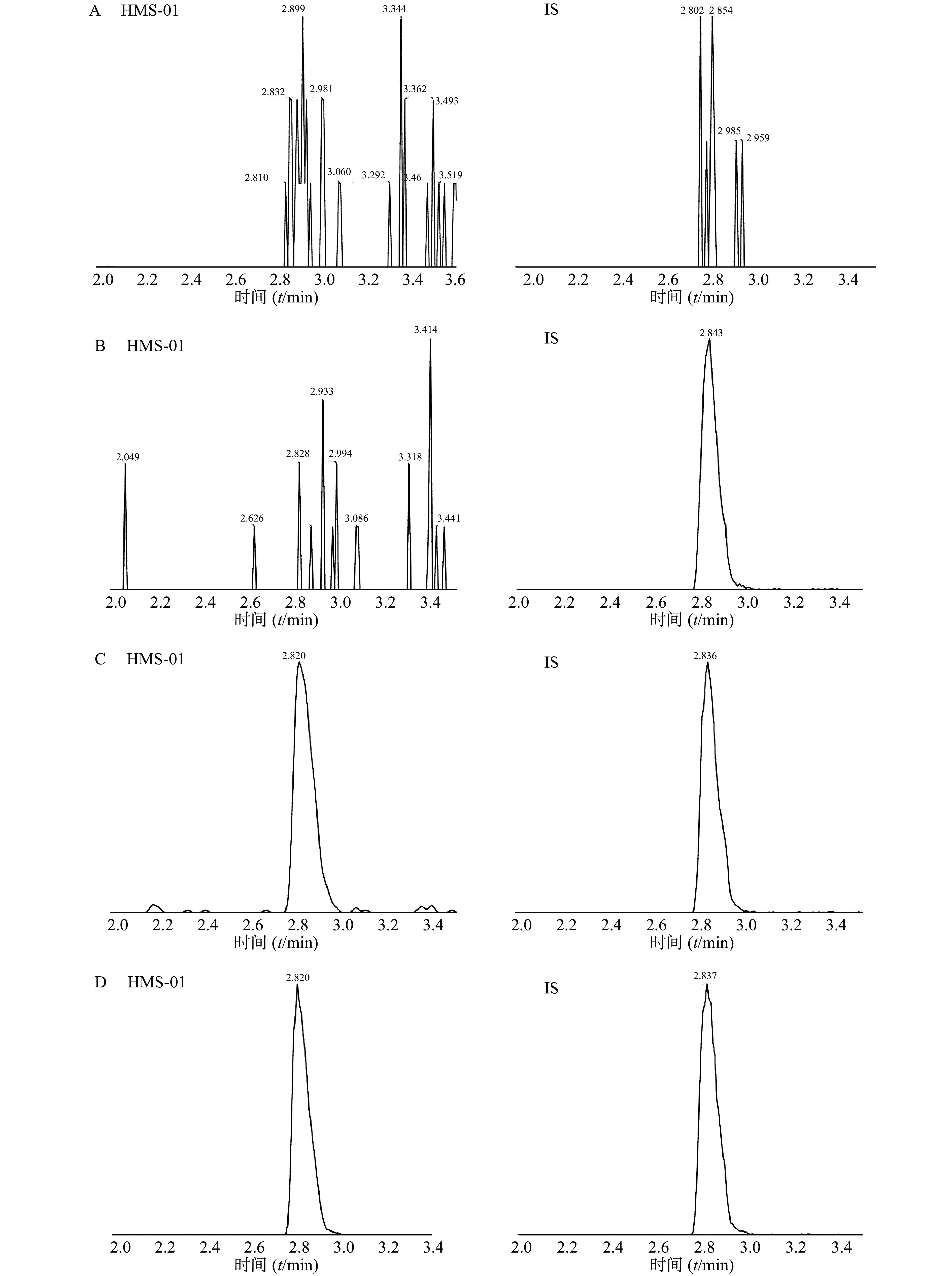
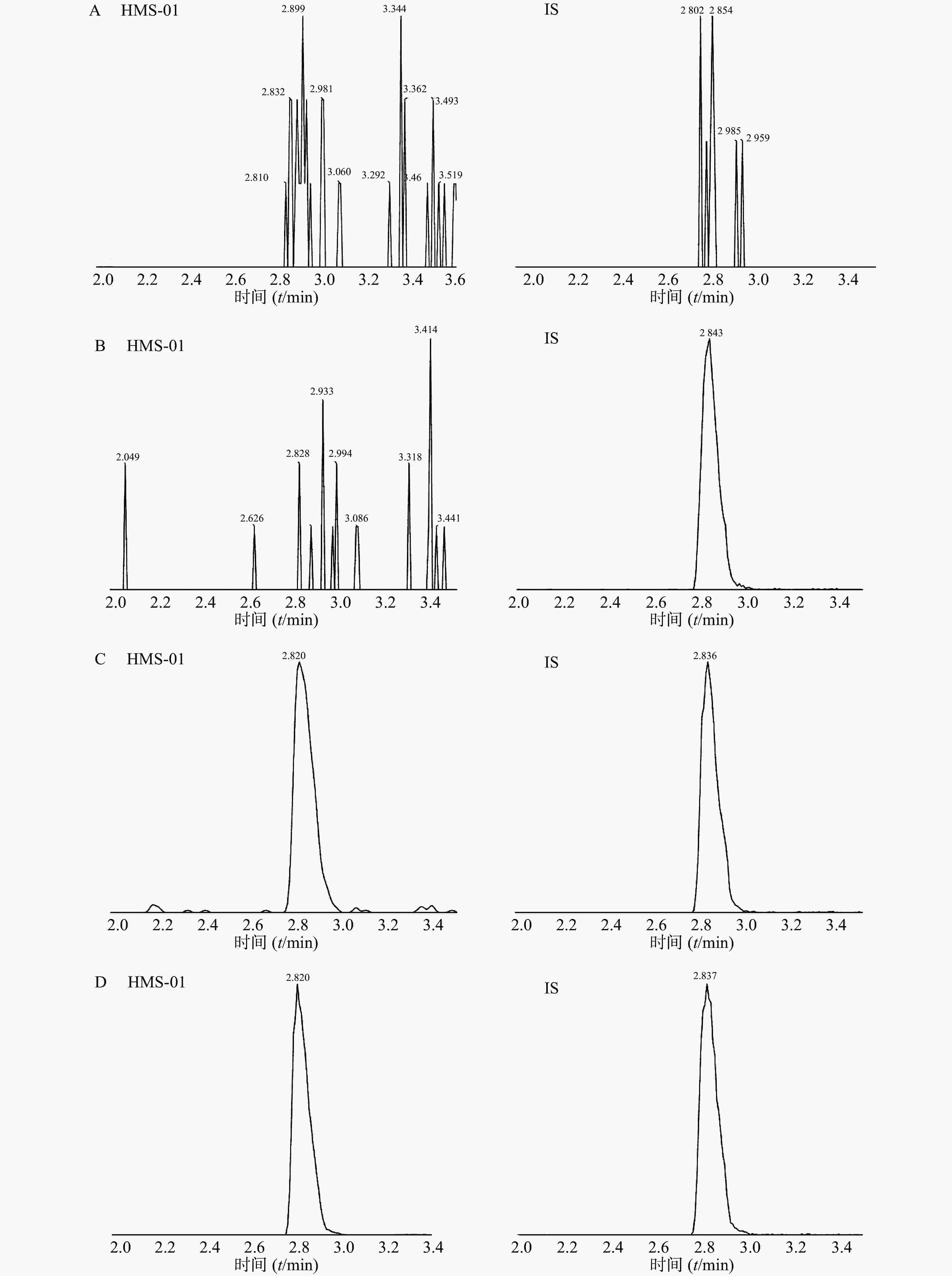
采用ESI正离子模式,多反应离子监测模式(MRM)进行二级扫描;动态反应监测的离子对参数:HMS-01 772.5→614.5;罗红霉素(IS)837.5→158.1。离子源参数设置:干燥气温度350 ℃;干燥气流速10 L/min;雾化器压力40 psi;鞘气温度400 ℃;鞘气流速11 L/min;毛细管电压4 000 V;喷嘴电压500 V。HMS-01保留时间为2.834 min,罗红霉素保留时间为2.839 min,色谱图如图1所示。
-
精密称取HMS-01对照品772.5 mg,置于10 ml容量瓶中,加甲醇溶解并稀释至刻度,摇匀,得质量浓度为77.25 mg/ml对照品储备液。再采用逐级稀释法配置质量浓度为772.5、386.25、193.125、96.563、48.281、24.141、12.070、6.035、3.018、1.509、0.754 ng/ml的系列含对照品血浆溶液;随行质控样品中HMS-01的低、中、高质量浓度分别为3.09、30.9、618 ng/ml。以上溶液置于4 ℃冰箱备用。
-
取50 μl血浆样品于离心管中,加入200 μl(含41.875 ng/ml的IS内标)乙腈溶液,涡旋60 s,4 ℃条件下3 000×g离心10 min,取上清液进样。
-
按“2.3”项和“2.4”项中的方法制备标准曲线,平行操作5份,按上述LC-MS/MS条件,连续进样分析,以对照品浓度(X)为横坐标,HMS-01的峰面积与内标的峰面积比值(Y)为纵坐标,进行线性回归,得线性方程:
Y=0.009 3 X+0.005 08, r = 0.999 3,
线性范围为0.976~1 000 ng/ml,以信噪比为3或5时测得HMS-01的最低定量限均为976 pg/ml。
-
按“2.3”项和“2.4”项中的方法制备低、中、高3种浓度的质控样品,平行操作5份,连续3 d,计算实测浓度。如表1所示,精密度用相对标准偏差(RSD)表示,结果日内精密度RSD≤12%,日间精密度RSD≤9%;准确度以相对回收率表示,实测浓度与理论加入浓度的比值即为相对回收率。结果表明日内、日间结果准确度范围在87%~106%。
浓度(ng/ml) 日内 日间 实测浓度(ng/ml) 精密度(%) 准确度(%) 实测浓度(ng/ml) 精密度(%) 准确度(%) 3.09 2.71±0.27 7.7 87.9 2.71±0.27 7.5 87.9 30.9 31.4±4.8 11.8 102 32.6±3.6 8.4 106 618 618±46 5.8 100 618±46 5.4 98.4 -
按“2.3”项和“2.4”项中的方法制备低、高2种浓度含药血浆,平行操作6份;取空白血浆按“2.4”项下处理,甲醇代替内标溶液,取处理好的空白血浆样品加入相应浓度对照品溶液,使之浓度与待测物的峰面积理论浓度一致,分别制备6份;将待测化合物标准溶液用甲醇稀释,使之与待测物的峰面积理论浓度一致,进样6次。基质效应等于(含基质样品的峰面积)/(80%乙腈溶液的峰面积),提取回收率等于(待测物的峰面积)/(含基质样品的峰面积),考察内标的基质效应和提取回收率操作步骤同上。低、高两种浓度待测物及内标提取回收率均在60%~75%之间,基质效应均在5.6%~6.1%之间,具体结果见表2。
待测物 浓度(ng/ml) 提取回收率(%) 基质效应(%) HMS-01 3.09 68±3 6.1 618 63±4 5.7 内标 3.35 73±2 6.1 670 73±2 5.6 -
按“2.3”项和“2.4”项中的方法制备低、高2种浓度含药血浆,分别考察样品前处理后室温放置24 h,3次冻融循环以及-70 ℃保存30 d的稳定性,测定样品浓度,计算平均值,并计算RSD(%)及相对偏差RE(%),计算公式:RE%=(实测值−真实值)/真实值×100%。结果见表3。测定结果的RE范围为2%~17%,RSD均小于7%,表明样本稳定性良好。
条件 浓度(ng/ml) RSD(%) RE(%) 室温24 h 3.09 3.7 16.5 618 1.0 2.6 3次冻融循环 3.09 6.7 4.5 618 0.6 5.9 –70 ℃保存30 d 3.06 6.8 8.7 6.18 0.6 10.1 -
SD大鼠12只,分成2组,每组6只,雌雄各半。给药前禁食12 h,自由饮水。按30 mg/kg的剂量单次灌胃、1 mg /kg的剂量单次静注给药。灌胃给药的,于给药前和给药后5、10、20、30 min和1、1.5、2、4、6、8、10、12、24 h分别眼眶采血约100 µl;静注给药的,于给药前和给药后3、8、15、30 min和1、2、3、4、6、8、10、12、24 h分别眼眶采血约100 µl。血液用1%肝素抗凝,8 000×g离心5 min,分离血浆。–70 ℃保存待测。采血过程冰浴避光,以防止光对药物稳定性产生影响。
大鼠单次静注给予1 mg/kg HMS-01后的药动学参数(非房室模型)总结于表4。大鼠静脉注射1 mg/kg HMS-01后,雄、雌大鼠药动学参数血浆浓度-时间曲线下面积(AUC)、平均清除率(CL)显示有极显著性差异(P<0.01),药动学参数血浆消除半衰期(t1/2)、表观分布容积(V)均呈显著性差异(P<0.05)。雄性大鼠AUC0-t为221 ng·h/ml,CL为4.53 L/h·kg,为大鼠肝脏血流量(约3.3 L/h·kg)的137%,体内清除快, t1/2约为0.786 h,V为5.13 L/kg;雌性大鼠AUC0-t为409 ng·h/ml,CL为2.41 L/h·kg,为大鼠肝脏血流量的73%,体内清除较快, t1/2约为1.27 h,V为3.82 L/kg。
性别 AUC0-t (ng·h/ml) AUC0-∞ (ng·h/ml) MRT0-∞ (t/h) t1/2z (t/h) CLz (L/h·kg) Vz (L/kg) cmax (ng/ml) 雄性 221±12.6 221±12.4 0.776±0.022 0.786±0.039 4.53±0.252 5.13±0.388 491±112 雌性 409±23.3** 416±21.0** 1.270±0.115 1.090±0.141* 2.41±0.120** 3.82±0.666* 571±55.1 合计 315±105 319±108 1.030±0.282 0.940±0.193 3.47±1.17 4.47±0.871 531±90.3 大鼠单次灌胃给予30 mg/kg HMS-01后的药动学参数(非房室模型)总结见表5。灌胃给予30 mg/kg HMS-01后,雄、雌大鼠药动学参数AUC显示有极显著性差异(P<0.01),药动学参数CL、F显示有显著性差异(P<0.05)。在大鼠体内血浆浓度达峰时间tmax为1.17 h,达峰浓度cmax为1 243 ng/ml,消除半衰期t1/2为2.00 h。雄、雌大鼠AUC0-t分别为2 271和8 529 ng·h/ml,生物利用度分别为34.3%和69.5%。
性别 AUC0-t (ng·h/ml) AUC0-∞ (ng·h/ml) MRT0-∞ (t/h) t1/2z (t/h) tmax (t/h) CLz/F (L/h·kg) Vz/F (L/kg) cmax (ng/ml) F(%) 雄性 2 271±666 2 279±667 2.58±0.156 1.43±0.130 1.17±0.289 14.00±4.31 28.5±7.04 729±263 34.3±10.1 雌性 8 529±1 920** 9 071±1 529** 4.79±1.39 2.58±1.060 1.17±0.289 3.38±0.629* 13.1±7.78 1757±584 69.5±15.6* 合计 5 400±3 661 5 675±3 867 3.68±1.50 2.00±0.924 1.17±0.258 8.69±6.44 20.8±10.7 1 243±694 51.9±22.6
2.1. 色谱条件
2.2. 质谱条件
2.3. 标准曲线溶液的配制和质控样品的制备
2.4. 血浆样品前处理方法
2.5. 线性关系考察
2.6. 精密度试验
2.7. 基质效应和提取回收率
2.8. 稳定性试验
2.9. HMS-01药动学研究
-
HMS-01在大鼠体内的药动学过程存在显著的性别差异。口服吸收的比较,雌性大鼠的生物利用度远高于雄性,体内的清除速率方面,雌性比雄性慢,与此同时,HMS-01在雌性体内的半衰期也更长。存在性别差异的原因有待进一步深入研究。本实验采用的分析方法的特异性、灵敏性、准确性、精密度及稳定性均满足定量分析的要求。鉴于HMS-01在大鼠血浆中不稳定的情况,在做动物实验时,课题组将采取以下措施:全血采集后立刻在4 ℃下离心2 min获取血浆,随即立刻取50 µl血浆样品加入至200 µl含内标的乙腈中,从而阻断血浆中的水解酶对化合物进行水解。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: